 Hi readers welcome to the new tutorial. In this post, we will learn Introduction to BC490. The transistor is a device that is used in different electronic projects as switch and amplifiers simulation. It has three pinouts that are emitter-base and junction. Normally central part is called the base that works as a control like a tap. While emitter and base are used for circuit simulation the doping area of the emitter is less than the collector but larger than the base.
Hi readers welcome to the new tutorial. In this post, we will learn Introduction to BC490. The transistor is a device that is used in different electronic projects as switch and amplifiers simulation. It has three pinouts that are emitter-base and junction. Normally central part is called the base that works as a control like a tap. While emitter and base are used for circuit simulation the doping area of the emitter is less than the collector but larger than the base.
In this post, we will learn the BC490 transistor working, features, operation, and some other parameters. So let get started.
Introduction to BC490
- The BC490 is a general-purpose transistor and it belongs to the PNP category of the transistor.
- Its structure is such that N-type material is placed between two P-doped materials. N side has electrons as charge carriers and P has a hole as the majority charge carrier.
- Normally silicone or germanium is used for transistor construction.
- There is minus eighty volts are given to the collector and emitter of this module and minus one amperes current about collector flows.
- These features help to use in different operations where high voltage is needed.
- It is employed where moderates level switching volts is needed.
- It is normally used as a switch due to its good function and less expensive nature.
- When volts are provided to it then one ampere current can flows about the collector and emitter.
- when there is no current flowing at the base then the condition of the transistor is called cut off.
- Its gain value is between forty to one sixty.
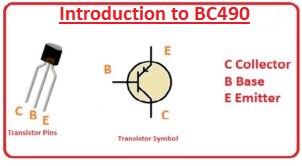
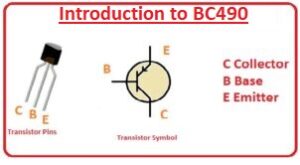
BC490 Pinout
- There are 3 main pinouts it has like other transistors.
- Base: it is working as a control
- Emitter: current flows from this point to collector
- collector: current get it from the emitter reased
Features of BC490
- Its main features are listed here.
- Its collector capacitance is about nine picofarads.
- Operating temperature lies between minus fifty-five and one fifty.
- The value of transition frequency is one fifty megahertz
- Collector dissipation is 0.625 watts
- Its packaging is TO-92
- Voltage about emitter and base terminals is minus four.
- Collector curent is one amperes.
Applications of BC490
- The main applications of this module are listed here.
- Used in amplification of signal circuits
- used in sound amplifier circuits
- used in sound systems as amplifiers
- used as switch
That is all about the BC490 i have covered all parameters of this module if you have any query ask in comments. Thanks for reading have a good day.