Hello, readers welcome new post. Here we will learn 10 Gauge Wire Amps – Everything You Need to Know. 10 gauge wire main part of the electrical system that offers different functions to handle current and different appliances connected. In this post, we will cover its details features and related working conditions and parameters. so let’s get started with 10 Gauge Wire Amps
What is 10 Gauge Wire?
10 gauge wire is an electrical conductor wire that has a value of dia and is used in different power distribution circuits and installations. The work gauge is used to define the thickness of the wire and its low value means the wire is thick. In the form of the high value of gauge wire is thin or has less dia. 10 gauge wire is thick and can handle a higher current than the high value of the gauge.
10 Gauge Wire Features
| AWG Gauge | Diameter (inches) | Diameter (mm) | Area (inches^2) | Area (mm^2) | Ampacity (60°C) | Ampacity (75°C) |
Ampacity (90°C)
|
| 10 | 0.1019 | 2.5882 | 0.0082 | 5.2612 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
What is Wire Gauge and Ampacity
Wire gauge affects the current carrying ability of wire. Ampacity is the highest current of wire that can be handled without having any damage or overheating condition. As wire gauge decreases ampacity 10 gauge wires have a high value of ampacity the thin wire makes it best for the high value of the current
Current-Carrying Capacity of 10 Gauge Wire
Different parameters such as conductor material, ambient temperature, and type of insulation are used to define the current carrying features of 10 gauge wire.10 gauge copper wire can handle thirty to forty amperes current and 10 gauge aluminum wire can handle twenty-five to thirty-five amps current
Applications of 10 Gauge Wire
This wire is commonly used in commercial buildings and residential applications. It is mostly used in house wiring that need high currents such as water heaters, air conditioners, and dryers wiring. Also, it is used in automotive systems and marine uses that need regular current supply
Advantages of Using 10 Gauge Wire
10 AWG ampacity value is high which provides power transmission without any power loss. It minimizes the chances of overheating and also controls electrical fires. 10 gauge wires also have good protection for voltage changes and can handle power devices
Safety parameters
As this wire handles high current so needed to have proper safety for them during their work. Make sure the wire is accurately connected and has the proper insulation to avoid damage. Accurate grounding techniques and circuit breakers can be used to prevent electrical hazards
Choosing the Right Wire Gauge
The use of an accurate wire gauge is a good option to have reliable and safe operation. If not have an idea to use the appropriate size of write must get the service of a technician or experts
Installation Tips for 10 Amp wire
Correct connection of wire is helpful to increase the effectiveness of 10 gauge wire. Make sure that all connections of wires are accurately connected and tightened to prevent voltage loss or loose connection. Proper label and configure the wiring to have correct maintenance and troubleshooting.
Maintaining 10 Gauge Wiring
The wire is accurately maintained than any fault can be found. Make regular inspections of the wire to avoid wear, damage, and corrosion helpful to the proper function of the wire
Upgrading to 10 Gauge Wiring: Is it Worth It?
If there is a need to upgrade the electrical system in case of high current applications using the 10 gauge wire can be the best option.it is good to use a reliable power source and have good efficiency of the electrical configuration
Common Myths About 10 Gauge Wire
There are some myths about the 10 gauge wire.
- Myth 1: The function of thick wire is good
- Myth 2: 10 gauge wire can only be used in industries
- Myth 3: Installation of this wire is difficult
10 gauge wire amp rating
The ampacity of 10 gauge wire is about thirty amps for 75 centigrade temperature which is used in the electrical wiring systems. it explains that this wire can easily handle thirty amps of current without overheating. But the length of the the wire can affect the ampacity of the wire also insulation and ambient temperature affect the ampacity. 10 gauge wire is 100 feet longer and can handle 23.3 amps at 75°C.
it is good to check that the breaker of the fuse and save the 10 gauge wire must have a rating value of not more than thirty amps. it will avoid overloading and save wire to get overheating
the ampacity of 10 gauge wire at different temperature values
| Temperature | Ampacity |
|---|---|
| 60 centigrade | 28 amps |
| 75 centigrade | 35 amps |
| 90 centigrade | 40 amps |
How Thick is 10 Gauge Wire?
