![]() Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between conductor, Insulator, and Semiconductor. There are 3 types of material according to their electric behavior and features first one is an insulator, the second one is the conductor and the third one is semiconductors. All these categories show different electrical behaviour according to their structure and availability of free electrons.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between conductor, Insulator, and Semiconductor. There are 3 types of material according to their electric behavior and features first one is an insulator, the second one is the conductor and the third one is semiconductors. All these categories show different electrical behaviour according to their structure and availability of free electrons.
In any solid pattern, the atoms are arranged in a symmetrical fashion. There are some types of bonds like an ionic bond covalent bond, etc. In any crystal, an atom is joined with one another by covalent bond this bond is created among the outermost electrons or valence electrons of an atom. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at conductor, insulators, and semiconductors and compare their different properties also discuss the role of these materials in electronic materials. So let’s get started with the Difference Between conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor.
Difference Between conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor
- Every substance is created with the atom these atoms explain the electric features of any substance and also explains the conductance of that substance.
- To an understanding of the electrical behavior of any substance, we can draw a physical structure of an atom that consists of valence shell electrons and internal shells and nucleus.
- In the given figure, you can see the carbon atom in the above explain the structure.
- You can see in the given figure that the caron atom consists of 4 electrons in outermost of the valence shell and 2 electrons in an internal shell.
- In the nucleus of the carbon atom, there are 6 protons and 6 neutrons six define the positive charge of 6 protons.
- The net charge on the core of the carbon atom is plus four.
What is Insulator
- Such substances that show a high value of resistance for movement of current under normal situations are called insulators.
- These insulators are available in a single element or compounds and provide a large value of resistance.
- The outermost electrons or valence shell electrons are strongly fastened to the structure of the substance and there are no free electrons for conduction or flow of current.
- Examples of insulators are quuartz, mica, plastic, rubber, etc.
Applications of Insulator
- Rubber is a very common insulator material used in different cloths, tyres are construed with a rubber,etc.
- Porcelain is an insulator material used for the construction of bushing to provide insulation among different conductors.
What is Conductor
- Conductor features are reverse to the insulators there are a lot of free valence electrons in their valence shells for conductance.
- The examples of these substances are iron, copper, silver, gold, etc.
Applications of Conductors
These are some applications of conductors.
- Iron is the very common conductive material used in different devices like the engine of vehicles for the conduction of heats.
- Silver is used in transmission lines for transfer of power and in different electrical machines either dc machines or ac like an induction motor, induction generator, synchronous motor, synchronous generator all consists of copper windings that is a conductor.
- Aluminum is also a conductor that is used in different cooking devices, that absorbs heat for cooking purposes.
What is semiconductor
- Semiconductor shows conductance behavior between insulators and conductors these are also conductor and insulator so-known as semiconductors.
- In intrinsic or pure conduction semiconductors not shows conductive behavior also not insulators behaviors.
- With the increment of temperature or external supply source, they start their conductance.
- The examples of these materials are silicon, germanium, arsenic, etc.
Applications of Semiconductor
- These are different types of semiconductor material that are used in a different circuit such as a transistor, diodes.
- Transistor are used for switching and amplification circuits and diodes are used for rectification purposes.
Conductors Vs Semiconductors Vs Insulators
| Conductors | Semiconductor | Insulator |
| A conductor is such a substance that allows current to flow through them. Like iron, aluminum, copper. | Semiconductors are such materials that show conductivity behavior among conductors and insulators. Examples are silicon, germanium. | Such substances that provide a high value of resistance for current movement are called insulators. Rubber, mica, etc. are examples. |
| The conductivity of these materials is very high. | This substance shows conductive behavior between conductors and insulators. | Their conductive behavior is zero. |
| This substance has no forbidden gap. | There forbidden gap is less. | These materials have a very high forbidden gap |
| This resistance of these materials is very less. | These materials show a moderate value of resistance. | The resistance of this substance is very high. |
| The temperature coefficient of these substances is positive. | The temperature coefficient of these substances is negative. | The temperature coefficient of these substances is also negative |
