Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of LED its working, applications, and uses. The full form of LED is a light-emitting diode, it is a semiconductor diode with 2 leads first one is anode and the second one is a cathode. Nowadays almost every electronic device either computer, mobile, calculators, etc are used led for an indication of different signals. Due to different features and properties, these diodes are preferred to use than older technologies.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of LED its working, applications, and uses. The full form of LED is a light-emitting diode, it is a semiconductor diode with 2 leads first one is anode and the second one is a cathode. Nowadays almost every electronic device either computer, mobile, calculators, etc are used led for an indication of different signals. Due to different features and properties, these diodes are preferred to use than older technologies.
Due to its smaller dimensions and less power consumption it is preferred. Its structure and assembly almost similar to the normal PN junction but the difference is led emits light. When its positive terminal anode attached with the positive terminal of battery and negative terminal negative point of the battery it starts to emit light. There are different colors of LED are available according to design and structure. In today’s we will have a look at its full form, working, types, and applications. So let’s get started with the Full Form of LED.
Full Form of LED
- The LED stands for light-emitting diode generate radiation of light when a current pass through it.
- As we know any semiconductor material is a combination of electron and hole, also LED is a semiconductor.
- So when current provided at the terminal of led then electrons get energy and combine with the hole and emit energy in the shape of light photons.
- The color of the emitted light depends on the energy needed for the electron move from the ‘N’ side to the ‘P’ side of the material after crossing the band gap.
- To emit white light from the LED cover the semiconductor material with the sheet of light-emitting phosphor.
- In 1962 led was uses as the most common element in different electronic devices and emit infrared light of less intensity.
- LEDs emit infrared light cues in remote control of TVs, led televisions, and to control different electronic devices at some distance.
- When the first white light-emitting diode was manufactured it produces red light of less intensity.
- Currently, different LEDs are available having different wavelengths UV, infrared and light providing output of high-intensity light.
- Older light-emitting diodes were used only for the lamps, indicators, replacement of less intense incandescent bulbs and in 7 segment displays.
- But nowadays LEDs are coming with high intensity and used to illuminate a room and your houses.
- LEDs are now used in different sensing devices and due to their high switching speed used in different communications techniques.
- If we compare LED with the older incandescent light when will come to know that led is less expensive, smaller size, operating life longer, less use of power and high-speed switching.
- There are numerous applications of LEDs such as headlights of vehicles, signals light, cameras, mobiles, laptops, medical instruments, illuminating light.
- As we know that light emitted from the laser is monochromatic and coherent but the light of led is nonchromatic and non-coherent.
Difference Between LED and LCD
- Now we compare the LED and LCD and find their differences.
| LED | LCD |
| This is a semiconductor device that releases light when current passes through it. | It is an optical instrument used to show any info in the shape of photos and text. |
| Its full form is Light-emitting diode. | Its full form is a liquid crystal display. |
| There is no need for light on the background of led. | But in this device cathode fluorescent lamp is used to deliver background light. |
| Its resolution is high. | Its resolution is less. |
| It uses high power. | It consumes less power |
| Its display area is less. | Its display area is high. |
| Its price is high | Its price is less |
| The material used for its construction is gallium arsenide phosphide. | It constructed with the liquid crystal and glass electrodes. |
| Its switching is fast. | Its switching is a slow speed |
| If it connects with the source of direct current there will be no effect of dc on it. | While dc will decrease the operating life. |
| It does not use mercury | It uses mercury. |
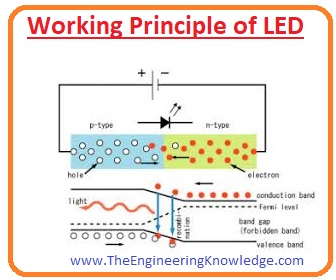
Working of LED
- The operation of LED follows that quantum theory of an atom. According to the quantum theory when an electron moves from upper orbit to lower orbit it releases energy.
- The amount of energy released is equal to the energy gap between 2 orbits around the atom.
- As we know when the positive terminal of the battery is linked with the anode and negative terminals of the battery with the cathode then-current passes through the diode.
- The movement of current is caused by the combination of holes and electrons in the semiconductor material.
- The insertion of electrons in the holes tells about the movement of electrons from the conduction band to the valence band by releasing energy.
- Due to the movent of electrons, energy releases in the shape of photons of light and this energy is equal to the forbidden energy gap.
- For further understanding let’s discuss the quantum theory.
Quantum Theory
- According to quantum theory, the energy released by the photon os light is equal to the multiple of a frequency of waves and Plank constant ‘h’.
E=hf—-(a)
- In this equation, ‘h’ is plank constant and ‘f’ frequency of lightwave emitted.
- As we know that v= fλ or c=fλ
- If we put the value of f in the equation a then we have.
E=hc/λ
- This equation explains that the wavelength of an emitted wave is in inverse relation with the energy among 2 bandgaps.
- In simple word led consists of 4 different layers, the first one die, the second one is a substrate, third one is phosphor and the fourth one is a lens.
