 Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss The Basics Of Time Domain Reflectometer. Maybe you know about the Time domain reflectometer if you are ever having work of network or cable maintenance or installation. You can use these tools to know the defects of cables like short circuits, breakage, and impedance mismatches.
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss The Basics Of Time Domain Reflectometer. Maybe you know about the Time domain reflectometer if you are ever having work of network or cable maintenance or installation. You can use these tools to know the defects of cables like short circuits, breakage, and impedance mismatches.
In this article, we will explain the different parameters of TDR and its works. So let’s get started with the Time Domain Reflectometer.
Introduction to Time Domain Reflectometer
- A time-domain reflectometer device that sends high-speed signal through cable or wires and measures reflections. These reflections are caused by variations in cable or impedance of wire like the break of short circuits. For finding issues with cable and wire installation TDR used in the telecom field

What does TDR Stand for
It stands for Time-Domain Reflectometry. TDR is a technique used for testing the features of electrical lines by measuring reflected pulses.
How does TDR work?
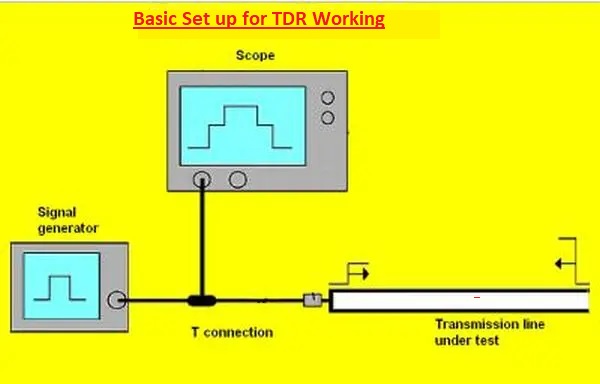
- The high-speed electrical single applied to cable or wire is tested by TDR. Pulse moves in cable or wire at the speed of light it’ll collide with impedance variation-like defects.
- The part of the pulse is partially reflected back to TDR. TDR correctly defines the distance to find fault by measuring the time between staring and reflected pulse. TDR screen displays a signal at the screen
Types of TDR
- TDRs are in analog and digital Types. Digital TDR has a display on the screen LCD and analog TDR shows a signal on a CRT screen. As analog TDRs are used in different applications and digital TDRs have fewer errors and are easy to use.
TDR Measurement
- TDR calculation is a technique used to find cable or wire installation features. It works by passing electrical signals from cable and then noting how many reflections are back.
- The TDR can find the length of the cable or wries also any error with length by measuring the time takes for the reflection to return and the amplitude of the signal
How does TDR measurement work?
- A high-seed electrical pulse is given to cable or wiring during TDR calculation. As the pulse moves on the cable, it moves in variation in impedances, bends breaks, and other errors. Some signals move back towards the source when the pulse moves one of these hinderances. TDR measures the distance to obstruction and the type of fault that exits through the timing amount taken for reflection to move and analyzing the signal’s amplitude.
Time Domain Reflectometry
- For dingi the error in cable or wiring system methods used TDR. It functions by firing fast single to cable, then checking reflections. The TDR can measure the distance to the fault and the type of fault that exists by measuring time taken for reflection and amplitude of the signal
Applications of TDR
- For finding issues with cable and wire connections TDR is mostly used in telecom. They are used for testing and maintaining wires and cable systems in aviation, and the power field
Benefits of using TDR
- it is best to locate errors that help to save time and money. With that, it minimizes downtime and increases network reliability
Preparing to use a TDR
- The cable or wire being tested is ready before using TDR. For the TDR signal to get interfered it is required to unplug the cable or wire from the system, confirm it is accurately connected to the ground, and make sure there is no hurdle or any other cable connected closely
Steps to Using a TDR
- A TDR attached to a cable has to be tested through an accurate connection. Use settings that are correct for cable or wire type and length. It must be operated and the signal looks on the screen
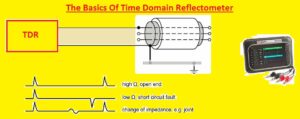
Interpreting the TDR waveform
- The reflected signal in graph form is shown through the TDR waveform. The waveform shows distance with default, size, and shape of the reflection signal and its magnitude. We can find any fault that exists and check its intensity
Troubleshooting using TDR
- it is used to find defects like breakage, open circuits, short circuits, and impedance mismatches, in cable and wire systems. We can find the problem and get the required action with the use of TDR for finding issues.
Limitations of TDR
- To save any damage use cables or wires tha are not energized. the signal can be weak for longer distances TDR is not used to find any fault in longer cable
TDR vs. OTDR
- For finding errors in cable and fiber optics structure, TDR and ORDR are used. but OTDR functions by sending the pulse down to the filter and TDR works by sending the electrical pulse to the cable. TDR is good for small cables and wires while OTDR is used for longer cable and fiber optics.
| TDR (Time Domain Reflectometry) | OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometry) | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | it checks reflection after seeing pulse to detect variation in cable impedance | Find featues of optic fiber to measure light reflected. |
| Cable Types | Used for differnt cables like Ethernet, coaxial, and twisted-pair cables. | used in fiber optic cables |
| Distance Range | can find distances for some meters correctly | measure tens of kilometers in distance |
| Spatial Resolution | it has high spatial resolution and high accuracy in fault-finding | offers less spatial resolution than TDR |
| Cost | high affordable than OTDR | expensive than TDR |
| Applications | Applied to telecommunications, aviation, and the military | used for maintaining and troubleshooting fiber optic networks in the telecoms sector |
.
Conclusion
When installing cables and wires, a Time Domain Reflectometer for finding errors. The TDR quickly and accurately find breakage, short circuits, and defects by sending a high-speed signal in wire and detecting reflection. it is an important tool for network or cable installation and maintenance, despite its limitations.
FAQs
What is a time domain reflectometer TDR used for?
- it produces an energy pulse or step on the cable to find the location and magnitude of cable faults, breake termination, and other faults
What does a time domain reflectometer measure?
- A Time Domain Reflectometer measures signal reflections, impedance mismatches, and faults like open shorts, or cable breaks within a cable or transmission line. It provdies information related to the distance to the fault and the severity of the reflection.
What is a TDR and what is it used for?
- A TDR is a device employed to measure the electrical features of a cable or other transmission line. It is employed for different purposes, like
- Finding breaks or faults in cables
- the impedance of cables
- Measuring the length of cables
- quality of cables
What is an example of a TDR?
- A basic example of a TDR is the Fluke Networks DSX-8800 CableAnalyzer. This type of TDR is used by network engineers to troubleshoot issues with cables and networks.
What is the reason for TDR?
- The reasons for using a TDR are
- To find breaks or faults in cables
- measure the length of the cables
- To test the quality of cables
- the impedance of cables
Is TDR necessary?
Whether or not a TDR is necessary according to the application. Such as a TDR is not used for a home user who is just connecting a computer to the internet. But a TDR is best for network engineers who are finding faults with cables and networks
How accurate is a TDR?
The majority of TDR can measure errors to in some centimeters, making them accurate
Is TDR be used on live cables?
- No electrical signal can be a hazard to cables or wires or cause safety risks, the TDR can used for unenergized cables or wires.
How much time does it take to become proficient with a TDR?
- With the proper instruction, using a TDR is simple and can be learned in a somehours.
Is TDRs expensive?
A TDR ranges in price based on the type and manufacturer, but, some tools are reasonably cost
Is TDR be used to locate faults in fiber optic installations?
A TDR is not good for use with fiber optic systems since it is created to handle metallic cables and wires.