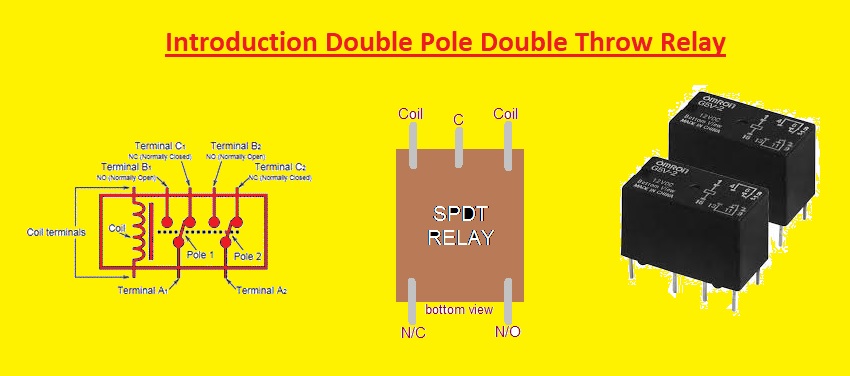
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a detailed look at What is Double Pole Double Throw Relay. The DPDT relay also called the 2-pole relay, and used for different projects like changing of direction of the motor. It has two terminals and 4 connections and it is equivalent to 2 single pole double throw SPDT relays. In this article, we will explore what a DPDT relay is, how it works, and its wide range of applications. So let’s get started with double pole double throw relay
Introduction Double Pole Double Throw Relay
The relay is a switch that is controlled by the electrical circuit. It comes with an input sequence and control signal since has a circuit. it operates by getting an input signal from a connected input power supply that works like normal switches.
What is a DPDT Relay?
- The DPDT relay is an electromagnetic device used in electric motors. It is also called the Double(D) Pole(P) Double(D) Throw(T) relay.
- There are 2 inputs for DPDT with two outputs.
- The DPDT relay comes with two coils terminals, two independent common C1 and C2, and 2 normally open, and 2 normally closed terminals.
- It makes two different connections and regulates coils with a single control signal.
- If no bias at the coil, the relay is in idle condition, with common terminals connected with N/C terminals.
- When DC bias exists at the coil, it magnetically energies and attracts common terminal levers, making the connection between common terminals and the N/O terminal.
Related: What is DPDT Switch and its Working
Working Principle of DPDT Relay
DPDT is an electromagnetic device used for separating two circuits electrically and connecting magnetically. They are used for interfacing electronic circuits, that operate at low voltage to electrical circuits that operate at high voltage. Relay normally comes in different voltage configurations like 6V, 9V, 12V, 24V etc.
Read also: What Is Double Pole Single Throw Switch
What is the difference between SPDT and DPDT relays?
The SPDT relay can used to switch between two different lighting circuits or to control the motor by switching the power supply on or off.
The DPDT relay is an electrical switch that comes with two pairs of switching positions
| Features | SPDT | DPDT |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | Single Pole Double Throw | Double Pole Double Throw |
| Poles | 1 | 2 |
| Throws | 2 | 2 |
| Number of Circuits Controlled | 1 | 2 |
| Applications | On/Off Switch, | Motor direction reversal, power source selector, |
| Number of Terminals | 3 | 6 |
Symbol of Double Pole Double Throw or DPDT Relay
DPDT Pinout
- This relay comes with a total of five pins or contacts, with 3 on one side and two on the other side. The middle of 3 contacts on the left side is common contact, other two are coil contact.
- On the right side, there are 2 contacts, NC and NO. The normally closed contact is NC and the normally open contact is NO.
- Coil connections are insulated from common, NC, and NO contact. There is no physical connection between coil contacts and other relay connections.
- Make a connection of 12 volts and GND with coil relay connections for testing this relay. Since the relay coil does not have a polarity, it is not different whether the side of the coil is connected with 12 VDC and which side is connected with GND.

How Does a Relay Work
- If there is no manual switching relay insulated coil automatically flips the changeover switches. In a result, it works as a control circuit.
- if current is provided relays mostly use components that are like transistors for handling electrical loads. But there is electromechanical really that can easily be understood.
- Relay uses low voltage for conversion electromagnetic in the magnetic field It has a contact switch for controlling magnetic circuit. Due to the working principle of a household switch, it remains in the state that left. If we are on it it will remain on until we turn it off.
- The relay coin works differently due to basic features that need electromagnetic actions. The electric switches relax when a magnet exists in the field during deactivation. it means if the current rating is off external circuit will switch on,
- The DPDT relay has two poles, As a result, a double pole can toggle the circuit on both sides. With that DPDT has double throw, since double throw can easily switch between wires and then control output through on and off with the use of electric power systems..
Read our latest post about: What is a Double Pole Switch? How its Work
What is the Advantage of DPDT?
The DPDT comes with a high switching current helping device to driver motor, pumps, and control relays.
