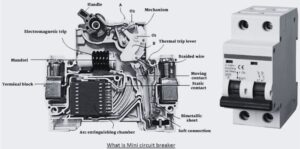
Mini circuit breakers (MCBs) are protection devices that are used for short circuit and overload conditions. It makes for automatic interruption for current flow if the defined value, avoiding damage to the circuit and connected devices. MCB is used for building homes and industries and provides a reliable and easy method for circuit breaking without replacing wires and fuses.
What is a miniature circuit breaker?
- A miniature circuit breaker is a small-capacity breaker that comes with a compact design. It is a low-voltage circuit breaker and part of different electrical devices for protection.
- Miniature breakers are used for protection of circuits from damage as a result of overcurrent and voltage.
- If there is overloading or a short circuit or other faults, tripping devices have features to work in the proper way and break the circuit.
- If the current is at normal conditions, its main connection will directly connect with the circuit, and the trip unit will not be faulty.
- The main failure mode of miniature circuit breakers comes with misoperation, failures, and refusal to operate.
Types of Mini Circuit Breakers
Different types of MCB are used according to tripping features that define their different current levels.
Type B:
- This type of MCB operates for 3 to 5 times the rated current. It is good to use for resistive loads like lighting circuits and outlets.
Type C:
- This type of MCB works from five to ten times the rated current. It is good to use for inductive loads like motors, solenoids, and transformers.
Type D:
- These breakers trip at 10 to 20 times the rated current. It is good for high inductive loads like welding machines, X-ray machines, and larger-sized motors.
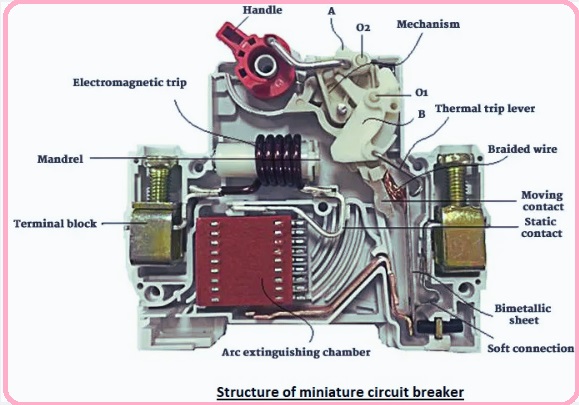
Structure of miniature circuit breaker
The miniature circuit breaker comes with different parts that are listed here.
Contacts
- The basic working of moving and static contacts is to make and break the process before and after circuit failure, and the technical demand of the connection of the MCB is to have features of making and breaking the limit of short circuit current.
- With that, it needed a current that gets longer working time, and there is no damage and tear after application of the process in the defined working life.
Arc extinguishing
- the arc extinguishing system used to extinguish the arc that generated as a result of contact disconnection.
- The arc extinguishing system comes with two main parts. One is a strong spring system that helps the contact of the low-voltage circuit to separate fast, and the other is an arc extinguishing chamber that exists over the contacts.
- If the main connection is disconnected, the grille in the arc extinguishing chamber detects magnetism. The arc is drawn in the grid and gets out of phase for the protection of the connection from damage.
Protective device
- Miniature circuit breaker trippers used for protection of distribution systems come with different types of trippers, like undervoltage, excitation, and overcurrent.
- Undervoltage protection uses an undervoltage tripper in the breaker for monitoring change in voltage values.
- If the voltage reduces from 70 to 35 percent of the rated voltage, it goes back to the circuit breaker and performs a breaking process that prevents the breaker from closing if the voltage is less than 35 percent.
Operating mechanism
- The operation mechanism of the miniature circuit breaker comes with a magnetic trip and a thermal trip. The magnetic trip comes with a composite magnetic system with a spring-loaded buffer having a magnetic spring connected in silicon fluid and a normal magnetic trip.
- the thermal tripping device is covered with a bimetallic strip and heater coils wound to produce heat according to current flow
MCB Features
Thermal-magnetic
- This MCB comes with a combination of a bimetallic strip and an electromagnet for providing thermal and magnetic protection. The bimetallic strip operated for average current with time, and the electromagnet worked for peak current for short circuit.
Residual current device (RCD)
- This breaker senses the difference between live and neutral current that shows leakage to earth. They trip when residual current crosses a certain value of about 30 mA, which avoids electric shock and fire hazard.
Arc fault detection device (AFDD)
- This type of breaker detects the existence of a race fault, which is a high-intensity discharge of current for two conductors. They trip if an arc fault crosses a value that is 75 amperes to avoid a fire hazard and affect insulation.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Working
- The main types of MCB breakers are thermal magnetic and thermal magnetic release. Thermal magnetic breakers use a bimetallic strip that is heated if current flows.
- The heating resulted in the strip expanding and resultingping, trip in the circuit opening.
- • The TMR mini breaker operated the same but uses an electromagnetic coil in place of bimetal strips for tripping purposes.
- It is used for tripping at high current as compared to what thermal breakers can handle.
- It also used air for a heat source, so they are called air-cooled circuit protectors.
- If an ACb trips, it is due to high current flow or temperature increase over the accepted value. So these breakers are used for high-voltage systems with high chances of fire.
Installation of a Miniature Circuit Breaker
for installing a miniature circuit breaker Create space for the panel to install in the new breaker. Make about 6 inches of space between the connected breakers, and no breakers should be connected adjacent to each other. Follow these steps for installation of a miniature circuit breaker.
