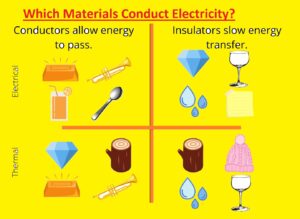
Hello readers, welcome to the new post. Here, we will discuss Which Materials Conduct Electricity? Electric conductivity is the motion of charged particles. All metals conduct electricity to some extent, but some metals are highly conductive. Most high-conductive metals are gold, copper, and silver.
Copper is highly conductive and used for metal wiring. Brass comes with copper, other materials used for conductivity reduction. Pure silver is a conductive metal
In this post, we will discuss details of electrical conductivity and study differnt materials and the features that make them conductors. So, let’s get started with Which Materials Conduct Electricity?
Introduction
Electrical conductors such materials that carry curent like iron or steel and insulators do not carry current glass and plastic.
Substance conducts electricity measured with electrons flowing in them. Electrical conductivity is based on electrons’ motion since neutrons and protons do not move.
What Is Electrical Conductivity?
Electrical conductivity defines the ability of a material to carry electric charge. In these materials current easily passes and makes them best for cables and wires, they are called conductive materials. Metals are highly conductive materials.
What are Conductive Materials?
Conductive materials are types of materials that conduct curent and help curent to flow through them. Materials not conduct current, non-conductive materials are known as insulators.
What is the Strongest Conductive Material?
Silver is considered the strongest material for conductivity. The strongest electrical conductors it used in many electrical devices and switches. However, it is not best to use silver for each device or project since its price is higher.
Copper is used in some applications since it is less costly and has high erosion resistance. When material like silver erodes it becomes a less conductive material.
Mercury is the weakest conductive material. But has some amount of conductivity due to metallic nature.
Conductive and Non-Conductive Materials
| Conductive | Non-conductive |
| Silver | paper |
| copper | rubber |
| aluminum | glass |
| gold | ceramic |
| platinum | plastic |
| plants | air |
| iron | Diamond |
| bronze | pure water |
| Mercury | fiberglass |
| concrete | wood (dry) |
| seawater | cotton |
| steel | porcelain |
| brass |
Graphene conductor
Graphene conducts heat and current effectively with its plane. The material strongly absorbs light of all visible wavelengths and is considered the color of graphite, the single graphene sheet is about transparent due to its extreme thinness
Superconductors: Zero Resistance
The superconductor is a material that conducts current with zero energy losses or resistance when cooled for temperature value. It does not have energy losses that cause continuously flowing electrical current.
10 Electrical Conductors
- Pure silver
- Pure copper
- Pure gold
- Aluminum
- Zinc
- Nickel
- Brass
- Bronze
- Iron
- Platinum
- Steel
- Lead
- Stainless steel
Why is Silver at the Top of the List?
The existence of valence electrons defines the metallic conductivity. Valence electrons are free electrons that help metals to current flow.
Free electrons in metal like billiard balls, transfer energy when colliding with each other.
Silver and copper are metals having single and free-moving valence electrons. The valence moves through metal with less resistance making these metals conductive.
Semiconductors metals come with multiple valance electrons, that reduce repelling forces.
Semiconductors can be effective electrical conductors when heated. Resistance of semiconductors based on the existence of impurities in metal. With the impurities, other factors can affect metal conduction such as frequency, electromagnetic fields, and temperature.
Silve has higher conduction featues than other metals but it can tarnish and make the surface less conductive.
What Does Electrical Conductivity Depend On?
Electrical conductivity measurement is based on metallic features to allow current to flow in the structure. High-conductive materials like copper and silver help the free movement of electrons in molecular shape.
Such material that has low conductivity like water and glass comes with fewer free electrons in molecular structure. Electrons are strongly connected and need high energy for the removal
10 Electrical Insulators
- Rubber
- Glass
- Pure water
- Oil
- Air
- Diamond
- Dry wood
- Dry cotton
- Plastic
- Asphalt
Is wood a conductor or insulator
Wood is an insulator it does not conduct electricity. Wood is a natural insulator due to air pockets in its cellular structure, which means it is 15 times better than masonry, 400 times better than steel, and 1,770 times better than aluminum. In addition, lightweight wood framing techniques help the simple connections of additional fiber or foil insulation.
What characteristics do conductive materials have?
- These materials do not have resistance to current flow helps to move free electrons.
- It helps free flow of electrons between particles that helps the conduction. Copper is used to measure and compare levels of conductivity.
- These materials come with larger free electrons that help the movement of charges from one point to another.
- it has an atomic structure that helps to current flow without needing energy for curent flow between different atoms.
- These materials are highly malleable and can be handled without breaking
- they come with high resistance to wear and can handle high and low temperatures without effect.
- It has an insulating layer so electric current not make a connection with the surface where it is used.
What types of conductive materials are there?
The main types of conductive materials are listed here
Metallic conductors:
- Free electrons carry charges so conduction is electrical. Both metals and alloys are in this category.
Gaseous conductors:
- These materials are in gaseous condition and casues an ionization process when lose electrons or gain electrons it provides them with features to conductive current.
Electrolytic conductors:
- The electrical conduction for these materials is caused by to chemical reaction that parted charge carrying materials in positive and negative poles. In this material, current passes matter is displaced.
How are conducting materials different from semiconductors and insulators?
Conductor
The conductor helps the easy flow of electrons from one atom to another when the voltage is connected. This is due to that there is no band gap between valence and conduction bands.
