A parallelogram is a quadrilateral that has two pairs that are parallel to each other and have equal length. We can get the parallelogram area by taking the base of the parallelogram and the height, and the base is the parallel side, and the height is related to the altitude made from one corner point to the polygon base.
In this post, we cover details about parallelograms and provide practical examples. Let’s get started.
What Is a Parallelogram?
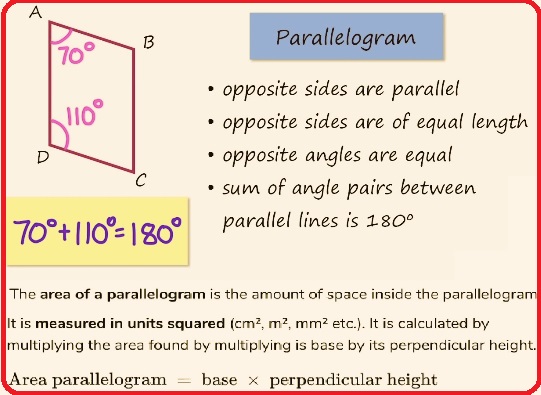
- A parallelogram is a two-dimensional shape that has parallel pairs of sides to each other.
- It is basically a polygon that comes with 4 sides, also called a quadrilateral, that has parallel side pairs of equal length.
- The adjacent angle sum of a parallelogram is equal to 180 degrees.
- The word “parallelogram” is taken from the Greek word “parallelogrammon,” which defines something bounded by parallel lines.
- In this shape, angles between adjacent sides can be different, but the measurement of opposite angles is the same.
- Opposite sides are always equal and parallel.
Properties of a Parallelogram
- Its opposite sides are of equal length and parallel to each other.
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- The adjacent angles sum of a parallelogram is 180 degrees. So, consecutive angles of a parallelogram are supplementary.
- If any angle of a parallelogram is 90 degrees, the other angles are also 90 degrees each. The resultant figure makes a rectangle.
- Parallelogram diagonals bisect each other.
- If we connect opposite corners of a parallelogram, the two triangles formed are congruent to each other.
- • The square sum of all sides is equal to the sum of the squares of the diagonals. That makes the parallelogram law.
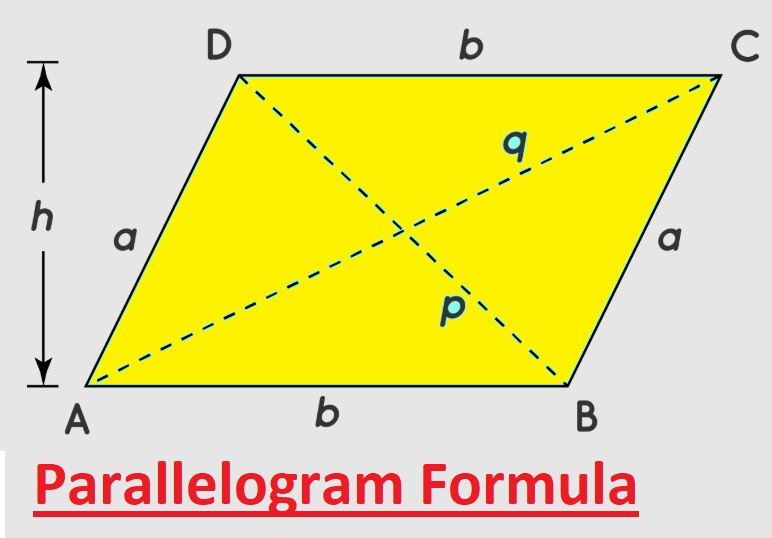
Parallelogram Formula?