- First of all, turn off all devices connected with the power system. that the lights, appliances, and other devices are working at your place.
- Now open the electrical panel box and check the empty area for the connection of the new breaker. If not, space exists, use an extra panel for handling more breakers or replace older breakers with new ones that are effective and use low energy.
- Disconnect large screw Hold down the connected breaker and disconnect from the slot. Get out the older breaker wire at the time of pulling it out through small holes in the side of the panel box. Note down wire locations on each terminal before removing their socket, so connect new wires on new miniature breakers and wire connected with each terminal.
- Remove 3/8 inches of insulation from each end of the wire before connecting to the new point. Try to avoid high removal of insulation since you need proper wire for connection.
- Connect each wire with the selected point by pushing the wire strongly into position until it is in position. After that, strongly tighten the screw with a screwdriver so there is no movement under normal conditions or at electrical surges.
Advantages of Miniature Circuit Breakers
- MCB breakers provide many benefits that make these components in power systems
- It is compact in size, so it can connect in limited space, and it also provides accurate protection from overload and short circuit.
- It gets tripped automatically if it faces high current flow. So it used to save devices and wiring, minimize the chance of fire, and enhance the safety of components.
- Their installation process is easy, and they use easy wiring and need low maintenance. It has a long working life and has a low cost, so it is used for commercial and residential applications.
- The main features of MCB are space efficiency, protection, easy connection, and simple maintenance.
MCBs vs. Other Circuit Protection Devices
- MCB provides a resettable protection system as compared to fuses that need to be replaced after tripping. MCB resets with flipping the switch to the on state after tripping due to overload or any other faults. So mCB makes it a low-cost and easy-to-use option that does not need component replacement.
- There is more accurate protection for overcurrent than fuses; MCBs come in adjustable trip current and time delay settings, providing customization based on circuit demands.
- Fuses provide a fixed current rating and have a slow response time.
- MCBs provide good selectivity as compared to fuses. Selectivity defines features to separate faults in certain parts of the electrical system and remain unaffected for other parts of circuits.
- RCCB provides protection from earth faults and residual current and complements the protection features of MCB.
- RCCB senses leakage current resulting from ground faults, tripping the circuit to avoid shock and fire.
- If we use them collectively, they provide strong protection from different faults.
Fuse vs. MCB
The basic difference between a fuse and an MCB is based on their design and ratings, which are explained here.
- MCB automatically turns off the circuit at the time of any fault conditions. The MCB is reliable for the detection of faults, and it is more sensitive to current changes.
- When the switch operating knob is at its off state at the time of tripping, the faulty zone of the circuit is easy to find. For use conditions, the fuse wire is checked with the opening fuse grip at the fuse base; that makes sure that the fuse wire blows.
- If a fuse operates due to a fault, the fast restoration of the fuse is not possible, since fuses need to be rewired or replaced with new ones. but the MCB did not need replacement; it restored the power supply after the fault was removed.
- We can handle MCBs safely as compared to fuses, and MCBs can be controlled at a distance, but fuses cannot.
How to Select a Proper MCB?
- The selection of MCB is based on certain applications for providing proper protection from overload and short circuit. If we do not use a proper rated MCB for the circuit, it can badly affect the circuit and connected appliances.
- If we use an MCB rated for less than the normal load current, it can cause frequent tripping. interrupt current with connected load since MCB normal current is less than load current demand
- If the MCB rating is larger than the nominal load current, the connected load is not protected in an effective way. In these conditions, the MCB does not trip, and also the current flowing is larger.
Applications of an MCB
The main uses of MCB breakers are as
Overload and Overcurrent
- MCB is used for protection of circuits and connected loads from overload and overcurrent conditions. If the current crosses the rated MCB capacity, it gets tripped and breaks the current flow, avoiding damage to the circuit and devices.
Short Circuit Protection:
- MCB also used protection from short circuits that result when there is a higher current flow than circuit resistance/MCB senses abrupt changes in current and gets tripped to control damage from overheating.
Ground Fault:
- MCBs also provide protection from ground faults that sense leakage current moving to ground. It is good for safety purposes since it avoids electric shocks and protects insulation.
Coordination selection
- MCB works in collaboration with other protective devices like fuses and larger-sized breakers that help the device close to the fault operate first and reduce damage.
read more; Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCCB
FAQs
What is an definition of MCB?
- Mini circuit breaker is a protection device that protects electrical faults from overloading, short circuits and ground faults
What is working principle of MCB?
- The MCB operated with the detection of current flowing in the circuit. if the current crosses the rated capacity of breaker, it stop the current flow in circuit.
What are tripping mechanisms in MCBs?
- MCB comes with thermal, magnetic or mix combination of tripping processes. thermal tripping work for overloading conditons and magnetic tripping work for short circuits
What are the different types of MCBs for tripping characteristics?
Type B:
- it is a general module that is used for inductive loads
Type C:
- it used for resistive loads having a moderate value of inrush current
Type D:
- It is used for motor cirucit where a high inrush current is required
What is the difference between an MCB and a fuse?
- MCB reset its operation after tripping, and the fuse needed a new model
- MCBs provide accurate and fast protection from overloads and short cirucit than fuses
How to choose the right MCB for a circuit?
- Find the maximum current for nominal conditons and choose a breaker according to those requirements. Load types also define the selection of breakers. Like resistive, inductive, or capacitive loads use (B, C, or D).
Can MCBs be used for DC circuits?
- MCB breaker is made for DC circuits and comes with different ratings modules for the breaker