 Hi, guys welcome to another interesting post. In this post, we will discuss What is Active Low-Pass Filters. Filter is such circuits which comprise of the operational amplifier as the active component offers a numerous benefit over the passive filter configuration such as R, L, and C. The operational amplifier has a value of gain, therefore, the signal will not be get attenuated when moves to the filter configuration.
Hi, guys welcome to another interesting post. In this post, we will discuss What is Active Low-Pass Filters. Filter is such circuits which comprise of the operational amplifier as the active component offers a numerous benefit over the passive filter configuration such as R, L, and C. The operational amplifier has a value of gain, therefore, the signal will not be get attenuated when moves to the filter configuration.
The large value of input impedance of the operational amplifier stops the extra loading of the running device and the less output value of output impedance of the operational amplifier stops the filter from getting affected to the load which is operating. The active filter can be easily set to different values of frequency without any variation in the required response. So let’s get started with What is Active Low-Pass Filters.
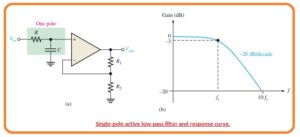
What is Single-Pole Filter
- The below figure indicates the active filter having a one low pass RC frequency-selective circuitry which offers a roll of over the critical frequency as shown in responsive graphical representation.
- The critical frequency of single-pole filter is fc=1/2Πfc. The operational amplifier in this filter configuration is linked as a non-inverting amplifier configuration to the closed-loop voltage gain in the passband adjust to the values of resistance R1 and R2.
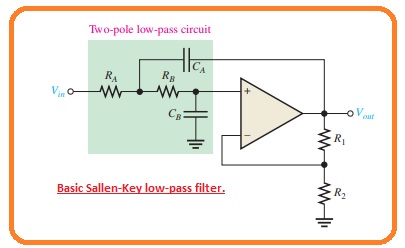
Sallen-Key Low-Pass Filter
- The Sallen Key is the very general arrangement for 2nd order filter configuration. It also called VCVS or voltage-controlled voltage source filter.
- The low pass type of the Sallen Key filter is can be seen in the figure below.
- Note that there is 2 lowpass RC circuitry which offers a roll-off over the critical frequency value.
- On the RC circuitry comprises of resistance RA and capacitor CA and 2nd circuitry comprises of RB and CB.
- The important feature of the Sallen Key low pass filter is the capacitor which offers feedback for creating the response close to the corner of the passband.
- The critical frequency for the Sallen Key filter is mentioned here.
fc=1/2Π√RARBCACB
- In this condition the equation for the critical frequency become.
fc=1/2ΠRC
- In the single-pole filter the operational amplifier in the 2nd order sallen key filter behaves like a noninverting amplifier configuration to the negative feedback offered by resistance and R1 and R2.
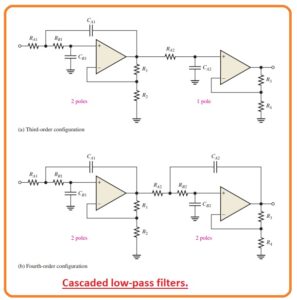
Define Cascaded Low-Pass Filters
- The 2 pole filter is needed to obtain a 3rd order low pass response -60db/decade/.
- It can be done with the use of cascading a 2 pole sallen key low pass filter and a single-pole low pass filter as can be seen in the below figure.
- the figure denoted as b indicates a 4 pole arrangments get by the cascading 2 Sallen key pass filter.
- In common, a 4 filter is normally used since it uses a similar quantity of operational amplifier to get a faster roll-off.
That is a detailed post about active low-pass filters if you have any further query ask in comments. Thanks for reading have a nice day.