Critical value act as a boundary that separates the rejection region (where the null hypothesis is rejected) from the acceptance region (where the null hypothesis is not rejected). The critical value is compared to the calculated test statistic to decide whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis. When the critical value is surpassed by the test statistics, the null hypothesis should be rejected.
The concept of critical value is a vital component in hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and decision-making processes. In this article, we will discuss the definition and formula of critical values. In addition, we will cover the solved example of critical values.
Critical value: Definition
The critical value is defined as the value that is compared to the calculated test statistic to decide whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis. Reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis if the test statistics are more extreme than the critical value.
In alternative terms, the critical value in hypothesis testing splits the distribution graph into two regions: acceptance and rejection regions. The null hypothesis is rejected when the value of the test statistic falls within the rejection region, which is determined by the critical values.
Conversely, the null hypothesis is accepted if the test statistic lies in the acceptance region. The critical value act as a threshold for deciding whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis based on the observed test statistics.
The critical value is derived from the chosen level of significance. Usually, the alpha (α) symbol is used to indicate the level of significance. The critical value is associated with a specific probability or confidence level related to the test statistic used in the analysis.
Formulas to calculate a critical value
The formula to find the critical value in statistics depends on the specific statistical test being used. Different statistical tests may have their specific critical formulas. Z, T, χ2, and F are the most commonly used test statistics.
The level of significance (α) is used in all critical formulas. Therefore, we will learn how to calculate alpha (level of significance).
- Select a confidence level, such as 95%, which is commonly used in statistical confidence levels.
- It is necessary to convert this value into decimal format. i.e. 95/100 = 0.95
- Subtract the confidence level from 1 to get alpha. i.e. α = 1 – 0.95 = 0.05
- In a two-tailed test, divide the result by 2. On the other hand, for the one-tailed test, do not divide by 2.
Alphas value will be used in the following statistical tests.
T- Critical value
The t-critical value is used when the population standard deviation is unknown, and the sample size is less than 30. T-critical value can be obtained by following steps:
- Calculate the level of significance (alpha).
- Determine the degree of freedom (df), Which depend on sample size (n). For one sample t-test, the degree of freedom is n – 1. For a two-sample t-test, the formula of a degree of freedom is df = (n1 + n2) – 2
- Look up at the t-table, locate the row corresponding to the degree of freedom (df), and find the column closest to your desired level of significance (alpha). The intersection of the row and column will give you the t-critical value.
Z- Critical value
The z-critical value is used when the population standard deviation is known, and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30. Z-critical value can be obtained by following steps:
- Calculate the value of the level of significance.
- For a two-tailed test, minus the alpha from 1. Minus the alpha level from 0.5, for the one-tailed test.
- Find the resulting value in the z- table. Add the values of intersecting a row and a column. The obtained value will be the z-critical value.
For the left-tailed test, write down the negative sign after the final calculation.
F-critical value
The utilization of the F-critical value is common in the comparison of variance among multiple populations. This is frequently applied in both ANOVA and regression and analysis. F-critical value can be obtained by following steps:
- Calculate the value of the level of significance
- For the numerator degrees of freedom (df1), Minus 1 from the first sample size. For the denominator degree of freedom (df2), Minus 1 from the second sample size.
- Use an F-distribution table, The intersection of the row corresponding to df1 and the column corresponding to df2 will be an F-critical value.
χ2 Critical value
It is used to compare observed frequencies with expected frequencies to assess whether the observed data deviates significantly from what would be expected under the null hypothesis. χ2 value can be obtained by following steps:
- Calculate the value of the level of significance.
- Determine the degree of freedom (df) i.e. df = n – 1
- Find the row corresponding to the degree of freedom. Locate the column that corresponds to the level of significance. The intersection of the row and column will give us the chi-square critical value.
Solved example of critical value
Example
Determine the one-tailed t-critical value if the sample size is 7 and the level of significance is 0.05.
Solution
Step 1: Here,
Level of significance = α = 0.05
Sample size = n = 7
Step 2: Evaluate the degree of freedom (df), For this minus 1 from the sample size (n)
df = 7 – 1 = 6
Step 3: Look at the t-table, and locate the row corresponding to the degree of freedom (df) that is 6 in this example. Find the column closest to your desired level of significance (alpha). The intersection of the row and column will give you the t-critical value.
The result will be 1.9437
Try online critical value calculators to find the results of critical value problems with table. Below we attached a screenshot of the above problem solved through a t critical value calculator.
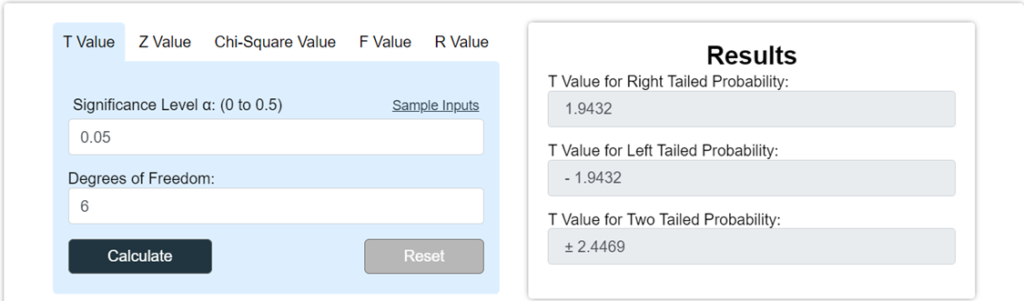
Hence, the degree of freedom (df) and alpha (α) intersect 1.9437, so 1.9437 is our t-critical value.
Conclusion
Thus, we have concluded that critical value plays a fundamental role in statistics. In this article, we discussed everything about critical value- its definition, its formula, and how to calculate it in different statistical tests. With the help of examples, we tried to understand this topic. After reading this article, you can find critical value for any statistical test. follow for more The Engreening Knowledge