Read also Kinematic Equations: Explanation, Review, and Examples
Here we made a parallelogram diagram with sides ABCD FOR finding the formula
We can find from this diagram according to the above details
- AB || CD, AC || BD
- AB = CD = b
- BC = AD = a
- h = parallelogram height
- DB = d, AC = d are diagonals
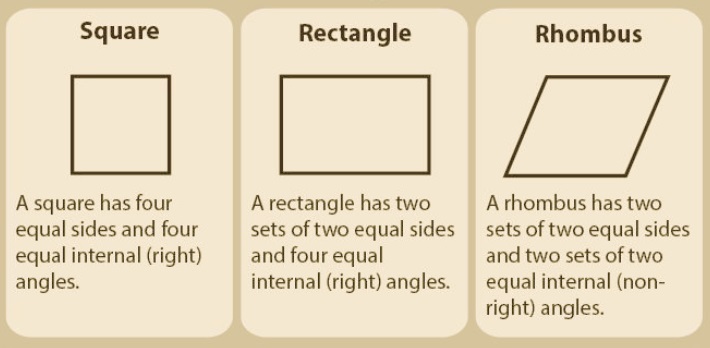
Types of Parallelogram
- Parallelograms come in different types, like squares, rectangles, and rhombuses, in terms of geometric shape.
- Each type has its own features.
Rectangle
- It is a type of parallelogram in which one angle measurement equals 90 degrees.
- Its two diagonals bisect each other. opposite side equal and parallel to the other
- Adjacent sides cross each other and meet at 90 degrees.
Square
- A square is a rectangle where all sides have the same length.
- Its four internal angles are 90 degrees to each other.
- Diagonals bisect at 90 degrees.
Rhombus
- A rhombus is a parallelogram that has 4 equal sides. Opposite angles are equal.
- Opposite angles are of equal length, and diagonals intersect at 90 degrees.
Rhomboid
- Rhomboid: a special type of parallelogram where adjacent sides have different lengths and angles that are not right angles.
- In this parallelogram type, opposite sides have equal length and are parallel to each other.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- A diagonal split of a rhomboid into 2 identical triangles.
- The sum of internal angles is equivalent to 360 degrees.
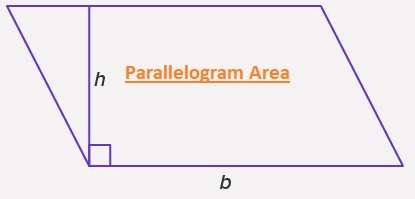
Parallelogram Area
Read also30 Basic Examples of Inclined Plane
- The area of a parallelogram is the surface covered by a two-dimensional plane. Here we have found the parallelogram area formula with different factors.
Area of a Parallelogram with Base and Height
- Area of a parallelogram = Base × Height
- Area of parallelogram ABCD = b × h
Area of a Parallelogram Without Height
- Let’s suppose we do not have the parallelogram height; trigonometry is used for finding the area.
- Area of parallelogram = a b sin A = b a sin B
Area of a Parallelogram Using Diagonals
- Diagonal is also used for finding the area of a parallelogram.
- Suppose diagonals are x1 and x2 intersecting at an angle x; the resulting area of the parallelogram is given by:
- Area of parallelogram formula = ½ × x1 ×x1×x2sin(x)
- Area of parallelogram ABCD = ½ × AC × BD sin (x)
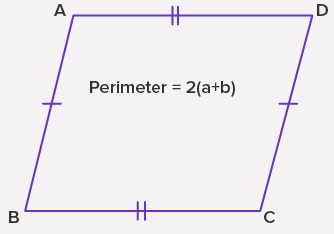
Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- perimeter of a parallelogram is found by taking the sum of the four sides. opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal, perimeter defined as 2 x the sum of adjacent sides,
2 (AB + BC)
Examples of Parallelogram
Paper
- Craft paper used for making artifacts of different sizes and designs. A parallelogram commonly used for making craft papers. That is a simple example of a parallelogram.
Desks
- • The desk also comes with a square or rectangular design. That is a parallelogram example; a rectangle table has two pairs of parallel sides with equal length.
Erasers
- There are static objects, and school kids’ things come with parallelograms. Such an eraser and sharpener are also parallelogram-shaped.
Tiles
- Tiles come in different shapes and sizes. Commonly used shapes for making floor tiles are square, rectangle, rhombus, and parallelogram.
- Tiles are an accurate example of a parallelogram shape that we can see in our daily life.
Buildings
- For making unique and special designs of buildings, engineers use geometric shapes. A parallelogram is a common and famous shape used for making buildings.
- In different building designs, you can see parallelograms as shapes.
