Hi friends, welcome to the new post. Here, we will learn 5G vs 5G Ultra Wideband – What’s the Difference? The development in mobile systems helps to use 5G, which provides high speed and fast connection of the network. With the 5 G there is another technology 5G ultra wideband.In this post, we will discuss different parameters to learn which is the best and fastest and their related features. So let’s get started with 5G vs 5G Ultra Wideband
Introduction to 5G vs 5G Ultra Wideband
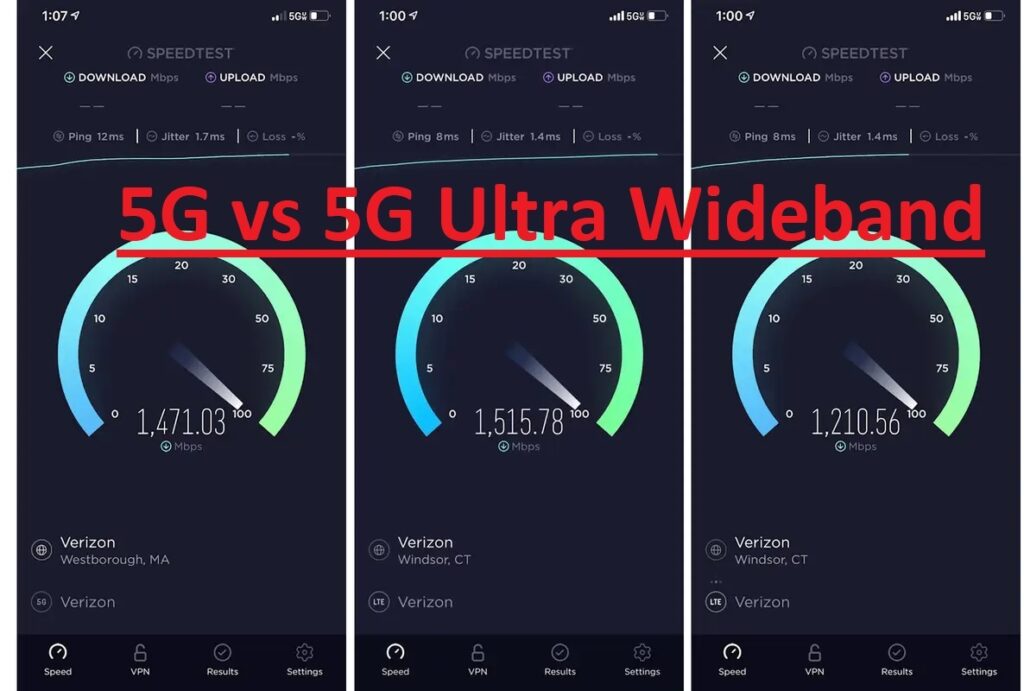
What is 5G?
The 5 G is defined as the fifth generation. It is an advanced technology used for broadband cellular networks. It is about 100 times high speed thatn 4G.
It offers high speed with non-zero lag for the faster and better mobile experience.
With the use of 5 G we can play games, do our work, and play games. This cellular broadband communication helps to provide a safe, sustainable future.
It was the first time used in 2019 since that time it has different features for users. Before the use of 5G there were some other technologies used such as 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G.
1G was first time used in the 1980s. That is the first data network and it has analog voice services.
2G was used in the 1990s and provides digital voice services and CDMA.
3G was used in the 2000s that has features of mobile data use.
5G not only best for mobile phones but has some compatible devices. In simple words we an connect out computer as well with 5G wireless technology.
What is 5G Nationwide?

5G nationwide has integration with 4G LTE network and low spectrum 5G. With that 5G nationwide uses antenna technology to operate 5G and 4G LTE with frequency band.
So 5G can employ in locations where service exists and also it can switch to 4G or 4G LTE where high-speed services do not exist.
The 5G nationwide is new standard for 5G connections. The mixture of 4G LTE and low spectrum 5G both helps to provide simple integration for 5G and 4G.
5G nationwide has services in some cities more thatn 2700 cities are covered. 5G nationwide has services for both outdoors and indoors due to the low band spectrum. It is mostly provided by 5G of Verizon.
5G nationwide is low band 5 G service that offered by Verizon in USA. It is made to cover more area and good speed than 5G.
