 Flexible PCB is called FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit), a quickly growing technology that is used for different electronic projects like automobiles, electro-medical devices telecom sector, and the aviation industry. The use of flexible boards has innovated electrical interconnection methods and is used for connecting different electronic devices. These boards have replaced different types of wiring done by hand reducing the expenses for wiring by about 70 percent.
Flexible PCB is called FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit), a quickly growing technology that is used for different electronic projects like automobiles, electro-medical devices telecom sector, and the aviation industry. The use of flexible boards has innovated electrical interconnection methods and is used for connecting different electronic devices. These boards have replaced different types of wiring done by hand reducing the expenses for wiring by about 70 percent.
What are Flexible PCBs?
The flexible PCB board comes with a mixture of different PCBs also components that are configured on a flexible substrate. These boards are also called flexible boards, flex PCBs, and Flex circuits.
These boards are made with the use of components used for rigid PCBs. The basic difference is that the board is made with flexible material for the required structure.
Flexible PCB Benefits
- There are different advantages of this board explained here
Lightweight Package:
- Flexible boards can easily confined in projects where other boards are not easy to configure These boards are thin less weight and easily folded and configured in parts where other components do not fit.
Accurate Designs:
- Flex boards are made and designed with the use of automated machines. It helps to reduce duces faults that are caused in hand made wires and provides accuracy, that is according to the requirements of devices
East to Design:
- The design of a flexible board does not come with only two layers. They can easily desing in different types. They are made single-sided with a single access, single-sided with double access, and multilayer combination also with rigid and flexible circuits. Their flexible design makes them best for complicated processes.
High Density Configurations:
- The flexible PCBs are a mixture of plated through holes and SMT components. This mixture helps to connect high-density of components with less separation. So denser, less weight conductors are made and free space exists for more components
Flexibility:
- These boards can connected with different planes during use. it helps to reduce weight and space covered with rigid boards. Flexible boards can flexed at different points at the time of use without any damage
Flexible PCB Applications
- Common examples of Flexible boards are
- Avionics
- Airbag systems
- Motion systems
- Satellites
- Antilock brakes
- Bar code equipment
- Battery packs
- Cameras
- Fuel pumps
- Semiconductor testing devices
- Ultrasound probes and other medical devices
Flexible boards Manufacturing Process
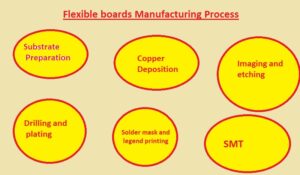
- Flexible PCB fabrication requires several stages, including:
1. Substrate preparation
Substrate materials are made that are polymer sheets like polyimide. For making traces on the substrate it is cleaned and covered with an adhesive substance layer.
2. Copper deposition
- The thin coating of copper is applied on substrates through the use of electroless copper plating. Conductive lines that connect different components is made with the copper layer.
3. Imaging and etching
- In this step circuit design shifted on a substrate with the use of a certain printing technique. Photoresist materials are used for transfer design on the copper layers that are made for showing points where copper-etched
4. Drilling and plating
- For vias creation that makes the connection of layers on the circuit, drilling holes on a substrate for component connections
5. Solder mask
- Solder mask is applied for covering copper traces and components printing on board where label exists
6. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
In this step, components are connected with the use of SMT on a flexible board. With the use of Pic and place machine accurately connect components on board
Structure of a flexible PCB
The flexible PCB board comes with single-layer, double-layer, or multilayer boards. The main components of single-layer flexible boards are
dielectric substrate film:
The base materials of the board used polyimide material, which comes with high resistance to traction and temperature.
electrical conductors:
It is made with copper and denoted traces of the circuit
protective layer,
It is made with the use of a cover coat
adhesive material (polyethylene or epoxy resin), employed for the connection of parts of the circuit together.
Advantages of flexible PCBs
Flexible boards can easily bend and help to make different design configurations and easy connections. Flexible circuits also come with small or irregular-shaped capes, that are not offered by rigid boards.
The main benefit of flexible circuits is they cover less space, and reduce the weight of the board. The use of available spaces provides good thermal management, reduces chances of head dissipation
These boards offer more flexible operation than rigid boards and easily handle vibrations and mechanical stress.
The interconnection standard process based on soldered wires and hand-wired connectors is replaced with flexible boards.
They are low in weight and thickness are come with high mechanical resistance and high resistance for high temperatures.
