Hi friends, welcome to the new post. Here, we will learn What it is. – Definition, Working, Construction, Spiral & Helix Strip Thermometer. The bimetallic thermometer is a temperature-measuring instrument that operates at the differential thermal expansion principle. It is used in industrial and domestic uses due to its reliable, simple, and cost-effective structure. Let’s discuss its definition, working principle, construction, and variations like spiral and helix strip thermometers. So What is a Bimetallic Thermometer?
What is a Bimetallic Thermometer? Definition:
The thermometer is a device that converts temperature change in mechanical displacement with the use of two differnt metallic strips.
Normally steel, brass, and copper are used to make a thermometer. When its strip is heated gets expanded at different speeds
Metallic expansions result in temperature changes, so bimetal thermometers work on these features.
Two different metallic strips with heat expansion coefficients make a bimetal thermometer.
Bimetallic Thermometer Working Principle
The working principle of a bimetallic thermometer based on two featues of metals that are.
- Metal comes with thermal expansion features, that cause the metal contraction and expansion with temperatures
- The temperature coefficient of all metals is not the same. The expansion or contraction of metal is different at the same temperature
Bimetallic Thermometer Construction
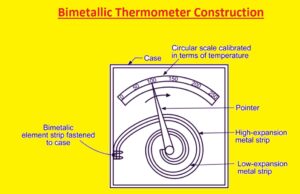
Bimetallic stripes are used to make thermometers. It is related to the creation of different thermal expansion coefficients. it is a mechncal device that are used to switch or offer electronic output through mechanical actions.
The two stripes are connected by the use of different methods such as bolting, riveting, welding, and fastening. These stripes are made of steel, copper, brass, etc
Spiral and Helix Strip Thermometer
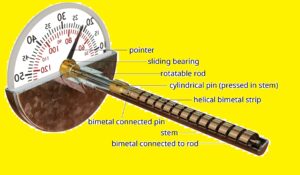
The helical type bimetallic thermometers are used in differnt industries. helical type bimetallic thermometer best where separating pointer from bimetallic coil can be needed in some conditions.
The temperature measuring sensors should be in the pipe and it is possible to show the temperature on the pipe externally.
The heli-shaped bimetallic thermometer is created with winding strip metal around another metal. Helix connected with bulb-like structure on one side and pointer on another end.
Bimetallic helix unwinds when heated due to different rates of thermal expansion of metals. As a result, the pointer glides over teh circuit scale to show temperature readings.
The temperature range of a bimetallic thermometer temperature is 30°C to 300°C.
Applications of Spiral Bimetallic Thermometer:
- It is used in industries and homes. It is also used at workplaces to measure the temperature the surrounding air.
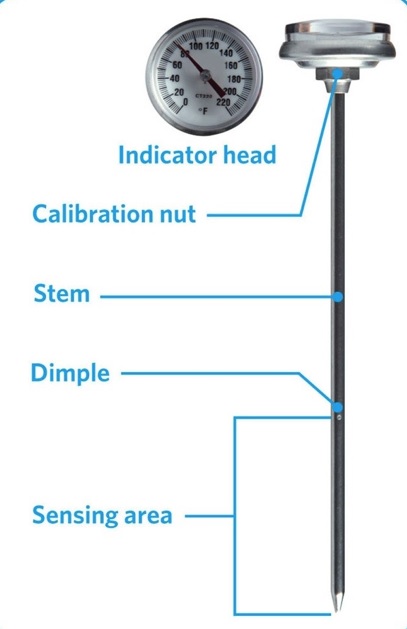
Bimetallic Stemmed Thermometer
A bimetallic stemmed thermometer uses two different metals for measuring temperature. Two metals with different coefficients of liner expansions are connected and fixed at one point.
When temperature varies, the two metals come with different degrees of thermal expansion. The pointer deflects to show temperature.
it is a bimetal thermometer. Normally layer of bimetal with a small coefficient expansion is known as the passive layer and the layer with a larger coefficient is called the active layer. It can measure the liquid of temperature directly, steam and gas also win range of -80℃~+500℃ in different production processes.
Characteristics of bimetallic stemmed thermometers:
- Low cost, easy to use
- durable and handle harsh conditions
- Accurate meter
- 80 to 500 degrees Celsius. temperate ranges
Bimetallic stemmed thermometer limitations:
- Slow response
- Damaged if not handled accurately
- It is not as accurate as other meters, such as digital thermometers
The bimetallic thermometer is used for
- Bimetal thermometers are used in industries such as machine building, heating technology, and air conditioning and refrigeration.
- It is used in thermostats that are on and off category
- it is part of a system where temperature regulation occurs.
- it is used in time delay circuits
- it used in refineries and oil burners
- it is used in lamp flashes.
- it controls the working refrigerators, electric irons, and ovens.
Bimetallic Thermometer Advantages and Disadvantages
Disadvantages
- it has a slow response time
- it is not able to measure temperatures that vary fastly. As a result, it is not suggested to use for such applications.
- The materials of bimetallic thermometers get distorted and do not come to the original shape for proper working.
Advantages of Bimetallic Thermometers:
- it has a strong structure.
- it has low cost
- it can be simple and small size.
- Easy to install
- Not break easily
- Cna work for different temperature ranges
- Accuracy is about +/-0.5%
Bimetallic thermometer calibration
- The best technique for calibrating a bimetallic thermometer is the use of the ice point method. For calibrating the bimetallic thermometer with this method fill the glass with ice, add cold water, and leave it for four to five minutes.