How To Get Verizon Pay Stub: Here’s The Easiest Way To Get I
How To View And Check Verizon Call History/log: Explained
Verizon Transfer PIN: What Is It And How To Get It?
devices that support 5G Nationwide
- iPhone 12 and later
- Samsung Galaxy S21 and later
- Google Pixel 6 and later
- OnePlus 9 and later
- Motorola Edge+
- Nokia XR20
What is 5G Ultra Wideband?
The 5G ultra-wideband is another standard wireless network operator of verizon and it is a marketing name of 5G technology by Verizon.
It offers both MMwave and C bands so has high speed and low latency than other technologies. it is made to offer best speed features for users.
The 5G ultra-wideband has a high level of service. It offer high speed high data transfer speed to mobile systems without affecting local data transfer. The 5G ultra-wideband has made a revolution in different sectors such as healthcare, public works, and automotive
The basic difference between 5G ultra-wideband and 5G Nationwide is location and speed. 5G nationwide comes with larger area service than 5G ultra wideband and the speed of 5 G ultraband is higher.
What Does 5G Ultra Wideband Offer?
Speed
The 5G ultra wideband comes with a download speed of 4+ Gbps. With that it uploading speed is 200+ Mbps which is higher than 30-35 Mbps of 4G and 4G LTE.
Latency’
Gamers use 5G ultra wideband because of the low latency it offers. With that, it also covers features of video calling. its low latency is due to zero buffering
Capacity
The capacity of this service is best to handle a larger number of users at the same time. It is not considered any location provdies the best services and it can offer the best results without affecting performance. it has a higher capacity than older networks
Benefits of 5G Ultra Wideband
- it has good speed than public WiFi. With 5G ultra-wideband, there is no speed issue to be done online streaming. It also offers high-speed browsing.
- It not only supports mobile phones but is used at homes and offices. it has high-speed internet and connects many devices. With that, there is no need to use cable for 5G ultra wideband.
- it also provdies high speed for downloading. It is 10 times faster than WiFi.
- It also has larger coverage. it is best to use for places where a larger number of people use the phone at the same time. Also, thousands of people can stream, post, and download easily.
- It also has the feature of HD audio and video.
5G Nationwide Vs 5G Ultra Wideband
- 5G ultrawideband can provide data transfer speed of about 10 Gbps and 5G has features to transfer data up to 2 Gbps. It means with use of 5 G ultra-wideband we can download 1 GB of data in some seconds and 5G will take time.
- The time taken by data to move from one point to another is called Latency. 5G ultra wideband comes with less latency about 3 milliseconds and 5G has 30 milliseconds. It means 5G ultrawideband is high responsive thatn 5G and best to use for communication systems.
- The coverage of 5G ultra-wideband is shorter thatn 5G. Since 5G ultra-wideband has a high frequency, that is susceptible to attenuation. 5G ultra-wideband is easily exists in urban areas and 5G exists in rural areas.
- The cost of ultra wideband is higher thatn 5G. Since 5G ultra wideband needed more instruments.
- Not all types of devices are compatible with 5G ultra wideband. Just devices tha come with a 5G modem supported mmWave spectrum can make connections with 5G ultra wideband. Most devices that supported 5G supported sub 6 GHz spectrum, that is less speed than the mmWave spectrum.
- 5G ultra wideband supported more MIMO antennas than 5G. it means that 5G ultra-wideband has features to handle more connections at the same time and has the best service for crowded areas.
C-band, Low Frequency, and mmWave
Low Frequency
In the radio frequency spectrum, the low-frequency term is used for all bands that are less than 30 MHz. 5G nationwide uses les frequency bands due to fast speed tha makes it useful for larger coverage area.
Such bands supported mobile services like voice calls and messages. They also support 4G cellular structure, so are low cost.
The 5G ultrawide band does not commonly use low-frequency bands. As 5G UWB is for video streaming that are not best for low-frequency bands
C-band
C band is part of the electromagnetic spectrum of 4.0 to 8.0 GHz and belongs to mid-frequency bands. C band is used in satellite communication and radar. High-speed 5G network than 4G is due to the use of C band.
In 5G nationwide C band offers broader overage and good connections. It is the main casues for a larger coverage area. 5G nationwide uses this service for mobile data services and provides consistent connections.
mmWaves Band
It is also called millimeter waves and has a range of 30 to 200 GHz. The short wavelength of this wave provides a range of one to ten mm. it is part of the HFB band.
