 Hello, reader welcomes to onboard. In this post, we will discuss magnetism. Electromagnetism is the force which creat when current passes through any conductor like a wire. When current passes through the conductor magnetic field is produced around the conductor and the direction of north and south poles can be calculated by the direction of moving current in a conductor.
Hello, reader welcomes to onboard. In this post, we will discuss magnetism. Electromagnetism is the force which creat when current passes through any conductor like a wire. When current passes through the conductor magnetic field is produced around the conductor and the direction of north and south poles can be calculated by the direction of moving current in a conductor.
Magnetism is amain part of electronic and electrical engineering as components which are used in these engineering like electrical relays, inductors, capacitors, chock coil, motor, transformer, etc, all use phenomena of magnetism in their working. So let’s get started with What Is Magnetism?
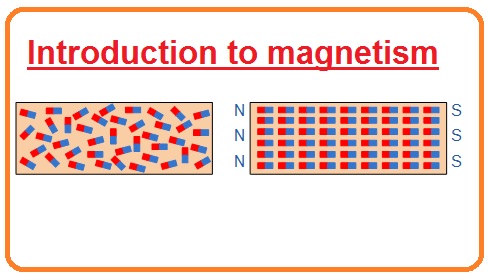
Introduction to magnetism
- Electromagnetism is the force which creat when current passes through any conductors like a wire.
- Magnets are found in a normal condition in the shape of mineral-like iron oxide and leading stone.
- If we tied these two natural magnets with a rope and suspend them in the air they will take such a position according to the earth magnetic field.
- A decent illustration of this consequence is the pointer of a compass. For applied submissions, these natural existing magnets can be omitted as their magnetism is very little and currently, non-natural magnets can be formed in numerous diverse forms, dimensions, and magnetic fortes.
- T here are two main kinds of magnetism permanent magnet and temporary magnets, at which form we have to work depends on their applications.
- There are numerous diverse kinds of ingredients accessible to creat magnets like iron, nickel, nickel alloys,.
- ·In natural form all these materials show power magnetic properties but when they mixed with each other they create very strong magnet like alcomax, hycomax.
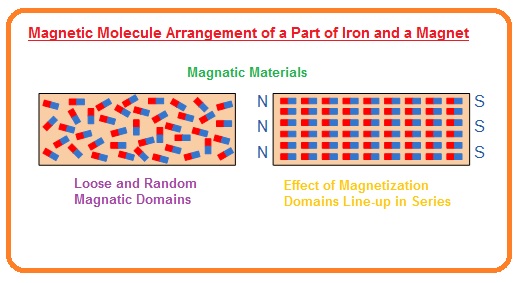
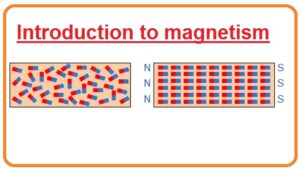
Magnetic Molecule Configuration of a Part of Iron and a Magnet
- When any conductor material is magnetic it molecules which has a random motion before magnetism will change their motion and become aligned. This phenomena of aligned molecules happen by a Weber’s theory.
- This theory works on the action that each atom has magnetic properties due to the spinning motion of electrons of atom.
- Collections of atoms link with each other so their rotating magnetic field are moving in same direction.
- Magnetic ingredients are self-possessed of clusters of minute magnets at a molecular level around the atoms, and a magnetized substantial will have a maximum of its minute magnets wrinkled up in one way only to yield a north pole in one way and a south pole in the other.
- Similarly, a substance which has its minute molecular magnets directing in all guidelines will have its molecular magnets neutralized by its neighboring magnet, thus counteracting any magnetic consequence. These parts of molecular magnets are named domains.
- Any magnetic component will yield a magnetic field himself which be contingent on the grade of the arrangement of domains in the substance established up by orbital and rotating electrons.
- This grade of arrangement can be stated by an amount recognized as magnetization, M.
- In an unmagnetized substance, the value of M is xwero nonetheless some of the domains endure allied in trivial areas in the substantial once the magnetic field is uninvolved.
- The result of smearing a magnetizing power to the substance is to bring into line some of the domains to yield a non-zero magnetization value.
- when the magnetizing energy has been detached, the magnetism within the substantial will either continue or decline rapidly contingent on the magnetic substance used. This aptitude of a substantial to hold its magnetism is named Retentivity.
- a substance that are essential to hold their magnetism will have an equitably higher retentivity.
- those substances essential to drop their magnetism rapidly like soft iron.
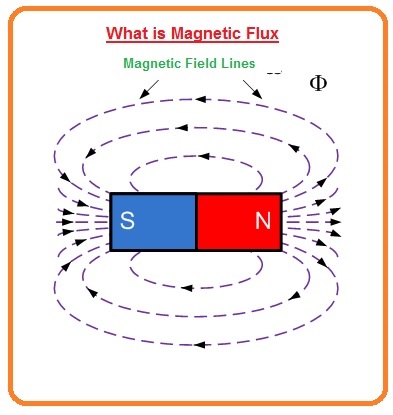
What is Magnetic Flux
- All types of magnets it doesn’t matter it has which type of dimension have two parts which named as poles.
- These magnets have its inside and outside pattern of invisible lone of flux.
- All these flux lines are jointly denoted to as the “magnetic field” of the magnet.
- The quantity of these fields are more at poles and these are weak in strength away from poles.
- The fields line cant is seen by a normal human eye but these lines can be seen by iron fillings spread onto a sheet of paper.
