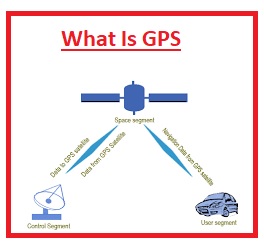
 Hello readers welcome to new post. In this post we will learn What Is GPS, Features, and Working & Applications. The full form of GPS is a Global positioning system that i is based n a satellite navigation system and have twenty-four satellite that locates and finds the accurate position of a person or any object on earth
Hello readers welcome to new post. In this post we will learn What Is GPS, Features, and Working & Applications. The full form of GPS is a Global positioning system that i is based n a satellite navigation system and have twenty-four satellite that locates and finds the accurate position of a person or any object on earth
GPS-enabled satellites are available in all weather conditions anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day, with no registration fee or setup costs. The U.S. Department of Defense (USDOD) had originally developed a few satellites in orbit around the Earth primarily for military use; were made available for public use in the late 1980s. There are currently 31 GPS satellites orbiting the earth with 3 satellites ready to be launched when needed. So let get started What Is GPS
How GPS Created
In 1973, the first time concept of GPS called NAVSTAR was introduced by USDOD or the united states department of Defense. It was first used in the military and then in the 1980s publically used.
GPS technology pays homage to its advances and advances in three people known to the scientific community that was clearly associated with the invention of this revolutionary technology.
Roger L. Easton, former head of the Naval Research Laboratory’s Space Application Branch, was the brainchild of a wide range of engineering and technological systems that led to the development of GPS. Another luminous in the construction of GPS was Ivan Get, former president of the founding of Aerospace Corporation in the USA. The discovery was honored by enhancing the satellite system to make data accurate in tracking and monitoring global traffic from vehicles to missiles. Another highlight in the GPS field is Bradford Parkinson, popularly known as the ‘Father of GPS’; Bradford was a great designer and used GPS in relation to evolution and its engineering.
GPS features
- The GPS has parts first one is satellite that is operating bout the earth, 2nd one is control and monitoring centers that manage GPS technology and rotation system of GPS and the third is GPS and humanly operated GPS
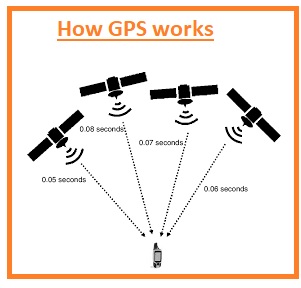
How GPS works
There are a total of 31 satellites orbiting the Earth in their predetermined routes. At any instant on earth, there are four satellites operating. Each GPS enables satellite imagery and recording of objects and moving objects and transmits information about the current position, speed, and video-graph time at regular intervals.
These GPS-enabled satellites transmit data signals to GPS receptors at various handsets at light speed: computer-generated data is received by a GPS-set receiver and translated into visual images; handset receptors calculate the rotating satellite range placed in the space of the received data period, that is between data transfer and data reception. Once the handset receptors have received all the information on orbiting satellites that focus on that particular location, the GPS receiver can pinpoint the exact location of the object or objects on the ground that may stop or use mobile through a process called Trilateration. When satellites are more focused on a given area, locations, images and speeds can be more accurate.
What is GPS tracking
GPS tracking enabled remote monitoring or monitoring of specific locations using GPS technology to track and monitor the location and route of one or more objects. GPS tracking is very important for police, firefighters, military and businesses that require constant monitoring of moving objects such as cars, arrows, and individuals. GPS tracking systems typically use Automatic Vehicle Locator (AVL) systems that use a car network, each equipped with a portable radio receiver, GPS receiver, and GPS antenna. In addition, GPS technology uses interactive maps instead of static maps to determine current traffic and highway conditions. GPS-enabled smartphones and other portable devices are often used to track and monitor targeted objects.
![]()
GPS trading
On May 25, 1989, the first GPS trackers in the consumer market by name and model were introduced with: Magellan GPS NAV 1000s. The hand-held measuring device measured 8.75 x 3.5 x 2.25 inches in size, weighed six eighty grams and sees like a large calculator with a rotating antenna arm.
The device had an LCD display of many types but had a relatively low operating time of just a few hours. Just as a simple hand-held calculator came with a high price at the time of their launch, the GPS handset was resold for USD $ 3,000 (approximately Rupees 54,000 at the time). In 1990, the famous car maker, Mazda, introduced its Eunos Cosmo model with a built-in GPS system, the first car to come with GPS tracking. Later in 1999, Benjonon, a mobile phone maker, introduced the first commercially available phone with GPS technology. That same year, Casio introduced the first GPS wristwatch called Casio GPS. From there, GPS technology quickly became the voice of every smartphone and the proud clock of GPS-enabled technology.