 Hello friends I hope you all are doing great. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to Power Transistor. The transistor is a semiconductor component that first time created in 1947 at Bell Lab. It is the main component of any digital device. The basic function of the transistor is to do amplification of the signal.
Hello friends I hope you all are doing great. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to Power Transistor. The transistor is a semiconductor component that first time created in 1947 at Bell Lab. It is the main component of any digital device. The basic function of the transistor is to do amplification of the signal.
It consists of semiconductor substances like silicon or germanium or gallium arsenide. The main two types of transistors are NPN and PNP that are BJT transistors. With the other type of transistor is FET its consists of three terminals. in this post we will cover the pinout working, application and some other related parameters of Power transistor. So let’s get started with Introduction to Power Transistor.
Introduction to Power Transistor
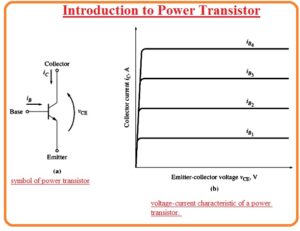
- The symbolic representation of the transistor can be seen in below figure.
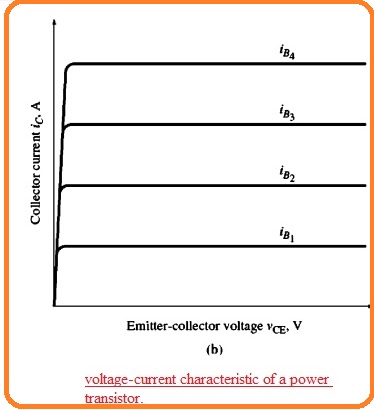
- The collector to emitter voltage with the collector current characteristic for transistor can be seen here
- It can be observed that in the above figure the transistor is a component that’s collector current is directly related to base current at different values of the collector to emitter.
- The power transistor are generally used in controls of different machines to off and on the supply.
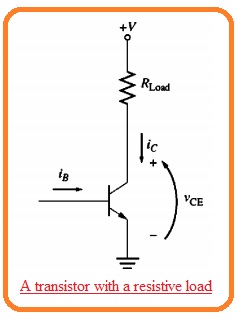
- The transistor consists of a resistive load can see here.
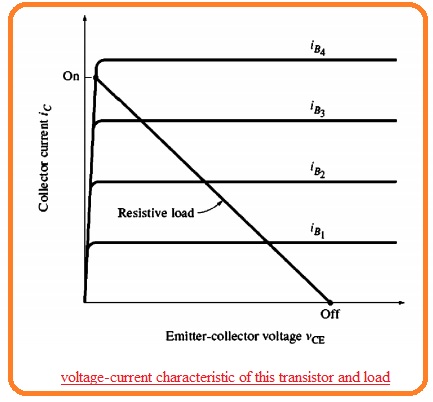
- The Ic-Vce curve can be seen here having a load line of resistance load.
- The base current IB4 will totally get on the transistor and the base current of 0 will totally off the transistor.
- If the value of base current of the transistor has a similar value to the IB3 then the transistor will not completely off no run.
- It no wanted to state because the larger collector current passes from the larger collector to emitter causing the very high-value power of transistor.
- To make sure the transistor operates without losing power it is compulsory to has base current larger value than totally do saturation of the transistor.
- Power transistor are generally employed in inverters circuitry The main disadvantage in switching applications is that high power transistor has less operating speed in varying on to off state as the comparatively high base current will give or eliminated when it gets on and off.
Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor
- The IGBT is created in some years ago or can say new to electronic industries. It is like to the power transistor with the difference that it can regulate through voltage given at gate than the current passing in the base that happens in the power transistor.
- The impudence of the control gate has a larger value at IGBT.
- Therefore the quantity of current passing in the gate is very less. The component is equivalent to the collaboration MOSFET and power transistor.
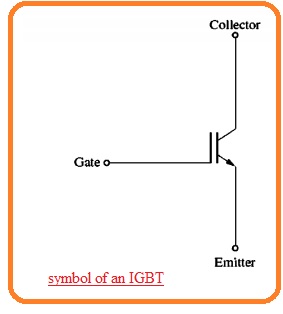
- The symbol of IGBT can be seen here.
- As the IGBT is regulated from the gate voltage having less current movement so its switching can be done with high speed over the normal power transistor.
- IGBT is so employed in such applications where high power frequency is needed.
Power and Speed Comparison of Power Electronic Components
- The below figure indicates the comparison between relative speeds and power handling features of SCR, power transistor, and GTO thyristors.
- We can see that the SCR has the ability of large power function over other components. GTO thyristor can work at large power and with high speed than SCRs.
- So power transistors can bear less power as compared to the other category of thyristor but its switching speed is larger ten-time high.
That is a detailed post about Power Transistor if you have any further query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a nice day.