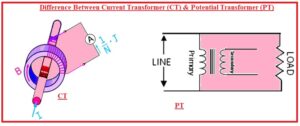
 Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Difference Between Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT). The transformer is a device that is used for changing the voltage from high to low or low to high. The transformer used for high to low volts is called step down and the other is called to step up that converts low to high.
Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Difference Between Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT). The transformer is a device that is used for changing the voltage from high to low or low to high. The transformer used for high to low volts is called step down and the other is called to step up that converts low to high.
There are different types of transformer are used with small level transformers called instruments are used like a current transformer and potential transformer. The current transformer is used for current measuring and the potential transformer is used for volts measure. Here we will discuss different points to find the differences between the Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT). So let gets start Difference Between the Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT).
Difference Between Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT)
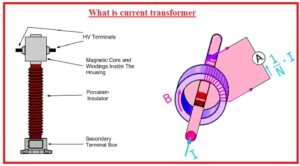
What is the Current Transformer
- A current transformer is a category of transformer used for decrement and increment in the ac current. It generates the current in the secondary windings that is directly proportional to the primary current
- The current transformer called the instrument transformer. It is used to for decrement the current and volts to a smaller level.
- This transformer separates the measuring circuits from the high volts of the main circuits.
- This transformer output is equal to the current flowing at the primary side and give very less load to the primary side
- It is used in power system generation point industries and substations.
- This transformer comes with primary windings core and secondary windings.
- This transformer is created to sustain the ratio among the current at primary and secondary circuits according to the define value.
- There is no effect of the CT connection at the main circuit
- In CT there is silicon steel ring core is used having numerous turns.
- The conductors having current is passes in the ring of CT.
- CT is used in series combination to the circuit
- It has less turns than the pt at primary and larger at secondary
- It can measure the current up to five amps
- Its input is current has a constant value
- It has two main types wound and core
- Its impedance is less
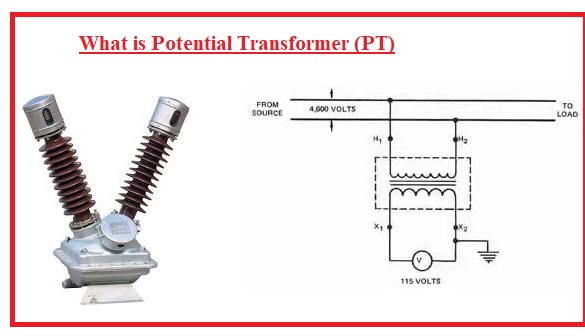
What is a Potential Transformer (PT)
- The potential transformer is used to protect and measure the potential of the system. It is used to measure the larger ac volts of the system
- It is step down transformer that has a larger turn at primary and less at secondary
- There is the use of low range volt meter for measuring the volts through PT.
- It comes with shell-type construction to give the good results
- It gives good protection to its users since connected to ground
- Its primary si linked to high volts and less range voltmeter of ac nature is linked to secondary of PT
- The relation among the line volts and voltmeter volts are given as line volts denoted as Vp and voltmeter volts as VS.
VP/VS=NP/NS
- It is created with steel having a high flux density
- It is connected in parallel combination
- Volts areng is one ten can be measured through it
- Its two types are Electromagnetic and Capacitor voltage
That is all about the Difference Between Current Transformer (CT) & Potential Transformer (PT) all paramerts has been explained if you have any further query ask in the comments. See you in next post.