In 5G nationwide less use of mmWaveBands since a lower cover area is provided. With that, these waves are restricted through buildings and other such obstacles
The common use of mmWave band is in 5UWB due to the high dense frequency range.
Read also
- How to Update Verizon Towers in Easy Steps
- Does Verizon Travel Pass Activate Automatically
- How to Start a Trading Business from Home
- Verizon Transfer PIN: What Is It And How To Get It? 2024 Guide
- Why Does My Phone Say SOS Only?
faqs
- Is 5G ultrawide better than 5G?
- The 5G ultra-wideband has a latency of less than 30 milliseconds and 5G has latency about 30ms. it means 5G ultra-wideband has good response than 5G and is best for real-time communication like video calling
- Is 5G ultra wideband real 5G?
5G ultra wideband 5G type of technology use ultra wideband radio frequency for data transmission to short distances
- What is the difference between 5G and 5G UC?
- 5G UC is a T mobile version of 5G that is called ultra capacity. it comes with high and 5G but is based on midband spectrum providing 2.5 GHz. 5G UC icon can seen on your phone if you are in the range of any towers. If there’s 5G without UC it means a lower-speed, low-band 5G network is used.
- Which type of 5G is best?
Mid-band spectrum is the best type of 5G since it carries larger data for longer distances with a frequency range of 1 to 6GHz
- Which 5G is faster?
5G Ultrawide is faster than 5G UC. it works on high-frequency values, that handle more data. But 5G UC has a larger range than 5FUltrawide.
- Does 5G ultra wideband drain battery?
- yes, 5G uses more battery than 4G LTE. So it suggested to use 4G for low battery use.
- Is 5G ultra wideband faster?
- If there is a need of high speed and latency then 5G ultra-wideband is best to use. But if there is a need of larger coverage then 5G is best option for the limited budget.
- Which iphones have 5G ultra wideband?
Ultra Wideband comes on iPhone 11 models and later, excluding iPhone SE (2nd and 3rd generation)
-
Is LTE better than 5G?
- 5G provdies high speed data than LTE but it supports more devices and users at the same network also. 5G has high capacity than LTE. it means 5G handles more data traffic.
- What is the difference between 5G+ and 5G UC?
5G UC, 5G+, and 5G UW all are same and will get you the fastest transfer speeds.
- What are the different versions of 5G?
- 3 main types of 5G have their own features and services, that are low, mid and high band named for the spectrum of radio frequencies they support.
- What is the range of 5G ultra wideband?
its range is 0.3-1 mile without the presence of any external obstructions
- What is ultra wide band used for?
Ultra Wide Band used as short-range wireless communication protocol to tracking the location within less than half an inch distance. This technique measures how much time time takes short radio pulses to travel between one device and another
- Why is 5G Ultra wideband slower?
- If there are many devices are connected on 5G home network at the same time pressure on the router results in slow speed.
- Who has strongest 5G signal?
T-Mobile comes with high-speed 5G in the USA
- What is stronger than 5G?
- 6G is new technology than 5G cellular technology. 6G network can use higher frequency thatn 5G network and offers higher capacity and much lower latency.
- Is 5G faster than fiber optic?
- Fiber download speed is higher thatn 5G download speed. But 5G can be of 20 Gbps and 10 Gbps upling, fiber optic has 1 Petabit per second. The measured speed on fiber cables is around 100 Gbps
- Is all 5G the same?
No, not all 5G is the same. There are three main types of 5G:
5G Sub-6 GHz: It uses frequencies below 6 GHz and has a range of about 1 mile.
5G mmWave: It is the fastest type of 5G. It uses frequencies 6 GHz and ranges about 1,000 feet.
5G Standalone (SA): it most advanced type of 5G. It does not rely on 4G LTE for coverage and offer faster speeds and lower latency.
Is iPhone 13 5G?
iPhone 12 mini, iPhone 12, iPhone 12 Pro, iPhone 12 Pro Max, iPhone 13 mini, iPhone 13, iPhone 13 Pro, iPhone 13 Pro Max, iPhone SE 3, iPhone 14, iPhone 14 Plus, iPhone 14 Pro and iPhone 14 Pro Max all supported 5G.
- Is iPhone 14 5G?
Yes, the iPhone 14 is also 5G-enabled.