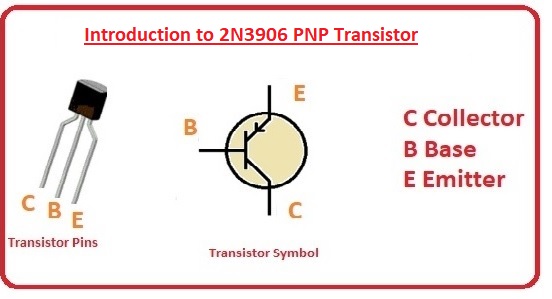
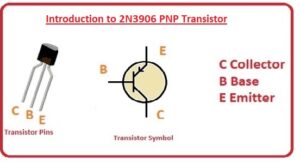
 Hello, readers, welcome to the new post. In this post we will read the Introduction to the 2N3906 PNP Transistor. A transistor is a device used for different switching and development applications. It has 2 main categories the first one is NPN and the second is PNP. The PNP transistor is so structured that there are three layers on both ends with a P-type device and the center of the N semiconductor is suspended.
Hello, readers, welcome to the new post. In this post we will read the Introduction to the 2N3906 PNP Transistor. A transistor is a device used for different switching and development applications. It has 2 main categories the first one is NPN and the second is PNP. The PNP transistor is so structured that there are three layers on both ends with a P-type device and the center of the N semiconductor is suspended.
There are three main terminals with the first one the emitter the second the collector and the third the base. Here we combine the various parameters about these components and learn how to apply them to different projects so let’s get started.
Introduction to 2N3906 PNP Transistor
- The 2N3906 has PNP configured BJT transistor and is very commonly used in circuits where the need of amplifiers and switches.
- Normally preferred for circuits where less value current i needed and less volts has the ability to work at high speed.
- It comes in packaging of T0-92 and three main pinouts emitter-base and collector
- The value of collector current given to it is two hundred milliamperes with the value of VCE is forty volts
- It was designed by the famous electronic company Motorola
- Its configuration is like to the BC557 transistor and used for the high value of current applications due to the large value of VCE.
- Its gain is less than other amplifiers normally has three hundred so not prefer for large amplifier circuits
- In switching applications it prefers since can handle the value of current up to 0.2 ampers.
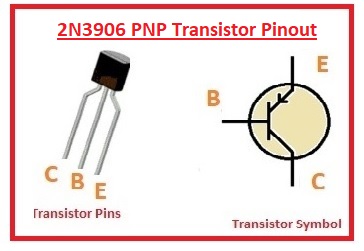
2N3906 PNP Transistor Pinout
- There are three main pinouts it has’
- EMitter: Current comes out from this point
- Base: Work as a control for components like tap
- Collector Larger than other two parts and get the supply
2N3906 PNP Transistor Features
- Its main features are listed here
- It comes in TO-92 packaging
- value of VCB is forty volts
- VBE is five volts
- IC is two hundred milliamps
- PNP general purpose transistor
2N3906 PNP Transistor Applications
- Its main applications are listed here
- It used in Darlington pair
- Lamp flashers are created with the device
- WOrk as switch
- Used in some cases amplifies