- The first die is material of semiconductor comprises with the gallium nitride (GaN) which releases the radiation of blue color light when the input supply is connected with the led.
- Color other than the blue can also get using different materials of phosphor.
Types of LED
- There are numerous types of LEDs that are mentioned here with the detailed.
Miniature LED
- This Catagory of LED consists of the single die and function as indicators, the physical dimensions of these led are two millimeters to eight millimeters.
- The packages of these LEDs are through-hole and surface mounted.
- The operating current values for these LEDs are one milliampere to twenty milliamperes.
- The physical shape of these LEDs are circular, diamond, flat, rectangle shape with the upper part flat.
- The miniature LEDs that emit infrared comprises of black tint to stop visible light and allow infrared radiation to pass.
- The light-emitting diodes that operate at five volts and twelve volts are miniature light-emitting diodes and have resistance in series when linked with the five or twelve volts power supply.
High-Power LEDs
- These light-emitting diodes are also known as high output light-emitting diodes that use the current hundred milliamperes to large than one amper.
- The light emitted by these LEDs is greater than one thousand lumens.
- To avoid damage from the overheating these LEDs are surfaced on the heat sink.
- If high power LEDs get overheated then it can damage within less time.
- The brightness provides by the one high power LED is equal to one incandescent bulb.
AC-Driven LED
- Almost all LEDs operate at the dc current but the LEDs constructed with the Seoul semiconductor material can operate on alternating current without any dc converter.
- For the first half of ac, cycle led releases light and second half remain dark and this polarity reverses in the second half. The efficiency provided by the high power light-emitting diode is almost the fourth lumen per watts.
- If you want to operate on 220 or 230 volts high power LEDs it very easily connects a large number of LEDs in a series and provides line voltage directly.
Features & Specifications of LED
- Now we discuss the features of the LED with the detail.
Flashing LED
- The flashing light-emitting diodes are used as indicators to get attention. These LEDs are similar to normal LEDs but they have additional multivibrator circuitry to blink after specific time intervals.
- The circuitry of multivibrator in diffused lens light-emitting diodes can be seen easily as a black color spot.
- Mostly flashing light-emitting diodes release the light of a single color but some release lights of more than one color.
Bi-Color LED
- The casing of these light-emitting diodes comprises of 2 different color light emitters.
- There are 2 types of Bi-color LEDs, the first category comprises of 2 dies attached with the 2 similar leads non-parallel to one another.
- When current passes in one direction release light of one color and when current flows opposite direction releases light of the second color.
- The second category of Bi-color comprises 2 dies each has separate LEDs and third sperate lead to connect with the common anode or cathode this way both dies can be regulated separately.
- Mostly used bi-color LEDs are red and green, other combinations of color are also available.
RGB Tri-color
- The casing of this LED comprises the 3 different LED emitters. Every emitter has its own separate control wire.
- There are four-wire or leads that are in this led one for common connection of anode or cathode and three for every color.
- RGB light-emitting diode comprises the three LEDs on green, blue and red color.
- Every LED is controlled with a separate lead.
Decorative-Multicolor
- This type of led provides numerous colors through the only 2 wires. Color varied internally by changing the input voltage.
Advantages of LED
- Now we discuss the advantages of led with the detailed.
Efficiency:
- The intensity of light emitted by the led is larger than the normal incandescent bulb. The emitted lumens per watts do not depend on the physical dimension of led like area size, as effected in a fluorescent light bulb.
Color:
- LED can produce light of various colors without any special color filter used as used for other lighting devices.
- So led produce many colors without any extra price.
Size:
- The size light-emitting diode is very less almost two millimeters and can be attached to the PCB board.
Warmup time:
- When connect with the input supply led start illuminating very fastly. Especially red color LED show complete brightness within some ms.
Lifetime:
- The operating life of a light-emitting diode is longer. Almost 35000 to 50000 Hrs it operates.
- While the operating time of the fluorescent bulb is 10,000 to 25,000 Hrs.
Disadvantages of LED
- These are some disadvantages of LED that is described here.
Temperature dependence:
- The continuous operation and performance of LEDs rely on environmental temperature.
- If it operates at a high temperature it longer time will damage.
- To increases, its operating time heat absorber is needed. It requires especially in such instruments that used in medical, vehicles, military.
Voltage sensitivity:
- The voltage provided to the led should be over their threshold voltage and current should be less their rated current value.
- Minor variation in the value of voltage will highly affect the current and operating life of the led.
- So current limiting resistance is used in the series of led to connected supply.
Efficiency Decreases:
- With the increment in the current provided the efficiency of the light-emitting diode decreases.
- The increase in the current also increases the heating that reduces the life of led.
- These factors decrease the use of led for such applications where high current required.
Use in winter:
- As the heat produced the LEDs are less as compared to the incandescent bulbs, so used in traffic lights can have snow obscuring that causes the accidents.
So, friends that is the detailed tutorial on the full form of LED, I tried my level best to make simpler and comprehensive for you. If you have any queries and questions about this post ask in comments. I will resolve your queries. See you in the next interesting tutorial. Have a good day.