- After that put the stem of the meter in ice water. Ensure that the stem is not touching the lower part of the glass on the side.
- Wait until the dial starts the movement. If the thermometer is correct reading will be 0°C or 32°F.
- If the meter is faulty rotate nut below the dial so it measures zero degrees. Check at some intervals for accuracy.
Bimetallic thermometer temperature range:
The temperature range of bimetal thermometers is between -70 and +600 °C (-94 and +1,112 °F) with accuracy classes 1 and 2 according to EN 13190. For applications where high vibrations exists, thermometers with liquid filling are used.
The factors that can affect the temperature range of a bimetallic thermometer:
- Type of metals used in the bimetallic strip.
- Thickness
- length of the strip.
- Shape of the strip.
- Calibration of the thermometer.
Factors that affect the Response of the Bimetallic Thermometer’s Temperature Sensing Element:
- Different thermal expansion coefficients for metals used in the strip must exist. So they expand at different rates when get heated. Metals with high coefficient of thermal expansion are used in thermometers that measure high temperatures.
- The thick bimetallic strip responses have slow temperature changes. As it takes more heat to bend
- The long strip is more sensitive to temperature change. The longer strip bends more when heated
- The shape of strips also affects the response to changes in temperature. Strips found in spiral shapes more sensitive to changes in temperature than bimetallic strips is in a straight line.
- The thermal conductivity of the bimetal strip is measuring how well it works. The larger thermal conductivity fast strip will affected with temperate change.
- Strip surface areas are surfaces exposed to heat. The large area exposed faster strip will respond to temperature.
How to select a Bimetallic Thermometer?
Follow these points for selection
- Connection type
- Range of temperature
- Dial type
- Stem or length of capillary
- Some errors like noise, response time, Potential, conduction, radiation, and other faults can occurs during temperature measuring.
What is the structure of a bimetallic thermometer?
Who invented the bimetallic thermometer?
| John Harrison | |
|---|---|
| Died | 24 March 1776 (aged 82) London, England |
| Nationality | English |
| Known for | Bimetallic strip Gridiron pendulum Grasshopper escapement Longitude by chronometer Marine chronometer |
What is the difference between bimetallic and thermocouple?
What is a thermistor?
Who is the father of thermometer?
What method is used in bimetallic components?
- Difference Between RTD & Thermistor
- What is the Difference Between Thermistors vs Thermocouples
- Introduction to Sensors and Transducers
- CR1220 Battery Equivalent, Features, Specification, Chat and Application
- What is a 10k Resistor? Explain 10k Ohm Resistor Color Code
- How To Use Variable Resistor in Proteus
Faqs
-
What is a bimetallic thermometer?
The bimetal thermoeter uses two metal spring for temperature measuring component. This method uses coil spring created with two differnt metals that connectd. Meals can becopper, steel, or brass.
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of bimetallic thermometers?
cheap requires frequent calibration to maintain accuracy durable fairly slow response can be used for thermograph
-
What are the parts of a bimetallic thermometer?
its main parts are a stem, a bimetallic strip, dial with pointer, and instrument connection. Dia of stem is 6-9.6mm diameter and a 63-1000mm length and bimetal helix facing away from the case.
-
What are the examples of bimetallic?
Some examples of bimetallic devices ares thermostats, oven thermometers, and car temperature gauges.
-
What is the principle of thermometer working?
its wokng based on thermal expansion of liquids. Heat sensitive liquids are used in meter such as mercury
-
What is the working principle of a bimetallic thermograph?
The working principle of bimetal thermometer is that two metals have differntexpansion coefficient. If temperarus cahgnes lenght of two metals also cahgnes. When two metals connected shape will bent
-
What is the range of a bimetallic thermometer in Celsius?
The bimetallic thermometer working rane is up to 300°C to within ±1% of the scale range
-
What are the uses of bimetallic thermometers?
Bimetallic thermometers used in indsutries. its nrmal range is from 40 to 800 (°F). So used for two-position temperature control in residential and industrial thermostats
-
Is a bimetallic thermometer a controller?
No, a bimetallic thermometer is not a controller. A controller is a instruemtns that uses a feedback loop to maintain a desired temperature. A bimetallic thermometer is just a device that measures temperature.
-
How do you calibrate a bimetallic thermometer?
To calibrate a bimetallic thermometer, compare it to a reference thermometer that is consider to accurate. it can be done by placing both thermometers in a bath of water that is at a known temperature. The 2 thermometers must read the same temperature. If they do not, you can adjust the bimetallic thermometer until it reads the accurate temperature.
-
What is the error of bimetallic thermometer?
The error of a bimetallic thermometer is the difference among the actual temperature and the temperature that the thermometer reads. The allowable errors of the thermometer are (+1.5) and (+1.0) in range
-
How accurate is a bimetallic thermometer?
it can be accurate to about 1% full span In general, bimetallic thermometers are not as correct as some other types of thermometers, like digital thermometers.
-
What is the ice point method?
It is comon technique used to calibrate dial and digital thermometer
-
How do you zero a thermometer?
Place meter probe in ice water. Esnrue the sensing area is in water. Wait 30 seconds or till reading stays steady. Sete meter so it can read 32˚F (0˚C).