It helps to control devices with a single flick
Applications of DPDT Relays
DPDT relays are used in control systems where they can used to switch between multiple circuits or control many devices. Suh as a DPDT relay can used to control motors by switching the power source to ON or OFF for every motor separately
How to Connect Dpdt Relays in the Circuit
12V SPDT Type Relay
It is a 12-volt SPDT relay, used for managing AC current loads. This relay can controlled with the use of 12VDAC which is the voltage used to energize the relay coil. This voltage is isolated from the voltage provided to relay common and CLosed or normally open contacts.
It has features to handle AC loads of about 7 amps at 250VAC, 10A AC loads at 125VAC, and 12A AC loads at 120VAC. This relay also manages DC loads with a voltage of 28VDC and a current of up to 10 amps.
DPDT Relay Wiring
Accurate wiring is important for the accurate operation of the DPDT relay. As we know DPDT has eight terminals
Wiring Diagram
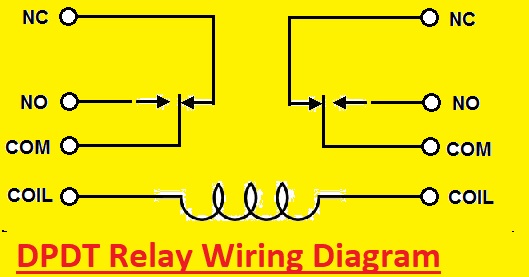
COIL
This terminal is where voltage is applied to the power coil. Polarity is not important for this point. One side gets positive voltage and the other gets negative voltage. There is no difference in order consideration use. Polarity is important when the diode is connected.
NO
it is normally an open switch. When the relay is energized, that means when the coil gets enough voltage, this terminal is where we can connect the devices that need to relay to power. If the relay is not powered, the device connected with NO will be off and when the relay is powered it will be ON.
NC:
The normally closed switch, when the relay does not get power, connects this terminal with the device you need to power. If the relay is not powered device connected to NC will ON and turn off when the relay is powered.
COM
It is a common pin of relay. COM and NO pin come with continuity if the relay is powered and the switch is closed. COM and NC come with continuity if the relay is not energized and the switch is open. It is the relay point where the starting point of the circuit is connected
How Many Types of Relay Are There?
- Electromagnetic Relay
It is a common type of electromagnetic relay. This relay comes with an electromagnet for operating the switching process, helping it to control the circuit on or off. If the current is connected to the electromagnet, it produces a magnetic field that moves the armature, closing or opening the switch. This relay is used in control systems, motor starters, and other uses where high current or voltage is needed for control.
- Delay Relay
This relay is made to delay the operation of a switch or circuit for a certain time. It can be best in different uses, like offering delay before the motor starts or helping the circuit to be ready before being switched ON. Time delay relay used in automotive systems, HVAC system
- Solid State Relay
This relay uses an electronic component and then an electromagnet to operate the switch. This relay is smaller in size and more reliable than electromagnetic relays and can handle high switching frequencies. It is also resistant to shock and vibration making it best for harsh conditions. This relay is also used in the control systems, industrial automation, and switch high-speed.
- Reed Relay
It is an electromagnetic relay that uses a magnetic field to operate a switch. It comes with a small glass tube having pairs of metal contacts, and reeds, that are sealed internally. If current is given to the coil, it produces a magnetic field that moves reeds, closing or opening the switch. Reed relay is used in applications where space is limited, like instrumentation, test equipment, and telecommunications.
How Many Terminals Does a DPDT Relay Have?
- Coil Pin 1
- Coil Pin 2
- (NO) Contact 1
- Common (COM) Contact 1
- Normally Closed (NC) Contact 1
- Normally Open (NO) Contact 2
- Common (COM) Contact 2
- Normally Closed (NC) Contact 2
. latest post: Solar System with Diagram
Why is SPDT Used?
SPDT switches are in between SPST and DPDT switches as easy middle ground. its features to alternate between two output circuits from a single input make them best for basic electronics to heavy-duty electrical rerouting applications
What is the difference between SPST SPDT DPST and DPDT?
Can you use a DPDT switch as an SPDT?
Read Also:
- How To Wire a Four-Way Switch
- What is Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Working & its Applications
- What is a Double Pole Switch? How its Work
- MOSFET Digital Switching
- What is Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Working & its Applications
FAQs:
Q1- Write the difference between a DPDT relay and an SPDT relay.
SPDT is single pole double throw and DPDT is double pole double throw. The DPDT can replace SPDT but SPDT not replaces DPDT. The SPDT controls one circuit but the DPDT has a feature to control a single circuit OR two circuits
Q2- When would you use a DPDt relay?
DPDT relays are used in control systems which can used to switch between multiple circuits or control multiple devices. Such a DPDT relay can used to control two motors by switching the power supply on or off for every motor separately.
Q3- Is a 4 way switch a DPDT?
The 4-way switch is a double pole, double throw switch, internally wired in the reverse connection between input and output, and has 4 external terminals.
Q4- What is the use of relay in motor control?
Motor control relay does protective functions for motors or motors components to make sure accurate and effective working. Phase monitoring relays sense faults in the 3-phase system, alternating relays balance load use, and pump seal damages relays monitor submersible pump shaft seals.
Q5- What is high frequency relay?
High-frequency relay transmits and switches RF signals without distortion. Hongfa’s high-frequency relays come with good RF features, small size, many coil features and different range of ambient temperature.