Roofs
- If we observe a gable roof on the side, we can observe a 2D geometric plane quadrilateral that has two pairs of parallel and equal sides.
- Roofs are a commonly seen example of parallelogram-shaped objects.
Solar Panels
- Solar panels come with 2 geometric shapes in their design, which are a rectangle and a parallelogram.
- Parallelogram-design solar panels are used since they easily connect with the roof. That is also a practical example of a parallelogram.
Striped Pole
- For pole painting, different slanting colored stripes are used that are also examples of a parallelogram.
- If we see a boundary line of inclined stripes on a pole that is a quadrilateral, like a rectangle. It is also a parallelogram shape seen in everyday life.
20 Parallelogram Examples in Real Life
Read also 20 Screw Simple Machines Examples
| Real-Life Example | Description |
| Tabletop | in our homes, offices, rectangular tables exist that are examples of parallelograms |
| Door | Rectangular doors have opposite sides parallel to each other |
| Book Cover | The front and back covers are also parallelograms. |
| Laptop Screen | The screen surface is a parallelogram design. |
| Mobile Phone Screen | The phone screen has parallel opposite edges. |
| Whiteboard | it normally rectangular, that is parallelogram. |
| Chalkboard | it is a rectangular parallelogram surface. |
| Window Pane | windows are parallelograms (rectangular form). |
| Building Brick | bricks are parallelograms. |
| Television Screen | Flat rectangular screens are parallelograms. |
| Floor Tile | Many tiles are parallelograms. |
| Car Window | Side windows often make parallelograms in shape. |
| Envelope | The envelope design is a parallelogram (rectangle). |
| Painting Frame | The frame shape is rectangular (a parallelogram). |
| Credit Card | A rectangle, a special kind of parallelogram. |
| Playing Card | Rectangular, that is, parallelogram-shaped. |
| Laptop Keyboard Base | The base surface is a parallelogram. |
| Monitor Screen | Opposite edges are parallel and equal in length. |
| Wall Mirror | Rectangular mirrors are parallelograms. |
| Tile Floor Pattern (Rhombus Type) | Rhombus tiles are also parallelograms. |
Rectangle vs Parallelogram
| Rectangle | Parallelogram |
| rectangle is a parallelogram that comes with squares and parallel sides. inrectangle adjacentsides are 90 degress each other | parallelogram has parllel sides 2 sets, adjacent sides are 90 degress to each other |
| internal angles are equal and 90 degress of rectangle | . Opposite internal angles same but not 90°. |
| it has two diagonals, they are equal and divide the rectangle in 2 right triangles. | it has 2 diagonals, but not of equal length. diagonals divided shape in two equal triangles, not needed right-angled triangles. |
| Area is measured using the formula: length x width. | The area is measured using the formula: base x height. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Read also 15 Examples of Convection In Daily Life
What are some real-world examples of parallelograms?
- Real-world examples are trusses of bridges, tile design, and slanted-wall buildings.
How to calculate the area of a parallelogram?
- For measuring a parallelogram, this formula is used.
Area=Base×Height
What is a parallelogram?
- A parallelogram is a quadrilateral that has opposite sides parallel and equal to each other. Its interior angles are opposite.
- Angles on the same side sum to 180 degrees or are supplementary to each other.
What are the examples of a parallelogram?
- Some shape examples that come with the same features as a parallelogram are
- Square
Rectangle
Rhombus
What are the area and perimeter of a parallelogram?
- area of a parallelogram is defined as a dimensional plane. its formula as
Area = Base x Height
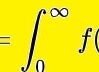
The area of a parallelogram if height does not exist
Area = ab sin x
- a and b are two adjacent parallelograms, and x is an angle.
- The perimeter is the length of the boundaries of a parallelogram. It is equal to the sum of all four sides.
Perimeter = 2(a+b)
What is the shape of a parallelogram?
- • A parallelogram comes with a 4-sided two-dimensional design having 2 pairs of sides parallel and equal.
What are the important properties of a parallelogram?
- Opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
- Consecutive angles are supplementary.
- Diagonals bisect each other
- Opposite angles are congruent.