| The conductivity value for these substances is 10-7 mho/m. | The conductivity value for these substances is 10-7 mho/m to 10-13 mho/m. Medium | The conductivity value for these substances is 10-13 mho/m. That is very less. |
| In these substances, there are many electrons for conductance. | Less electrons for conductors. | Almost zero electrons for conduction. |
| The resistivity of these substances is less than 10-5 ohm meter | The resistivity of these substances is between 10-5 ohm meter and 105 ohm meter. | The resistivity of these substances is greater than 105 ohm meter |
| In these substances, there is only one electron in valence electrons. | These materials have 4 electrons in valence shells. | These materials have eight electrons in valence shells. |
| In conductor’s valence and conduction bands are overlapped with each other. | In these materials valence and conduction bands 1.1ev energy difference. | Valance and conduction bands are separated from each other 6ev to 10ev. |
| In conductors, a metallic bond is exited. | Semiconductors are consists of a covalent bond. | Insulators have ionic bonds. |
| Their examples are iron, copper, gold. | Silicone and aluminum are examples of semiconductors. | Mica, rubber, and wood are insulators. |
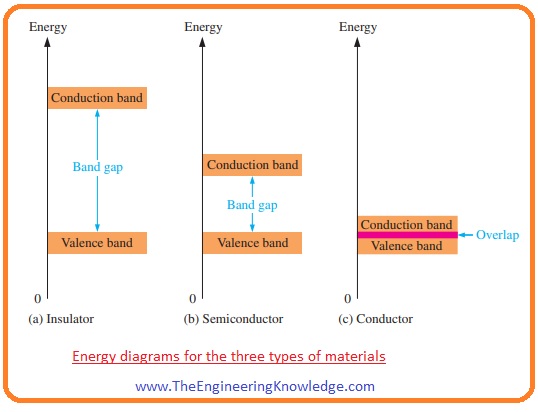
Band Gap
- As we know the valence shell of an atom define the band of energy that will tell about any electron in valence shell for required energy.
- When valence electron gets specific energy it will leave the valence electron and move to the band called conduction band.
- The energy required for an electron to move from valence shell to conduction band is called band gap.
- when electron moves to the conduction band then it can easily move freely in the atom.
- In the given figure, you can see the energy diagrams of conductors, insulators, and semiconductors.
- We can also define the band gap as it is the energy difference among 2 energy levels that an electron should have to move among them.
- In the case of insulator and semiconductor in the band gap there are no electron exits while in conductor electrons exit or may not exits due to free movement of electron.
- If we apply a high voltage across the insulator then it will possible for an electron in an insulator to cross the band gap.
- In the above figure, insulator band gap is explained.
- While in the case of semiconductor you can see band gap is less so in semiconductor less amount of energy is required for an electron to cross the band gap.
- If we observe the conduction band then you can see that the conduction band and valence band are overlapping with each other so there is less amount of energy is required for electrons to move from valence to conduction band.
Comparison of a Semiconductor Atom to a Conductor Atom
- Now we do a comparison between two atoms the first one is from conductor and a second one from the semiconductor.
- For this, we take silicon as semiconductor and copper that is a conductor. In given both atoms are shown.
- You can see that the total charge on a silicon atom is four while on the carbon is one.
- The valence electrons of a copper bear force of attraction from one side while in silicone at valence electrons four attractive forces are applied.
- So we can say that at the valence electron of silicon four attractive forces are applied.
- The valence electron of copper is in 4th shell while silicon’s valence shell is in the third shell.
- As we know that electron at a larger distance from the center have high value of energy so the energy of copper valence electron is larger than the energy of silicon atom.
- So after getting less amount of energy in copper atom electron will leave the shell while in silicone large amount of energy is required.
Comparison between Silicon and Germanium atoms
- The internal structure of silicon and germanium atoms is shown in below figure.
- You can see that in both structures there are 4 valence electrons.
- But the difference is that the valence electrons in germanium atom are in 4th
shell while in silicone are in 3rd it shows electrons in germanium are at high energy levels then the silicone.
- So a small amount of energy is required for the germanium electron to leave the atom. It also tells about the less stable behavior of germanium while silicone is more stable.
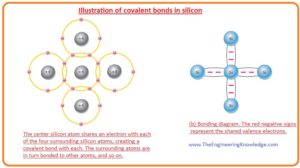
What is Covalent Bond
- In the given figure, you can see the every silicon atom is connected with the further 4 numbering silicon atom and create a silicone crystal.
- Four valence electrons of silicon atoms are paired with the other four electrons of another atom and this makes all silicon atoms stable.
- This sharing of valence electrons makes the covalent bonds that make a strong connection among atoms of silicon.
- The covalent bond of a pure or intrinsic atom is shown in a given figure. Covalent bonding of germanium is also similar to the silicon because there are 4 electrons in valence shells of germanium.
So friends this the detailed post Difference Between Conductor, Insulator, and Semiconductor I have mentioned each and every factor related to these materials. If you still have any query ask in comments. See you in the next tutorial.







Hi Sir, I have searched many online materials to learn this concept. But I haven’t found an explanation for this concept with this much clarity anywhere. Thanks for sharing your knowledge with us.