 Hello friends I hope you all are doing great. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to TRIAC. TRIAC are electronic devices that employed in applications where ac power control needed. They use to switch the high value of voltages and larger current during both polarities of AC signal. Lights used in homes comprise of dimers that consist of triac also used in the regulation of motor electronic switches it used.
Hello friends I hope you all are doing great. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to TRIAC. TRIAC are electronic devices that employed in applications where ac power control needed. They use to switch the high value of voltages and larger current during both polarities of AC signal. Lights used in homes comprise of dimers that consist of triac also used in the regulation of motor electronic switches it used.
It also works for the less to intermediate power circuits of switching elements in place of thyristor they are used in some circuits. In this post, we cover details about its working, construction applications, and related parameters. So let’s get started with Introduction to TRIAC.
Introduction to TRIAC
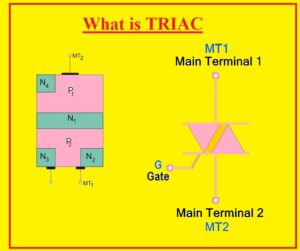
- The TRIAC also called bidirectional triode thyristor, or tridiode for AC consists of 3 terminals through them current can flow any direction gets triggered.
- TRIAC belongs to the thyristor family also has some features of the relay with that also shows specifications related to SCR.
- The main difference between TRIAC and SCR is that current flows in SCR only a single direction and in TRIAC in two directions.
- TRIAC can be operated through the application of both negative and positive polarity voltage but SCR operates from positive polarity.
- After trigger both retain their operation either supply is disconnect from the gate terminals till the point the main current losses to value less than the specific point known as holding current.
- GTO or gate turn off thyristor shows similar features to TRIAC with that offers larger regulation and control through tuning off in case there is a gate that has zero signal.
- Due to two-direction operation, it is used for switching of AC with that used for triggering at a regulated phase angle of ac in the circuitry which permits control of average current passing towards the load.
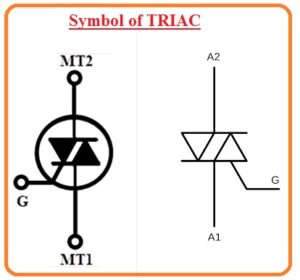

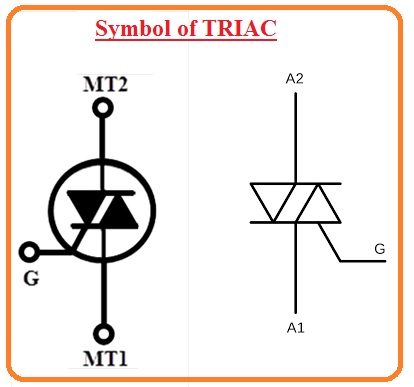
Symbol of TRIAC
- The TRIAC is a combination of 2 equivalent SCR connected in reverse parallel combination their gate terminals are lined to creates one single gate.
- Here you can see the triac symbol that has 3 terminals first one is MT1 second one is MT2 and the third one is Gate.
- MTI called anode and MT2 known as the cathode.
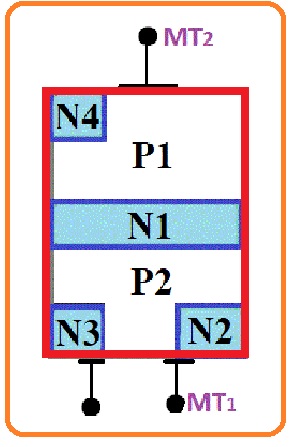
Construction of TRIAC
- In the below figure, we can see the construction of TRIAC. It has 4 layers which comprise of further 6 doping areas. The gates of this device is created in such a technique that has an ohmic connection to the N and P parts due to this assembly TRIAC gets triggered from the negative and positive supply.
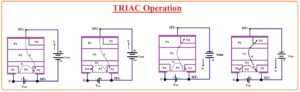
TRIAC Operation
- TRIAC starts conduction if the voltage given lies in the breakdown voltage with that the commonly used technique for TRIAC is offering a gate pulse through positive or negative supply.
- If the value of current is large then a smaller quantity of voltage is good to on TRIAC.
- There is TRIAC is two-directional devices become on with the two polarities given at the gate so it runs in the 4 different operation states or four quadrants.
- These 4 modes of operation are listed here.
- In first mode, the MT2 has a positive state reference to MT1 terminal and the gate is positive according to MT1.
- In 2nd mode MT2 is positive according to MT1 gate polarity is negative according to MT1 terminal
- MT2 terminal in the third mode is negative according to MT1 and gate is negative according to MT1.
- In the fourth mode there is MT2 is negative according to MT1 and gate is positive according to MT1.
In below figure four mode of operation of TRIAC are shown in below figure and the current direction also shown in the figure.
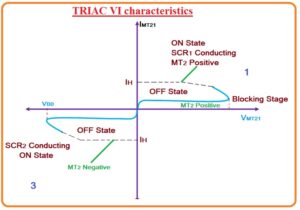
TRIAC VI characteristics
- As this device is two-directional so its VI curve lies in the ist and thrid quadrant which is like to the VI characteristics of thyristor.
- If the voltage level at MT2 is positive according to MT1 terminal then TRIAC is operating in forward mode of operation.
- In the starting phase resistance offered by the TRIAC there will be less leakage current passing from the component as given voltage is less than the breakdown voltage.
- If the voltage rises and it moves to the breakdown voltage the TRIAC is getting on and the large current flowing from the triac.
- With rising the voltage of component, the TRIAC gets on through offering gate signal if the voltage provided has less value than the breakdown voltage.
- A similar work can be done in the negative polarity of the TRIAC that will be an opposite state of the similar curve shown in the negative quadrant.
- The voltage given over the TRIAC conduct will rely at the gate current given to the TRIAC.
- If the gate current is large so voltage needed to run the ON TRIAC will be less.
- The characteristic curvature which can seen working of TRIAC is first and third quadrant.
That is a detailed post about TRIAC if you have any further query ask in comment. If you have any further query ask in comment. Thanks for reading have a nice day.