- Magnetic fields are permanently revealed visually as lines of force that spring a certain pole at the piece end of the substantial where the flux lines are more thick and concerted.
- The lines that go to create a magnetic field viewing the way and strength are named usually “Magnetic Flux” and denoted by the Greek symbol ( Φ).
Lines of Force due to a Bar Magnets Magnetic Field
- As we discussed earlier the magnetic field has larger strength near to pole where flux lines are compacted.
- The direction of movement of flux is from the north to south pole.
- Some significant rules we should follow during drawing lines of force.
- Fields lines NEVER cross each other.
- Filed lines are continuous.
- Fields lines permanently procedure separate FASTENED RINGSaround the magnet.
- These lines have a certain direction from north to south.
- Those Lines which are adjacent to each other designate a ROBUSTmagnetic field.
- If lines are away from each other designate a FEEBLEmagnetic field.
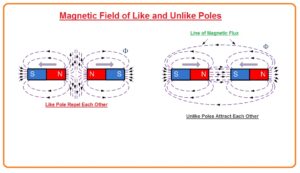
- Magnetic forces entice and resist similar to electric forces and when two fields lines are took nearby to each other the interface amid the two magnetic fields sources one of two things to happen,
- First line is that When head-to-head poles are similar they will repel each other.
- When head-to-head poles are not the similar they ENTICE one another.
Magnetic Field of Like and Unlike Poles
- When we draw lines of force by compass it can be observed that the flux lines are creat in such a way that they show specific north and south pole and it can be easily observed that lines are coming out from the north and entering in the south pole.
- Magnetism can be demolished by heating or beating the magnetic material with a hammer, but cannot be isolated by only flouting the magnet into two fragments.
- Consequently, if you break a magnet into two pieces now you do not have two parts of a magnet but you have a separate magnet having a north and south pole.
What is Magnitude of Magnetism
- As we have discussed that the lines of force around a magnetic substance is denoted by ( Φ ) and having unit Weber, ( Wb ).
- the quantity of lines within a certain unit area is named the “Flux Density”and denoted by .
- Flux density is proportionate to the lines of field and inverse proportionate to the area, so we can describe Flux Density
Flux Density =We can denote flux density by a B symbol and its unit is Tesla.
- It is significant to recollect that all intentions for flux density are ended in similar units like flux in Weber’s, area in m2, and flux density in Tesla.
Main Cause of Magnetism
- The source of magnetism is electromagnetic force which is one of four forces of the universe.
- Any movable charge produces a magnetic field at 90 degrees to its motion.
- In the case of current-carrying wire magnetism is produced by the spin motion of electrons.
- So we can say every substance has magnetic properties because electrons around its nucleus is in a motion state and create a magnetic field.
- If there is a magnetic field atom and molecules of different material make dipoles by positive nucleus moving in the direction of filed and electrons move away from the field.
Properties of Magnets
- Magnets form when ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic materials are exposed to an electromagnetic field. Magnets display certain characteristics:
- There is a magnetic field surrounding a magnet.
- Magnets attract ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials and can turn them into magnets.
- A magnet has two poles that repel like poles and attract opposite poles. The north pole is repelled by the north poles of other magnets and attracted to the south poles. The south pole is repelled by the south pole of another magnet but is attracted to its north pole.
- They always exist as dipoles. In other words, you can’t cut a magnet in half to separate north and south. Cutting a magnet makes two smaller magnets, which each have north and south poles.
Main Types of magnetism
Magnetism can be classified as rendering to its source and comportment. The main types of magnetism are discussed below. Let’s discuss them in detail.
Diamagnetism:
- Diamagnetism is a property bu which material shows repulsion to the magnetic field.
- Such type of materials shows this effect which has no un pair electrons.
- Once electrons couples are existing, their spin motion cancels each other.
- In a presence of a magnetic field, diamagnetic ingredients are feebly magnetized in the different route of the pragmatic field.
- Samples of such substance are gold, quartz, water, etc.
Paramagnetism:
- This type of material has unpair electrons. These electrons can easily move to make their alignments.
- In filed these electrons along in direction of field easily and magnetized easily. The example of such a substance is molybdenum, lithium, and tantalum.
Ferromagnetism:
- These type of materials make permanent magnet when field is no present they also shows magntic properties so that these called permanent magnet.
- These materials has iron. Cobalt, Nickle,etc.
Antiferromagnetism:
- Indifference to ferromagnets, the inherent magnetic instants of valence shell electrons in an antiferromagnet are lies opposite to each other.
- This causes no magnetic field.
- This phenomenon is happening in transition metallic mixes, like hematite, iron manganese, and nickel oxide.
Ferrimagnetism:
- Similar to ferromagnets, ferrimagnets show magnetism properties where they are out og foiled, but their adjacent pairs of electron starts moving in the opposite direction.
- This makes the magnetic moment in one direction strong and in the other direction weak.
- This phenomenon is happening in magnetite and supplementary ferrites. Such as ferromagnets, ferrimagnets are fascinated to magnets.
Magnetism Conclusion
- Magnetism arises from the electromagnetic strength of a stirring or moving charge.
- Every magnet has an imperceptible magnetic field adjacent it and two ends named poles.
- The north pole of magnet has direction in alignment with the earth noth pole and the south pole of magnet has a direction towards the earth south pole.
- The north pole of one magnet is attracted by south pole if other and rep by the north pole of the other magnet.
- If we cut a magnet in two pieces each part is separate with having separate north and south pole.
So that is all about Magnetism if you want to get some more information please mention in the comment