 A Passive Attenuator is a distinct kind of bidirectional electronic circuit that is created by totally resistive components.The attenuator is a two ports resistive system intended to deteriorate the power provided by a supply to a point that is appropriate for the associated load. A passive attenuator lessens the quantity of power supplied to the linked load through a solo permanent quantity, an adjustable quantity, or in a sequence of recognized switching mode phases. Attenuators are usually cast-off in wireless and broadcasting links submissions to deteriorate (weaken) a strength of the stronger signal.
A Passive Attenuator is a distinct kind of bidirectional electronic circuit that is created by totally resistive components.The attenuator is a two ports resistive system intended to deteriorate the power provided by a supply to a point that is appropriate for the associated load. A passive attenuator lessens the quantity of power supplied to the linked load through a solo permanent quantity, an adjustable quantity, or in a sequence of recognized switching mode phases. Attenuators are usually cast-off in wireless and broadcasting links submissions to deteriorate (weaken) a strength of the stronger signal.
The Passive Attenuator is a totally passive-resistive system (henceforth no source) used in a varied range of electronic apparatus for spreading the vigorous assortment of gaging apparatus by regulating signal intensities, to deliver impedance corresponding of amplifiers to decrease the properties of unsuitable input or output ends or to merely deliver separation amid diverse circuit phases dependent on their solicitation.
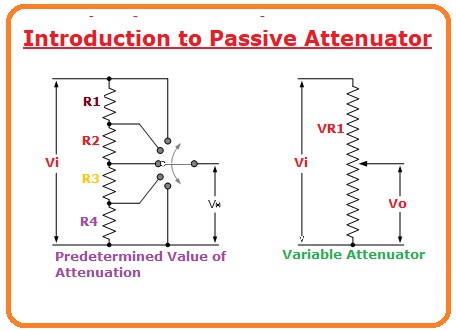
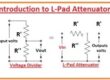
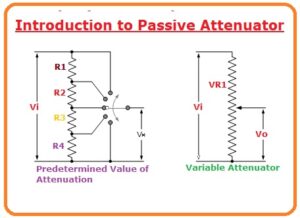
Introduction to Passive Attenuator
- A Passive Attenuatoris a distinct kind of bidirectional electronic circuit that is creat by totally resistive components.
- Attenuators are the opposite of amplifier circuits in which they lessen gain by the resistive voltage separator circuit being a distinctive attenuator.
- The quantity of attenuation in an assumed system is measured by the ratio of Output to Input.
- For instance, if we supply the input voltage one volt (1V) and the output voltage of circuits is one milli-volt (1mV) then the quantity of attenuation is 1mV/1V that is like to 0.001.
- Though, by consuming voltage, current or power proportions to govern the quantity of attenuation which a resistive attenuator system might have, named as the attenuation factor, it may be puzzling, so for the passive attenuator, its amount of attenuation is usually articulated by a logarithmic gage which is assumed in decibels (dB) building it calmer to work with such minor statistics.
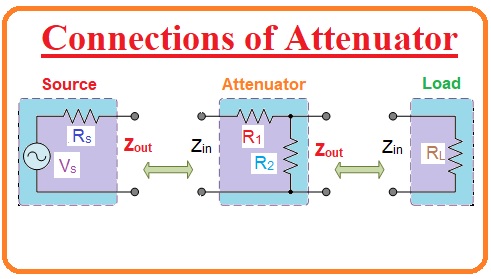
Connections of Attenuator
- Attenuator systems can be intended to make a stable gradation of attenuation or to provide an adjustable quantity of attenuation in pre-measured phases.
- Typical static attenuator systems usually recognized as an “attenuator pad” are accessible in precise standards from zero decibels greater than one hundred dB.
- Adjustable and swapped attenuators are fundamentally changeable resistor systems that show an adjusted upsurge in attenuation for each swapped phase, for instance, stages of -2 dB
- an Attenuator is a two-port which is four-terminal passive-resistive systems (active sorts are also obtainable which uses transistors and combined circuits) intended to yield “alteration less” attenuation of the output electrical indication at all given frequencies by an equivalent quantity with no angle change dissimilar a passive kind RC filter system, and therefore to attain this attenuator must be prepared of pure non-inductor and not cable coiled resistances, meanwhile, reactive rudiments will give frequency discernment.
