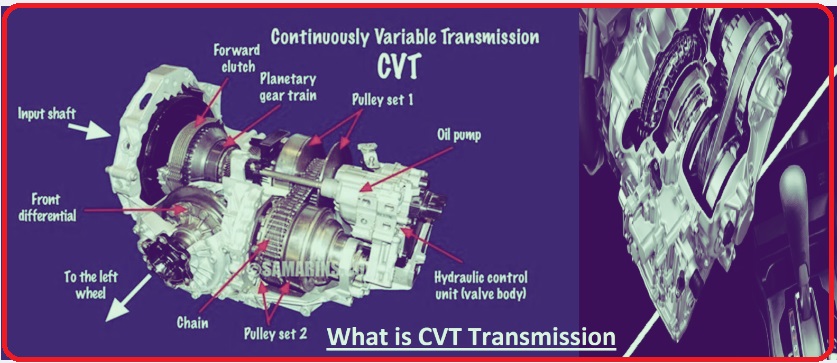
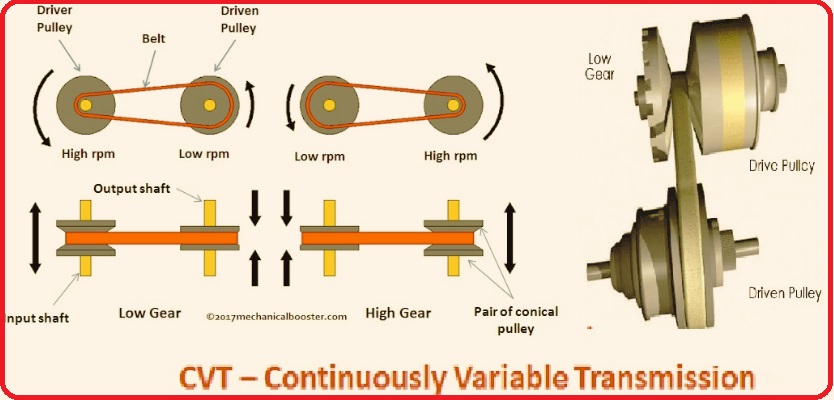
CVT, or continuously variable automatic transmission, is an automatic transmission system that transfers power to the drive wheels via a belt or chain. cvt provides flexible powertrain features by controlling engine speed in response to wheel speed. cvt basically changes engine speed, avoiding shifts and jolts as in a conventional automatic transmission.
In this tutorial, we will get details of CVT transmission and its importance for vehicle drive. Let’s get started
What is a CVT
- Continuously variable transmission is basically an automated transmission process that is controlled with the help of a gear ratio, causing superior fuel efficiency in gasoline.
- It has a high gear ratio compared to other transmission systems that have low gear ratios. CVT’s flexible nature helps good control for the engine to work at a constant angular velocity, and the vehicle moves with variable speed.
- CVT comes with a simple design, longer working life, and a durable nature. It also uses low fuel and releases less hazardous material than a conventional automatic transmission.
- It is commonly seen in tractors, motor scooters, bicycles, etc. The commonly used CVT type employs 2 pulleys configured with a belt, with some other design assembly existing.
- CVT provides easy changes from a larger gear ratio to a low gear range. In this way, the engine works at an effective rpm and also increases fuel efficiency and provides high power.
- CVT structure is such that it provides easy gear shifting.
- A car transmission based on smooth gear changes provides good speed, which helps easily find transmission faults to avoid costly repairs.
CVT Working
- CVT automatic transmission system since it performs shifting gears automatically without shifting forward gears.
- As compared to a conventional automatic CVT, it does not have a fixed preset gear number, but it operates with an infinite gear ratio for controlling speed according to driving conditions.
- Since it causes smooth changes without difficult shift points, CVT transmission is called “single-speed” or shiftless.
- CVT provides an infinite gear ratio through a chain-driven two-pulley system. This structure is like a chain working over bicycle gears.
- One cone exists on the engine output shaft, and another delivers power towards the driveshaft and drive wheels.
- The gear ratio varies through pulley movement; in a result chain or belt moves up and down the cone sides.
- Through this movement, the diameter movement increases or decreases the chain, which changes the gear ratio according to the power used. All these variations occur when the vehicle moves.
CVT Types
Pulley-based cvt
- It commonly uses CVT types that employ V-belts that operate between two variable-diameter pulleys. Pulleys have two cone-like halves that move at the same time. A V-belt operates between these two halves; as a result, the diameter of the pulley is based on the distance between the two pulley halves.
- The V-shaped design of the belt helps move it on one pulley and lower it to the other, so the gear ratio set is configured through moving two sheaves of the pulley closer and the other pulley sheaves farther apart.
- • The distance between the pulley and the belt length does not vary, but the pulley is adjusted for accurate tension on the belt.
- CVT with a combination of centrifugal drive pulleys having a spring-loaded driven pulley employs belt tension for effecting a conforming setting of the driven pulley.
Toroidal cvt
- This CVT comes with discs and rollers. The discs are like two conical parts configured point-to-point and have sides dished like two parts configured into a torus with a central hole.
- One disc is used as input and the other as output. Rollers exist between rollers, whose ratio changes and transmits power from one side to the other.
- If rollers are at 90 degrees to the axis of the discs, the diameter is the same for input and output discs and provides a 1:1 drive ratio.
- If other ratios get rollers rotating over the surface of discs, so we make connections with discs at points having different diameters, we get a drive ratio compared to 1:1.
- The main feature of a toroidal CVT is that it has a feature to handle high torque compared to loads than a pulley-based CVT. For some toroidal systems, the force direction reverses in the CVT, and extra components for reverse gear are not used.
