Ceramic tube, cylindrical shape, tube made with non-metals and inorganic materials, and employed for applications where high temperatures are involved. Ceramic tubes come with good insulation and handle high temperature and chemical corrosion. These features make them the best replacement for metals and polymers.

Ceramic tubes are also employed as protective sleeves and insulation barriers and provide structural support. In this article, we will discuss what a ceramic tube is, how it works, its key properties, common types, and major industrial applications.
What Is a Ceramic Tube?
- A ceramic tube tubular design module that is made with the help of ceramic materials has different features, such as a hard structure and thermal resistance, and provides dimensional strength.
- Compared to metallic tubes, ceramic tubes are not affected by high heat and provide structural strength for harsh conditions.
- These tubes are used as part of different industrial machines, as insulators and thermal protection sleeves. Its commonly used type is alumina tube, which provides good mechanical strength, thermal stability, and a thermally stable design.
Ceramic Tube Working
- ceramic tubes used as a barrier for isolating heat, current, and chemical materials to connect with surroundings. It has a rigid layout for structure maintenance and also works easily in high-temperature and harsh conditions.
- These tubes also help to control current leakage and short circuits since they have strong dielectric insulation.
- For thermal applications, it protects internal parts from flame or radiant heat. In applications where fluid is involved, ceramic tubes allow gases or liquids to flow without reaction.
- The nonconductive and inert behavior of the ceramic structure helps ceramic tubes work well in conditions where safety is important.
Ceramic Tubes Electrical Features
Ceramic tubes come with different features that make them different from metallic or polymer-based tubes.
- They provide high temperature resistance and work well at different temperatures.
- It also provides electrical insulation, since it has high dielectric strength and low conductivity.
- They provide oxidation-resistant, stable designs for acids and corrosive gases.
- Their high mechanical hardness provides resistance to compression and wear.
- It provides low thermal expansion and a stable design for thermal cycling.
Types of Ceramic Tubes
Ceramic tubes are made with different ceramic materials according to applications. so it comes with different types
Ceramic tubes are produced using different ceramic materials depending on application requirements.
Alumina Ceramic Tube
- • The alumina ceramic tube structure comes with aluminum oxide and commonly used ceramic tubes for industrial loads. It has good electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and resistance to high temperatures.
- Alumina tubes are part of laboratory tools and furnace devices and provide thermal protection to the system.
- Their reliable design makes them effective for industrial and scientific projects.
Zirconia Ceramic Tube
- Zirconia ceramic tubes have high fracture toughness and better resistance to bearing thermal vibrations than alumina.
- These tubes are part of applications where temperature varies and provide mechanical strength.
- Its main uses are sensors, precision instruments, and advanced thermal systems.
Silicon Carbide Ceramic Tube
- Silicon carbide ceramic tubes work well in harsh conditions. It has good thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength for high temperatures.
- Their main uses are heat exchangers and industrial loads.
Ceramic Tubes Manufacturing Process
different steps involved for making ceramic tubes that explained here
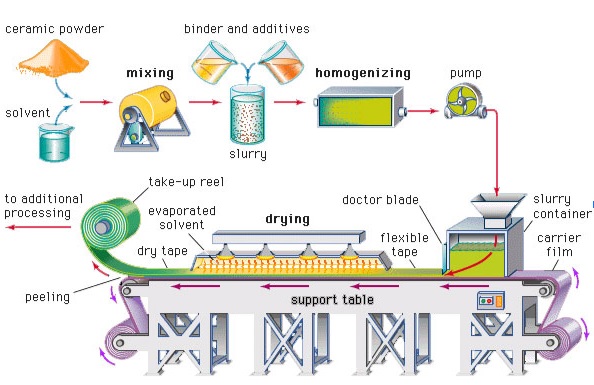
Raw material
- In this step, ceramic powder is refined and mixed with binders.
Forming
- tubular-like structure made with the help of isolating presses.
Drying
- In this step, moisture is removed from the mold design.
Sintering
- Ceramic structure densifies with applications of high temperature
Machining and finishing
- Through application of grinding and polishing, we get accurate dimensions.
Ceramic Tubes Advantages
Ceramic tubes have more features than conventional materials.
- It has a longer working life for harsh temperature conditions.
- It has better insulation than metals.
- It has high corrosion resistance and manages chemicals.
- It manages thermal stress and causes low deformation.
- It uses low-maintenance features.
- Minimal deformation under thermal stress
Dsiadanavtages of Ceramic Tubes
It also causes some limitations.
- It is affected by high pressure and tensile loads.
- Its brittle nature affects tensile strength.
- With that, its manufacturing cost is higher than steel tubes.
- It shows limited flexible design.
Industrial Applications of Ceramic Tubes
There are different applications of ceramic tubes, such as
- It is used for providing insulation and as part of laboratory tools.
- Parts of the kiln and furnace are made with these tubes.
- They provide thermal protection for heating components.
- It’s employed in high-temperature and chemical processing systems.
Conclusion
Industrial ceramic tubes have high-strength materials that are part of different industries since they have good features. Industrial ceramic tubes, compared to conventional ceramic tubes, provide different features like a tough design, high strength, wear resistance, and low surface roughness, which minimizes the friction coefficient, forming quality wire.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the uses of ceramic tubes?
- Ceramic tubes are part of various applications since they have good insulating features, provide structural support, and exhibit chemical handling behavior.
Are ceramic tubes conductive materials?
- Ceramic tubes show low electrical conductivity and are employed as electrical insulators.
Can ceramic tubes handle high temperatures?
- Yes, according to materials, they work at high temperatures compared to metals and polymers.
What is the common ceramic tube material?
- Alumina-made ceramic tubes are common materials since they have good performance and are part of different applications.