What is an Attenuation degree?
- An attenuators working is uttered by the numeral of decibels the input signal has reduced per frequency time.
- The decibel, which is the abbreviation of “dB”, is usually described as the logarithm extent of the voltage, current or power proportion and signifies one-tenth of a Bel (B).
- We can also say that it receipts 10 decibels to sort one Bel. Then by description, the ratio amid an input signal (Vin) and an output signal (out) is given in decibels is described below.
dBv = 20log10 (dB)
- We can see in the above-given equation that the decibel (dB) is a logarithmic proportion and so it has no units.
- In passive attenuator circuitries, it is frequently suitable to allocate the input assessment as the 0 dB reference.
- This tells that no matter what is the real assessment of the input signal is cast-off as a reference point with which to equate the output of attenuation and consequently allocated a 0 dB.
- This shows that every quantity of output under this reference will be stated as a negative dB quantity, ( -dB).
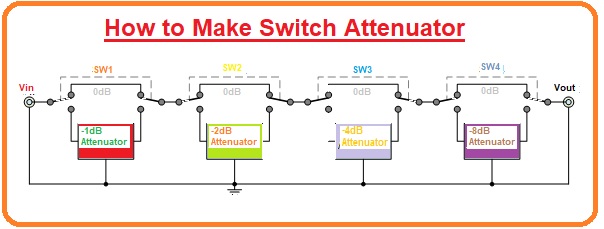
How to make Switch Attenuators
- In its place of taking only one attenuator to attain the requisite grade of attenuation, discrete attenuators can be linked to upsurge the quantity of attenuation in certain stages of attenuation.
- Multiple poles rotating adjustments, rocker switch or ganged button can also be used to attach discrete static attenuator systems in any wanted order from 1dB to 100dB or additional, building it informal to enterprise and make switched attenuator systems, also recognized as a step attenuator.
- By swapping in the suitable attenuators, the attenuation process can be augmented or reduced in static phases as shown in the given diagram.
Switch Attenuator
- In the given diagram there are four liberated resistive attenuator systems poured together in a sequence stepladder system with each attenuator have a rate twice that of its precursor, (1-2-4-8).
- Every attenuator system can be switch “in” or “out” of the signal track as essential by the related switch creating a stage alteration attenuator circuitry which can be swapped from 0dB to -15dB in 1dB phases.
- So, the entire quantity of attenuation providing by the circuitry be the sum of all four attenuators systems switch are switch “IN”.
- So for instance an attenuation of -5dB would need switches SW1 and SW3 to be linked, and attenuation of -12dB would need switches SW3 and SW4 to be coupled, and so on.
Features of Attenuator
- An attenuator has four terminals that decrease the amplitude of a signal without altering the waveform of the signal, an attenuator presents a particular quantity of loss.
- The attenuator system is introduced among a supply and a load circuitry to decrease the supply signal’s extent by a recognized quantity appropriate for the load.
- Attenuators can be immovable, completely adjustable or variable in identified phases of attenuation, such as -0.5dB, -1dB, etc.
- An attenuator can be regular or irregular in the system and either stable or unstable.
- Immovable attenuators also recognized as a “pad” are work to “match” imbalanced impedances.
- An attenuator is efficiently the conflicting of an amplifier. An amplifier delivers gain while an attenuator offers loss, a smaller than one (unity).
- Attenuators are typically passive strategies prepared from modest voltage separator systems. The swapping amid unlike resistances products adaptable step attenuators and uninterruptedly adaptable by using potentiometers.
Applications of Passive Attenuator
- Immovable attenuators in electrical circuits are used to lesser voltage, dissipation of power, and to increase impedance.
- In gaging signals, attenuator connectors are used to lesser the largeness of the signal a recognized quantity to permit calculations, or to shield the gaging expedient from signal levels that can harm it.
- Attenuators are also used to ‘match’ impedances by dropping deceptive SWR
In the coming tutorial related to Attenuators, we will discuss the L-type attenuator system.