 Hi, readers welcome to another interesting post. in this post we will have a detailed look at Concept of Voltage Regulation In Electronics There are 2 common types of voltage regulation are used first one is line regulation and the second one is load regulation. The main function of line regulation is to retain the output voltage at a constant level when there is a change in the input voltage.
Hi, readers welcome to another interesting post. in this post we will have a detailed look at Concept of Voltage Regulation In Electronics There are 2 common types of voltage regulation are used first one is line regulation and the second one is load regulation. The main function of line regulation is to retain the output voltage at a constant level when there is a change in the input voltage.
While the load regulation retains the output voltage at a constant level when there is change in the load. In this post, we will discuss these two regulations with the details and related factors. So let’s get started with Concept of Voltage Regulation In Electronics.
What is Line Regulation
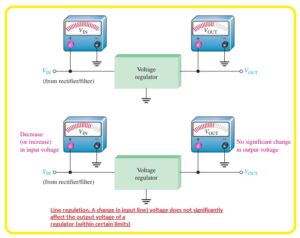
- When there is a change in the input voltage that is ac voltage of the power source the circuitry used known as a regulator which retains the constant value of voltage at the output. You can see it in below figure.
- Line regulation is known as a percentage variation in the output voltage according to resultant variation in the input voltage.
- According to range of input voltage line regulation is defined as a percentage with the given form.
- Line regulation= (VOUT/Vin)x100
- Line regulation also defined in percentage voltage. For instance, the line regulation of 0.05 percent volts indicates that the output voltage varies 0.05% when there is input voltage has increment or decrement single volt.
- Line regulation can be found with the use of a given formula.
Line regulation=(Vout/Vin)100%/Vin
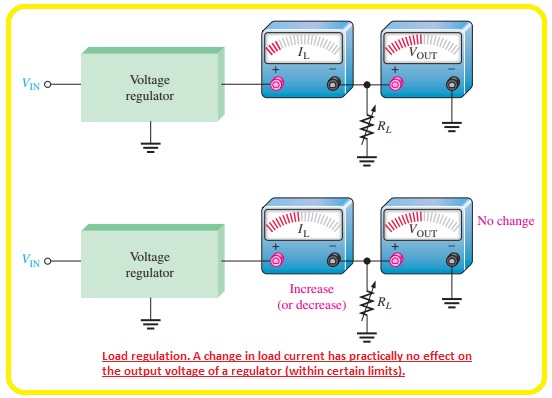
What is Load Regulation
- The quantity of current passing in the load varies according to the change in load resistance the voltage regulator should retain an almost constant output voltage about the load as shown in below figure.
- Load regulation can also be defined as the percentage variation in the output voltage in the variation in the load current.
- The other way to define the load regulation is percentage variation in the output voltage from no-load state to full load state.
Load regulation=(VNL-VFl)/VFLx100%
- In an alternative way the load regulation can be defined as percentage variation in the output voltage for every milliampere alteration in the load current.
- For instance, the load regulation of 0.01 percent millimeter indicates that the output voltage varies by 0.01 % when the load current rises or decreases one milliampere.
- In some cases, the manufacturer of the power source define the equivalent output resistance of power supply instead of its load regulation.
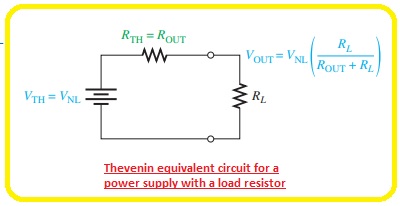
- We can construct the equivalent Thevenin circuitry for 2 terminal linear circuitry.
- The below figure indicates that equivalent Thevenin circuitry for power source having load resistance.
- The Thevenin voltage is the voltage from the supply with the absence of load and the Thevenin resistance is the certain output resistance. In the ideal case the value of output resistance is 0 resultant to zero percent.
- In the case of practical, the value of Rout is very less.
- By placing the load resistance the output voltage is determined with the voltage divider formula.
- VOUT= VNL(RL/ (ROUT + RL)
That is all about Concept of Voltage Regulation In Electronics if you have any further query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.