Types of Flexible Board
Single-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards:
- It is the basic type of flexible baord that comes with a single layer of flexible polyimide layer in a thin layer of copper. The conductive layer is easy to access from one side of the board
Single-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards with Dual Access:
- These circuits are single-side and copper sheets or conductive materials are easy to access on both sides
Double-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards:
- These boards come with two layers of conductive on every side of the base polyimide layer. The electrical connection between 2 conductive layers is made with the use of metalized plated through holes.
Multi-Layered Flexible Circuits:
- These boards are made with the use of different double-sided and single-sided flexible circuits. These boards are interconnected through plated through holes or surface mounted in a cohesive pattern
Flexible PCB from JLCPCB
- If you are working on projects where you need flexible PCB but your budget is too low to afford that PCB don’t worry. Here I am providing you with a $25 discount on a flexible PCB board that you can get with great quality and good features. These discounted and quality boards can be get from JLCPCB
- There is currently a new base material available at JLCPCB for the consideration of their devoted clients. FPC (flexible printed circuit), which has a high level of dependability and outstanding mechanical flexibility, is now offered by JLCPCB and is ready to help engineers with their additional project demands.
- Quality flex PCBs are now available from JLCPCB for a low price beginning at $25. Also supported for your flexible PCB projects is standard PCBA.
- For an immediate quote, submit the Gerber file here: https://cart.jlcpcb.com/quote?checkedPlate=7. Join today to receive new user discounts of up to $54.
- You may get premium flexible PCB on JLCPCB, which is created with quality raw materials from top suppliers across the world.
- This allows for outstanding flexibility and ultra-lightweight PCB that can be readily bent to match your specific electrical design form in the best way.
- JLCPCB flexible PCBs provide unrivaled performance and quality assurance thanks to comprehensive AOI and flying probe testing on every flex PCB. The minimum trace width and spacing are 0.08/0.08 mm.
- EMI Shield, Polyimide Stiffener, FR4 Stiffener, Stainless Steel Stiffener, and JLCPCB FPC are all supported. They are giving new users $54 OFF Sign-up Gifts. To register and receive all of the PCB coupons at once, click “Get Coupons” on the right.
JLCPCB Flex PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
Flexible PCB Capabilities
|
Feature
|
Capability
|
|---|
|
Overall size
|
8×12 mm to 234×490 mm |
|
Minimum trace width/spacing
|
0.08/0.08 mm (0.10/0.10 mm for 1 oz Cu) |
|
Through-hole diameter
|
0.20~6.50 mm (tolerance ±0.05 mm) |
|
Minimum slot width
|
0.6 mm |
|
Minimum annular ring
|
0.1 mm |
|
Copper-to-hole clearance
|
0.2 mm |
|
Soldermask expansion
|
0.1 mm (single-sided) |
|
Minimum solder bridge
|
0.3 mm (any solder bridge narrower than this will be removed) |
|
Minimum text thickness & height
|
0.1/0.7 mm |
|
Pad To Silkscreen
|
≥0.15mm |
|
Quality control
|
Fully AOI & flying probe tested |
|
FPC Outline
|
Laser cut (tolerance ±0.1 mm; copper to edge ≥ 0.15 mm) |
Single-Sided Flex PCB
|
Layer
|
Thickness(mm)
|
Note
|
|---|
|
ENIG
|
1μ” / 2μ” |
Nickel thickness: 80~120u” |
|
Silkscreen
|
10 μm |
White |
|
Polyimide (external)
|
12.5 μm / 25 μm |
Yellow / black (opaque) |
|
Adhesive
|
15 μm / 25 μm |
/ |
|
Copper
|
0.5 oz / 1 oz |
Electrolytic copper |
|
Polyimide (internal)
|
25 μm |
/ |
|
Stiffener
|
0.05~0.25 mm (Drawing required) |
Support Polyimide / FR4 / stainless steel / 3M tape |
|
EMI shield
|
18 μm |
single- / double-sided |
|
Total thickness
|
0.07 / 0.11 mm |
Excluding stiffener |
Double-Sided Flex PCB
|
Layer
|
Thickness(mm)
|
Note
|
|---|
|
ENIG
|
1μ” / 2μ” |
Nickel thickness: 80~120u” |
|
Silkscreen
|
10 μm |
White |
|
Polyimide (external)
|
12.5 μm / 25 μm |
Yellow / black (opaque) |
|
Adhesive
|
15 μm / 25 μm |
/ |
|
Copper
|
0.33 oz / 0.5 oz / 1 oz |
Electrolytic copper |
|
Polyimide (internal)
|
25 μm |
/ |
|
Copper
|
0.33 oz / 0.5 oz / 1 oz |
/ |
|
Adhesive
|
15 μm |
Yellow / black (opaque) |
|
Polyimide (external)
|
12.5 μm |
/ |
|
Silkscreen
|
10 μm |
White |
|
ENIG
|
1μ” / 2μ” |
Nickel thickness: 80~120μ” |
|
Stiffener
|
0.05~0.25 mm (Drawing required) |
Support Polyimide / FR4 / stainless steel / 3M tape |
|
EMI shield
|
18 μm |
single- / double-sided |
|
Total thickness
|
0.11 / 0.12 / 0.20 mm |
Excluding stiffener |
JLCPCB Flex PCB Ordering Instruction
- If you select adhesiveness electro-deposited copper with an ENIG surface treatment as the base conductor. Overlapping silkscreen writing on ENIG pads will be carved out as hollows in the pad.
