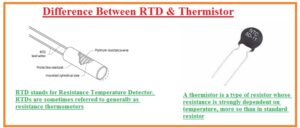
 Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between RTD & Thermistor. Both of these thermistors and RTD are used to find the value of temperature. But the basic difference between them is that RTD is constructed with metallic material and the thermistor is constructed with semiconductor material. Due to construction with the semiconductor materials, there are 2 temperature coefficients of thermistors positive and negative. But most thermistor has a negative temperature coefficient their resistance value reduces with the increment in temperature.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between RTD & Thermistor. Both of these thermistors and RTD are used to find the value of temperature. But the basic difference between them is that RTD is constructed with metallic material and the thermistor is constructed with semiconductor material. Due to construction with the semiconductor materials, there are 2 temperature coefficients of thermistors positive and negative. But most thermistor has a negative temperature coefficient their resistance value reduces with the increment in temperature.
. The RTD is used to find a large values of temperature. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both RTD and thermistors with the details and compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between RTD & Thermistor.
Difference Between RTD & Thermistor
RTD
- The instrument that used to find the variation in temperature is called RTD or also called the resistance temperature detector.
- It is constructed with metallic substances such as platinum, nickel, copper, etc.
- Its accuracy is less than the thermistor.
- It is an expensive device.
- It provides high resistivity.
- The physical dimensions of this device are larger than the thermistor.
- It used in different industries to find the temperature of machines.
- Its hysteresis effect is less.
- Its time response is less than the thermistor.
- Its measurable temperature range is -230 centigrade to 660 centigrade.
- Its characteristic curve is linear.
- It is a less sensitive material.
- It operates on different types of curvature and tolerance values normal operation curve for this device is DIN.
- The type of RTD is UPRT which offered a high value of accuracy.
RTD Types
- There are 2 basic types of RTD that are normally employed like thin-film coils and the third one is wire.
- The above types are generally used at the industrial level there is some other types that are used for measurement of less temperature than higher temperature devices that are used in industries.
Carbon resistor RTD
- These modules are less expensive and generally used for less-value temperature measurement. There is no effect of strain and hysteresis forces for devices
Strain-free RTD
- These devices used to measure temperature values close to 961 centigrade. There is a platinum-crated coil is wounded on it and there can easily change their state according to temperature change to show temperate values.
Thin-film RTD
- In this device temperatures, a measurement module is created through the use of platinum or plated ceramic substance.
- The thickness of the platinum material layer is almost one to ten nanometers. To save this layer from outer environment there is coted of glass is exist on it
Thermistor
- It is a heat-sensitive device whose resistance value varies with the change in temperature.
- It is manufactured with semiconductor materials.
- It provides high accuracy. So we can measure a small change in temperature due to the negative temperature coefficient.
- It provides fast response time.
- It is a less expensive material.
- A thermistor is a combination of thermal and resistor.
- Its practical applicaton are inrrcu currnet handler as tempratuer mesurig device.
- It has two temperature coefficients firs one is positive and the second one negative
- Its resistivity is less than the RTD.
- Its hysteresis effect is large.
- Its graphical representation is nonlinear.
- Its sensitivity is larger than the RTD.
- Its physical size is less than the RTD.
- It is used to find the temperature of devices used in a home.
- Its measured temperature range is -60 to 15 centigrade.
- It has two types NTC and PTC in NTC resistance drop with temperature rise and in PTC resistance rises with temperature rise.
- PTC is used to control overcurrent and used in series combinations.
RTD Vs Thermistor
| Characteristics | RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) | Thermistor (Thermal Resistor) |
|---|---|---|
| Operating principle | Its resistance varies with temperature change | its resistance also changes with the temperature |
| Material | Pure metals wire wounded on ceramic or glass core | it is created with Semiconductor material |
| Temperature range | -200°C to 850°C | -50°C to 150°C |
| Accuracy | its accuracy lies within 0.1°C | its accuracy lines within 1°C |
| Response time | It’s larger size and high thermal mass causes a slow response time | its response times are faster due to its small size and temperature dependant resistance |
| Stability | it is more stable and less susceptible to drift with time | It can drift with time and need calibration |
| Linearity | it is linear across the temperature range | it is not a linear temperature |
| Cost | Its prices are high than thermistors | its cost is less than RTDs |
| Power consumption | it uses less power low power consumption | it uses High power |
| Self-heating | it has a less self-heating effect | It is significant to the self-heating effect |
| Sensitivity | it has less sensitivity to temperature changes | it is highly sensitive to temperature changes |
| Output signal | it provides a linear output signal | it has a Non-linear output signal |
| Hysteresis | it has less hysteresis | its hysteresis is high |
| Frequency response | it provides a good frequency response | frequency response is poor |
| Packaging | it is configured in a metallic sheet | its packaging is surface-mount and through-hole |
| Resistance value | it has a higher resistance value | it has a lower resistance value |
| Aging | Aging effects can be ignored | Aging effects are significant |
| Environmental factors | it can be affected by vibration and shock | it is affected by moisture and humidity |
| Durability | it is more durable than thermistors | Less durable than RTDs |
| Applications | it is the best option for high-temperature projects like industrial processes and automotive | it is best for low temperature true like refrigeration and air conditioning |
FAQs
| FAQ | RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) | Thermistor (Thermal Resistor) |
|---|---|---|
| What is the operating principle of the sensor? | Resistance varies with temperature | Variation in resistance with temperature |
| Write the temperature range of the sensor. | normally from -200°C to 850°C | generally from -50°C to 150°C |
| Which sensor is more accurate? | RTDs are generally more accurate, within 0.1°C | Thermistors are accurate to within 1°C |
| Which sensor has a faster response time? | Thermistors provide faster response time | RTDs have a slow response time since its large size and high mass |
| Which sensor is better for high-temperature applications? | RTDs are best option of r high-temperature applications | Thermistors good solution for for low-temperature applications |
That is a detailed post about the difference between RTD and Thermistor if you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.