Ratcheting
- Ratcheting CVTs come with one-way clutches or ratchets that perform rectification and add forward motion. It comes with on/off features that show some designs do not provide continuous operation, but provide the same features, and ratcheting CVT causes zero output speed according to input speed.
- drive ratio set through varying linkage design in oscillating components that add the highest controlled linkage speed, and also when the linkage speed is constant.
- Ratcheting CVT easily torques since static friction increases according to torque throughput, which makes slippage difficult in an accurate design.
- causes high efficiency since mostly dynamic friction is produced through conventional clutch speed variations.
- Its limitation is that CVT produces vibrations due to variation in speed needed for parts acceleration that supply previous operating and decelerating power-transmitting parts.
Hydrostatic CVT
- This CVT type employs hydraulic fluid for power transmission. It follows a hydraulic pump and motor for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic pressure, and it reverses to provide continuous changes in gear ratio.
- It is used in industrial machines and provides accurate control, and is preferred for tools where reliable power is needed.
Symptoms of Transmission Problems in Vehicles
Delayed Gear Shifts
- Rough shift. Gear shifts mean there is a faulty transmission system. if you feel sudden gear changes or jolts during a shift. a faulty valve body. That means bad fluid transmission, damaged gears, and a valve body not working well.
Noises during Gear Changes
- Normally, gear changes are a silent process, especially when all components are working well in the gearbox. So if you hear any grinding noise, it means improper fluid in the transmission or also faults with the reverse idler, gearset, reverse gear, bearings, or other parts not working well that affect rotational motion.
Fluid Leaks
- Transmission fluid is important for easy gear shifting and transmission cooling, and is normally red in color. if you found burnt, low-aging gearbox fluid that causes faults in the gearbox.
- If you found brown or dark red fluid leaking in the car, that means a transmission error exists. Fluid leaking also causes overheating and transmission effects if not working well.
Slipping Gears
- Vehicle transmission provides easy acceleration when we press the pedal; if overheating occurs in the system, the CVT gearbox does not work well and takes longer than normal.
- If you are facing slipping gears or find power losses during acceleration, it means the transmission is not working well. that faults are due to worn gears, low transmission fluid level, and damaged valve body, also due to low fluid levels
- Hybrid cars have these errors commonly since the transmission is important for delivering power from the electric motor and combustion gears to provide high efficiency.
Overheating
- CVT systems commonly face overheating in the transmission system of the vehicle. If you find some signs like overheating, a burning smell, and a warning light on the dashboard, it means the CVT is overheating. Overheating results from low fluid, a faulty cooling system, and hot weather, which causes heating.
Transmission system noise
- The transmission system also causes noise like whining and rumbling, which means a faulty CVT. These sounds are the result of bearing damage and some other transmission parts.
Transmission Sounds’ Effects on CVT
- CVT causes some sounds that help to detect some faults early and avoid serious damage.
Whining noise
- High intensity: A whining sound produced from the CVT shows faulty fluid in the transmission. This shows low fluid levels, old fluid, and improper fluid addition.
- To solve this error, check the fluid level and its conditions. If the fluid level is low, then refill according to requirements. If the fluid is burnt or dirty, change it. If noises still exist, move to the technicians for inspection.
Clunking sound
- A clunking noise shows damaged internal parts like bearing pulleys and belts. That shows mechanical faults with the transmission.
- This noise needs to be solved as soon as possible, since driving with a clunking transmission causes serious damage and also affects the transmission system badly.
Humming
- •A humming noise means a transmission fluid pump fault. These parts are used for controlling fluid transmission regulation and managing the working of the transmission system. If a humming noise is produced, then check the vehicle for details of the faults of the solenoids and fluid pump. then repair parts or replace
Grinding noise
- Grinding noises show high damage on parts of the transmission system, like the CVT belt bearing and gears. Grinding noises are serious faults. gets help from technicians for finding fault and solving it as much as possible
Rattling noise
- A rattling noise is produced due to damaged components of transmission parts or external connections. It can be loose heat protection. Take these faults seriously and solve them as soon as possible.
Hydrostatic CVT Advantages
scalability.
- hydraulic CVT capacity that can be managed through accurate pump size and configuration of hydraulic motor(s).
Flexible design
- power transformer from engine-operated pump to hydraulic motor with oil flow medium; motor configured in point through applications of hoses to deliver oil from pump towards motor that makes simple design of all-wheel-drive articulated vehicles.
Smooth operations
- It provides an infinite CVT gear ratio without torque variations as seen in conventional, geared transmissions.
easy control
- Working with the complete value of forward and reverse speed can be regulated with a lever and foot pedal for the operation of the diversion valve.
Limitations of a hydrostatic CVT
Low efficiency
- Gears are an effective technique for transmitting mechanical power that has efficinecy about 90 percent. Some hydrostatic transmission system gets more than 65 percent efficiency. that due to inner losses of pumps and motors, and pipe valve losses
High cost
- for getting high power transmission hydrostatic CVT, a higher cost than that generated by geared transmission. For the pump and motor, the hydrostatic system oil reservoir is used.
High weight.
- Due to high oil pressure where the CVT works, the pump motor faces high pressure for high power and loading applications. so it must have a strong structure for managing heavy parts. Some extra weight exists in oil reservoir, and oil also exists in the piping and valve.
CVT Advantages
- Its main feature to operate without a fixed gear ratio helps CVT-based cars to move engine peak power and hold when the driver pins the accelerator pedal.
- CVT-based cars also manage fuel use for power steering low.
- There are no gears for changing, providing smooth acceleration, and the transmission is free from jolts, having multi-geared transmissions.
- CVT also comes with fewer moving components compared to conventional automatic transmissions.