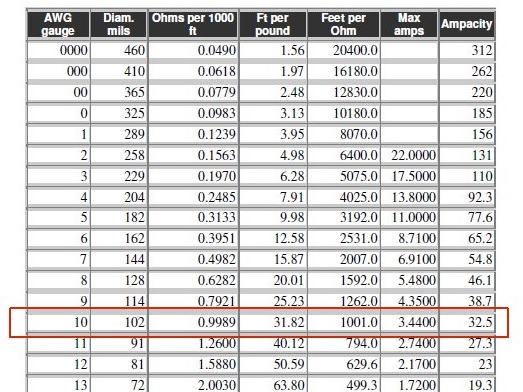
It is almost 0.1019 inches in diameter. That means its thickness is about lead pencil. Gague used to measure teh wire thickness with a low gauge means the wire is thick. 10 games wire is highly thick and used where high current need
the thickness of 10 gauge wire in different units:
| Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 0.1019(inches) |
| Diameter | 2.588 (mm) |
| Cross-sectional area value | 5261 (circular mils |
| Cross-sectional area | 5.26 (mm²) |
the ampacity of 10 gauge wire for different temperatures for the wires of 50, 100, 150, and 200 feet:
| Temperature | 50 feet | 100 feet | 150 feet | 200 feet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 centigrade | 21.8 | 20 | 18.4 | 17.1 |
| 75 centigrade | 25.4 | 23.3 | 21.5 | 20 |
| 90 centigrade | 28.9 | 26.6 | 24.7 | 23.2 |
10 Gauge Wire Cables: 10/2 Wire, 10/3 Wire, and 10/4 Wire.
- 10/2 wire has two conductors and bare copper ground. It used to dryer and oven that need 240 volts.
- 10/3 wire comes with three d conductors and bare copper ground. It is used for projects where 120/240 volts need values and air conditioners.
- 10/4 wire has 4 conductors with insulation and bare copper ground. it is used in electric stoves and hot
| Wire types | Conductors | Grounded Conductor | Insulation used | Ampacity at 75 centigrade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10/2 | 2 | copper | Rubber | 20 amps |
| 10/3 | 3 | copper | Rubber | 25 amps |
| 10/4 | 4 | copper | Rubber | 30 amps |
How many amps can a 10 gauge wire handle?
Insulation and temperature values are defined as the highest value of amps that a 10 gauge wire can carry. According to NEC 10 gauge wires having rubber insulation can handle thirty-five amps at seventy-five centigrade. if the wire is under high conditions of temperatures like outdoors its ampacity will be low
the ampacity of 10 gauge wire at different temperatures and insulation types:
| Temperature | Rubber Insulation | THHN Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| 60 centigrade | 28 amps | 25 amps |
| 75 centigrade | 35 amps | 30 amps |
| 90 centigrade | 40 amps | 35 amps |
Can I use a 10 gauge wire for 20 amps?
Yes, it can be used for 20 amps. it is a commonly used wire size for 20 amp circuits. The 10 gauge wire can easily mange thirty amps at seventy-five centigrade which is higher than the features to handle a 20 amp circuit.
The NEC explains that the gauge wire has rubber insulation for several temperatures and can handle thirty-five amps. So for 20 amps circuits, it is a good option, and for high-temperature conditions not used
Can I use a 12 gauge wire for 35 amps?
No, we cannot use 12 gauge wire for 35 amps. The value of ampacity for 12 gauge wire is for twenty-five amps 35 amps. according to NEC 12 gauge wires with rubber insulation can handle 25 amps
Can I use a 10 gauge wire for 40 amps?
No, 10 gauge wire not be used for 40 amps. As 10 gauge wire ampcity is 35 amps it becomes overloaded for a 40 amp circuit.
The main factors determining the amp for 10 gauge wire
- wire temperature. High temperature affected the ampacity of the wire and deceased it. 10 gauge wire with rubber insulation can carry thirty-five amps. For high temperatures, the ampacity decreases
- insulation. Wire insulation also affects the ampacity. A wire with rubber insulation has less ampacity than THHN insulation.