There is an overlapping of conductors and a valence band exists which means electrons can move from two overlapping bands. Since there is an area for electrons to move in the conduction band, valence band electrons move in each other and conduction is done.
Silver is the best electrical conductor as compared to other metals like gold, copper, steel, aluminum, and brass which are also good conductors. These materials can seen in differnt devices and projects.
Solids are the best conductors but some liquids like metals such as mercury are also good conductors. Some types of metals are superconductors that at low temperatures conducted without resistance
Semiconductor
Semiconductor has a conductivity between conductor and insulator. The resistance of these materials reduces with temperature increase. COmponetn like silicon, germanium, and selenium compounds such as gallium arsenide, and indium antimonide are semiconductor elements. Silicon denotes a common semiconductor.
There is a gap between valence and conduction bands for semiconductors. But it is a small size that helps to move electrons at room temperature and conduction occurs. the increase in temperature casues the conduction of semiconductors since more electrons have the energy to move the condition band.
Gases are poor conductors due to large areas between their atoms. If there are larger ions of gases that exist become semiconductors.
Insulator
The insulator avoids the flow of energy between particles. Such as insulators can avoid the flow of curent heat or sound.
Thermal insulators decrease heat transfer between two objects of different temperatures. Theraml insulators perform through this reflecting of thermal energy. The insulative features of these materials is inverse of thermal conductivity so these materials with low thermal conductivity have high insulation featues or resistance values.
Some other features to define the parameters are product density (ρ) and specific heat capacity ©.
The materials that do not conduct current is dielectric materials. These materials can be polarized through the application of an electrical field that stops the flow of current throw them like conductors. So inner electrical field minimizes the overall field in dielectrica.
Insulators have larger gaps between conduction and valence bands. Electrons do not move to the conduction band and do not current flow in these materials.
Conductors Vs. Insulators
Conductor
- Definition: The current flow in these materials
- Electric Field: In the conductor, the field is zero and exits at the surface
- Magnetic Field: Store energy
- Potential: Has the same potential at all point
- Thermal: Conductivity High
- Covalent bond: Weak
- Conductivity: high
- Resistance: Low
- Electrons: move freely
- Resistivity high to low changes
- Temperature coefficient: Positive temperature coefficient of resistance
- Conduction band: electrons
- Valence Band: Empty
- Forbidden gap: No forbidden gap
- Examples are Irons, silver, copper, aluminum,
- Application of electrical wires and conductor
Insulators
- Definition: curent not flow in these materials
- Electric Field: Not have a field
- Magnetic Field: no
- Potential: zero potential
- Thermal: Conductivity : Low
- Covalent bond: Strong
- Conductivity: Low
- Resistance: High
- Electrons: Do not move freely
- Resistivity High
- Temperature coefficient: Negative temperature coefficient of resistance
- Conduction band: Remain empty
- Valence Band:Full of electrons
- Forbidden gap: Larger forbidden gap
- Examples wood, Rubber, Paper, etc
- Application insulation for electrical cables or conductors, for supporting electrical equipment, etc
What material can not conduct electricity?
Which of the following materials conduct electricity?
What are 5 poor conductors?
- Plastic.
- Rubber.
- Cloth.
- Polythene.
- Wood
What are 4 materials that conduct electricity well?
- What is Semiconductor? Working, Types, Features, & Uses
- What Are the Common Causes of Multi-conductor Cable Failure?
- Difference Between Semiconductors and Superconductors
- Differences Donor and Acceptor Impurities in Semiconductor
- Difference Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductor
- Difference Between Conductor and Insulator
- Difference Between Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor
Faqs
-
Is wood a conductor of electricity?
- No, wood is not a conductor of electricity. It is an insulator.
-
Is wood an insulator or a conductor?
- Wood is an insulator.
-
Why is wood an insulator?
- it is an insulator because of its cellular structure. Timber is made with small air pockets that trap air and slow the heat transfer in result affect the thermal conductivity.
-
Why is wood a bad conductor of electricity?
- it does not have free electrons so it is a bad conductor
-
Is wood a good conductor?
- No, wood is not a good conductor of electricity.
-
Is wood a good conductor of heat and electricity?
- Wood is a poor conductor of heat since it has a covalently bound compound. So it does not come with free electrons that move to conduct electricity
-
Is wood a good conductor or a bad conductor of electricity?
- It is not a good conductor.
-
Is wood a conductor of fire?
- Wood is a non-conductor. So kinetic energy of flame in wood is absorbed by molecules and accumulates until kinetic energy results in bonds between molecules and atoms starting to break.
-
Is paper a conductor of electricity?
- Normally paper insulator and not a conductor. But paper can absorb contaminants that increase the conductivity of paper.
-
Is wood a good conductor of heat or a bad conductor of heat?
- It is a bad conductor of heat
-
Is wood a better conductor than copper?
- Put both of them on a sunny day under sunlight. After five to six hours, we can check both pieces and note that copper is hotter than wood, so copper is a better conductor of heat.
-
Is wood a conductor of metal?
- wood is a good insulator of electricity
-
What material can not conduct electricity?
- Materials not allow current to flow are called electrical insulators. Some materials are plastic, rubber, wood, and glass. Air is also an insulator.
-
Can rubber conduct electricity?
- rubber does not conduct electricity. It is an insulator.
-
Is cotton a conductor?
- Cotton is a good electrical and heat insulator. it comes with trapped air in it. Air is a poor heat conductor.