 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will learn Introduction to BC547 Transistor. The transistor is a semiconductor component that has three pins and comes in NPN and PNP configurations. It is used in different circuits as amplifiers and switches. BC547 is NPN configured transistor that also comes in three pins structure emitter, collector, and base.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will learn Introduction to BC547 Transistor. The transistor is a semiconductor component that has three pins and comes in NPN and PNP configurations. It is used in different circuits as amplifiers and switches. BC547 is NPN configured transistor that also comes in three pins structure emitter, collector, and base.
In this post, we will discuss different parameters for BC547 like structure, pins working, and applications. So let’s get started
Introduction to BC547 Transistor
- BC547 transistor is used in amplifier circuits to amplify the input signal. It uses the small value of current at the base terminal to regulate the high current between the collector and the emitter
- It is mostly preferred for amplifiers and switching circuits.
- It has a gain value from 110 to 800 that defines its amplification range. The highest value of current that can pass through this collector is 100mA so try to avoid a high current.
- For biasing of the transistor current at its base pin is provided and must be less than five milliampere
- If the transistor is in a completely biased state so one hundred milliampere current can pass through the collector and emitter. This phase of the transistor is called the saturation region and the voltage of transistor VCE or base-emitter is about two hundred to nine millivolts.
- If there is no base current provided transistor is in off state and called cut off region of the transistor and base-emitter volts can be 660 millivolts

BC547 Technical specifications
- It has a noise value of about two to ten decibels
- Its operating temperature is about minus sixty-five to one-fifty centigrade
- It has DC current gain is 110 to 800
- The transition frequency for this transistor is three hundred megahertz
- 500 mW is collector dissipation
- VEB is six volts
- VCE is 45 volts
- collector current if forty-five volts
- the highest collector current is one hundred milliamps
- It is NPN configured transistor and To-92 its packaging
BC547 Transistor Equivalent
- The equivalent transistor of BC547 are mentioned below
- BC548, BC549, BC636, BC639, 2N2222 TO-92, 2N2222 TO-18, 2N2369, 2N3055 and 2N3904
How to buy BC547?
- You can by using the below link
buy BC547
2N3904 VS BC547
- There is a pin configured at different sequences for both transistors. The pin sequence for 2N3904 is Emitter base and collector and for BC547 is collector, base, and emitter
- VCE for BC547 is 50 volts and for 2n3904 forty volts
- base current 100mA for BC547 are 200mA for 2N3904
- Power dissipation of 2N3904 is 626 mA and 500mA for BC547
- frequency for bC547 is three hundred and others also have the same value
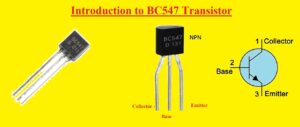
BC547 Transistor Pinout
- It has three pinout collector base and emitter
- Emitter used to get current from the transistor
- The base is a control point like tap here biasing volts are provided
- At the collector current moves toward the inner circuit

BC547 as Switch
- There is a cut-off region and the saturation region are operation region of BC547 as the switch is working.
- The operation of the transistor is an open switch for forward biasing and a closed switch for reverse biasing and for getting the biasing their required current is provided at the base pin.
- Above we discussed that the base current for BC547 is five milliamperes so try to follow this value. A larger current can damage the transistor and must use current limiting resistance with a base pin in a series combination
- TO find the value base resistance use this formula
- Rb= VBE/IB
- VBE must be five volts and the base current can base on the collector current
BC547 as Amplifier
- When BC547 work as amplify it has an active region and helps to amplify power volts and current at different values
- For amplification, some common circuits are used
- Common base amplifier
- Common emitter amplifier
- Common collector amplifier
BC547 Applications
- Common applications are discussed here
- It is used in LED drivers, Relay driver
- High-speed switching circuits
- PWM circuits
- signal amplifiers
- Darlington pairs
That is all about the BC547 Transistor, all details has explained if you have query ask here