- The FPC’s edge should be 0.2 mm from any exposed connection pads. Above this distance, areas will be eliminated.
- Optional extras include an EMI shield and stiffener. In the case of stiffeners, they should be defined by a separate CAD design or distinct Gerber layer that is annotated with the material and thickness needed. The stiffener kinds available are seen in the photographs below:
Material of flexible pcb
Several materials are used to create flexible PCBs, depending on the needs of the individual application. The most popular substrate materials for flexible PCBs are listed below:
- The most popular material for flexible PCBs is polyimide (PI). It is perfect for a variety of applications thanks to its outstanding flexibility, thermal stability, and chemical resistance.
- Polyester (PET) is frequently utilized for lower-end applications since it is less costly than PI. It is less thermally stable and flexible than PI.
- Liquid Crystal Polymer or (LCP): This substance can work in high-temperature conditions and provides dimensional stability, so it is an ideal option for high-reliability applications. It costs more than PI and PET.
- Excellent electrical qualities make PTFE (Teflon) a popular material for high-frequency applications. It has less flexibility and is more costly than other materials.
Flex Circuit Overlay
- The electrical traces on a flexible circuit board are shielded and insulated by a layer of material called a “flex circuit overlay,” or FCO. It is a thinner layer of material created with polymer-like polyimide, that is placed on the flexible board surface with an adhesive.
- The FCO protects the electrical traces against damage brought on by environmental factors like as moisture, dust, and temperature variations. Also, it provides electrical insulation between any other materials that could come into contact with the conductive lines and the flexible circuit board.
- Flex circuit overlay can be used to add labels or graphics to the surface of the flexible circuit board in addition to providing protection and insulation. This can help distinguish between various parts, or it can be used to incorporate branding or other aesthetic components.Overall, the flex circuit overlay is a crucial part of a flexible circuit board since it shields the conductive traces from harm and the effects of the environment, ensuring the circuit’s dependability and lifespan.
Flexible PCBsComparsion with other PCB Boards
- Here we have made a detailed comparison table between flexible PCBs and other types of PCBs:
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flexible PCB | Rigid-Flex PCB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Board Material | FR-4 | Polyimide | FR-4 + Polyimide |
| Board Thickness | 0.2-6mm | 0.05-0.5mm | 0.4-4mm |
| Bending Capability | Not Flexible | Highly Flexible | Flexible |
| Number of Layers | 1-50+ | 1-8+ | 2-20+ |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Higher |
| Design Complexity | Limited | Limited | High |
| Weight | Heavy | Light | Light |
| Component Mounting | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Trace Width/Spacing | 0.1mm/0.1mm | 0.05mm/0.05mm | 0.1mm/0.1mm |
| Thermal Resistance | Good | Good | Good |
| Signal Integrity | Good | Good | Good |
| Reliability | High | High | High |
| Environmental Limits | Limited | High | Limited |
Flexible PCB Electrical Features
Dielectric Constants (Dk):
- This feature defines speed when an electrical signal moves from flexible boards. flexible board such as polyimide, comes with a lower Dk than FR, and material used for rigid-flex boards, which helps the highspeed signal transmission. The dielectric constant of base materials also affects FPC impedance.
Loss Tangent (Df):
- This value is based on energy lost in the form of heat when the signal moves through the FPC circuit. The low Df means a lower single loss and good signal quality. FPC has a lower DF value thatn rigid boards and is best for high-energy solutions.
Conductivity:
- The electrical conductive of copper traces in FPC measures features to carry current. FPC supplier uses high-conductivity copper to reduce signal losses and make sure efficient current flow.
Thermal Stability:
- It features to handle high temperature that increases board reliability for manufacturing and end-use.
Tensile Strength:
- They are robust materials irrespective of flexibility, resistant to mechanical stress like stretching and tearing during manufacturing and applications
Flexibility:
- Core featues that help boards to be used for new electronic board designs without affecting due to bent or folded.








1 Comment