 Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Introduction to S9013 transistor. The transistor is very basic component of any electronic projects used and devices. It comes with three main inputs emitter-base and collector. Each pin performs its function regularly to run the transistors as a tap. Its structure is that it has three parts first one is NPN which has electrons as the majority and P have holes as the majority.
Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Introduction to S9013 transistor. The transistor is very basic component of any electronic projects used and devices. It comes with three main inputs emitter-base and collector. Each pin performs its function regularly to run the transistors as a tap. Its structure is that it has three parts first one is NPN which has electrons as the majority and P have holes as the majority.
In this post, we will discuss details of the S9013 transistor with more information. So let’s get started.
Introduction to S9013 transistor
- S9013 is created with a plastic TO-92 casing. Comes with three main pinouts like other transistors.
- It is medium power use NPN transistor employed in different switching and amplifier circuits.
- It comes with a larger value of transition frequency which is one forty megahertz so prefer projects where a high frequency is needed.
- It used to control the current till the value of five hundred milliamperes.
- Such frequency where current gain becomes one called transition frequency.
- It comes with Ic values of five hundred milliamperes. For a large value of current gain reduces and Ib value of fifty milliamperes required to larger IC current up to five hundred milliamperes
- It is NPN configured transistor that has two N and one P regions. N regions are doped with the electrons as the majority and N regions are doped with the holes as the majority of current flows in a transistor due to electrons and holes movement.
Features of S9013 Transistor
- The main features of S9013 are discussed here
- Its structure is placed in the TO-92 packaging
- Its power dissipation is a six-fifty megawatt
- The transition frequency is one forty mega hertz
- IC value if five hundred milliamperes
- VCE is twenty-five volts
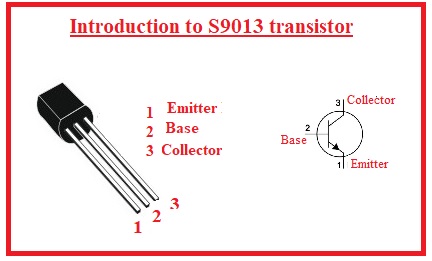
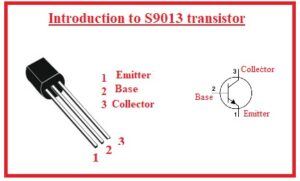
 S9013 Transistor Pinout
S9013 Transistor Pinout
- There are three main pinouts it has that are described here
- Emitter: Current move out from this part
- Base: It is a thin part of a transistor that works as tap between emitter and collector
- Collector: It is larger part of transistor current goes into this part from the base
S9013 Applications
- Common applications of this transistor are discussed her
- It used in high current driver circuits
- It used as a switch and amplifier
- CIrcuit where high frequency needed use this component
That is all about the S9012 NPN transistor that is used in different electronic projects. All details has been explained. If you have any further query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a nice day.