- Wire length. The longer wire comes with less value of ampacity. Because the large length has high resistance it can handle high currents without overheating
- ambient temperature. it is the temperature of the air. That reduces the ampacity of the wire
- type of load. The load connected has affected the wire ampacity.
Maximum Length for 10 Gauge Wire at Different Currents
| Current | Ambient Temperature ( centigrade) | Maximum Length (ft) |
|---|---|---|
| 20 amps | 75 centigrade | 165.23 |
| 20 amps | 60 centigrade | 200 |
| 30 amps | 75 centigrade | 57 |
| 30 amps | 60 centigrade | 75 |
| 40 amps | 75 centigrade | 38.1 |
| 40 amps | 60 centigrade | 50 |
Max amps for 10 gauge wire
The max amps for 10 gauge wire are about 30 to 35 amperes of current in different uses. However, the exact ampere capacity is based on insulation of the wire, temperature rating, and local electrical code.
How many amps can 10 AWG wire carry?
10 AWG wire can carry 30 AMPS
How many amps will the 10/2-wire handle?
10/2 wire amp rating is up to 30 amps
Does Distance Affect 10-Gauge Wire Amp Rating?
yes, distance affects the rating. Since distance affects the length of the wire. If length increases resistance increases and high resistance casues heat. So heavy-duty devices use short power cords.
How Far Can You Run 10-Gauge Wire?
| Wire Size | Voltage (Single Phase) | Maximum Distance (ft) | Voltage (Three Phase) |
Maximum Distance (ft)
|
| 10 AWG | 120V | 55 | 120V | 64 |
| 240V | 11 | 240V | 128 | |
| 480V | 222 | 480V | 256 |
Is Material (Copper/Aluminum) Affects 10 AWG Amp Rating?
yes, the materials affect the ampere rating of the wire. Copper wire handles high current since copper is high conductive than aluminum. For high gauge aluminum is used. The replacement for 10 AWG copper wire is 8AWh aluminum wire..
How many amps can 10 gauge wire carry?
The 10 gauge wire has featues to handle about 30 to 35 ampers current in different applications. But accurate ampere capacity is based on the type of wire insulation, temperature, and electrical codes.
Will #10 wire carry 40 amps?
The 10 AWG wire and 12 AWg wire are not good for a 40 amp circuit breaker. 10AWG and 12 AWG copper wire have 35amp and 25 amp wire ampacity. So connecting them with a 40-ampere circuit is not good and can cause electric accidents.
Will 10 gauge wire handle 35 amps?
10 gauge wire can handle about 35 ampers.
Is 10 gauge wire good for 30 amps?
In some conditions, 10 gauge wire is good to use for a 30 amp circuit breaker. But based on load demand there is a need of a high gauge wire that is 8 gauge.
What is the maximum voltage for a 10 gauge wire?
Can you run 20 amps on 10 gauge wire?
What color is 10 gauge wire?
Orange Sheathing
How thick is 10 gauge wire?
Can I use 10 gauge wire for 240 volts?
a 30-amp circuit used for 10-gauge wire
What outlet is 10 gauge wire?
Read our related posts:
Faqs
- How far can you run 10 gauge wire for 30 amps?
10 gauge wire can handle 30 amps for 57 feet for 120 volts and 114 feet for 240 volts. It is for dry conditions installed wire and for copper wire. If the wire has a high size voltage will be increased affecting the device’s operating
- How far can you run 10/2 wire on a 30 amp breaker?
10/2 wire comes with two 10 gauge conductors and a ground conductor. So can carry 30 amps about 50 feet for 120 volts, and 105 feet for 240 volts.
- How far can I run a 10 gauge wire?
The highest distance for which ten gauge wire can be used is based on voltage, current, and conditions. Normally, avoid to use10 gauge wire for more than 150 feet distance
- Does distance affect the amp rating?
Yes, distance changes affect on amp rating of a wire. Longer wires have high losses that cause the wire to overheat. Must consider distance before selecting the wire size
- Where can I use a 10 gauge wire?
- Electrical appliances: it uses wiring that works on 30 amps or less such as dryers, electric water heaters, and ovens.
- Outdoor outlets:
- Heavy-duty circuits: wiring heavy-duty circuits, like power electric motors, uses these wires
Can I use a 10 gauge wire for 220?