Manifold absolute pressure, also called a MAP sensor, is the main part of a car engine. Its main function is to measure the air pressure of the intake manifold, which helps to provide the required mixture of fuel and air in the engine. that helps determine the engine’s operation and fuel efficiency. In this post, we will cover the details and features of MAP, find the causes of faulty MAP, and find a solution. Let’s get started.
What is a MAP Sensor?
- MAP sensor, called the manifold that is normally the main part of the internal combustion engine ECU system.
- Engines operated with a MAP sensor are fuel-injected. The manifold absolute pressure sensor provides the ECU system of the engine with data from the measured instantaneous manifold pressure.
- That data helps us to get information on air density circulating and engine air mass flow rate, which helps to measure fuel metering for the combustion process.
- Fuel-injected employees use a mass airflow sensor to get the value of intake airflow.
- The MAP sensor makes a connection with the intake manifold through a vacuum tube.
- When engine speed and load vary, check changes in pressure of the intake manifold. These detected values are converted into electrical signals and transmitted to the ECU for controlling fuel and ignition for the required efficiency.
- Map sensor is part of the engine management system for finding engine load.
- If the MAP sensor is giving faulty data, the ECU will not work well for circulating the air-fuel mixture and will affect overall engine working.
- The map sensor is also employed for onboard diagnostics applications for the EGR testing valve to work well. OBD II vehicles use motor engines.
MAP Sensor Working
- The map sensor is connected with the intake manifold close to the throttle body design. In the internal design of the map sensor, a sealed chamber exists that comes with controlled pressure or a vacuum for engine calibration.
- The sensor vacuum and intake manifold vacuum are separated with a flexible silicon wafer when current flows.
- The MAP sensor also works as a barometric pressure sensor when we are on ignition.
- When the key is turned on, no vacuum is given to the MAP sensor; in this condition, the ECM performs as a barometer and measures air density.
- When the engine starts working, intake manifold pressure reduction causes a vacuum that works for the MAP sensor.
- With pressure on the gas accelerator pedal increasing, the pressure of the intake manifold increases and decreases to a vacuum.
- The pressure difference causes upward movement of the chip in the sealed chamber, which changes the resistance to voltage. As a result, the ECU transmits more fuel into the engine.
- When pressure is released on the pedal, intake manifold pressure reduces, and the set clip position is normal.
- ECU uses all values like manifold pressure value of sensor, IAT data, ECT values, engine speed, and baro values and gets air density and finds engine air mass flow rate for getting the required air-fuel ratio.
Read also :The Role of Smart Sensors in Material Processing: Quality Control
MAP Sensor Features
instant air pressure detection
- This sensor measures air pressure instantly. It is continuous work without taking a rest. With the application of the throttle, intake manifold pressures vary; with that, altitude rises through accurate load distribution.
- The MAP sensor monitors minute changes and transmits them to the ECU. With these regular value measurements, the engine sets the fuel-air mixture for combustion.
High Accuracy
- Values taken from the sensor are accurate when the vehicle stops moving, and the sensor continues working and monitoring readings.
- But if the engine is not working well or fuel wastage occurs, then there are chances of errors. The MAP sensor uses high-grade materials, like piezoresistive components, for accurate results.
low weight
- This sensor is lightweight and small in size. that provide easy installation. It does not take extra spaces since it has a non-intrusive layout, making its use easy.
working in harsh conditions
- Either engine has a high temperature due to dust or moisture, but the MAP sensor continues to work. That means either driving in winter or summer, the sensor continuously works without affecting internal parts.
Fast Response Time
- sensor works fast for any changes in pressure. Its fast response time helps to perform different functions like acceleration, deceleration, and engine load variation.
- Sensors’ slow speed affects engine performance.
Engine Load Detection
- The MAP sensor works according to the detection of engine load rather than airflow measurement. The detection of inner pressures causes the measurement of intake manifold pressure.
- For high pressure, the engine works hard for high air coming. Fuel injection and ignition timing are set according to load, and the engine works with high efficiency.
not depending on Airflow Sensors
- Some vehicles have MAF AND MAP sensors. The map sensor does not based on the airflow sensor.
MAP Sensor Failure Symptoms
Check Engine Light
- The ECU recorded all sensor values of the car engine during driving. If any sensor is not working well, the check engine light gets on.
- For the map sensor, faulty data check engine light showed faulty data on the dashboard.
incorrect air-fuel mixture
- The MAP sensor checks air pressure in the intake manifold for ensure a low air-fuel mixture of the engine. If the MAP sensor is faulty, it sends a bad air-fuel mixture.
- In opposite conditions, the air-fuel mixture is very high, also caused by faulty sensors and the ECU adding high amounts of gasoline to the engine. That also affects working performance.
Engine Stalling or Rough Idle
- faulty sensor that causes variation in the air-fuel mixture, causing stalling of the engine. Some other faulty parts also cause engine stalling which also need replacement when engine stalling occurs.
Misfires
- Misfires occur when combustion is not performed in the engine cylinder, which results from the wrong air-fuel or a faulty map sensor due to the wrong air-fuel combination.
- Misfires can be detected through bumps on the engine or changes in sound from normal working.
high emission level
- Due to a damaged map sensor, a faulty signal is transmitted to the powertrain control module (PCM).
- Air-fuel mixture also provides a good emission level. since a bad map affects the air-fuel mixture for faulty emission levels.
The engine not working well
- Bad fuel mixtures affect engine performance. A low mixture results in poor working, and an overmixture also affects working.
- Misfires also cause a bad engine to work badly.
Backfires
- if fuel in the engine is not burning burningaccurtely causes backfires. if fuel is not ignited in the combustion chamber, move to the exhaust pipe.
- As a result, the temperature increases for the exhaust pipe, and so the air-fuel mixture burns in the exhaust pipe. that causes explosions and chances of catching on fire.
DIFFICULT Engine starting
- A faulty map sensor affects car starting, since the trip computer employs a MAP sensor for measuring air pressure for engine starting.
- accurate level of air-fuel mixture needed for engine starting, so any changes affect engine starting
Causes of MAP Sensor Failure
- Dust and different contaminants accumulate on the sensor, resulting in a faulty reading of the sensor.
- Different electrical wires and connections become loose and affect signal transmission between the sensor and the engine control unit (ECU).
- The sensor can be damaged at different parts due to temperature changes, engine vibrations, and improper handling.
- If the map sensor is very old, its materials degrade due to harsh conditions, which also affects sensor readings.
- If the sensor is not installed accurately, so it is not work well, causing faulty readings and engine performance faults.
- Some related parts, like the ECU or vacuum system, not working well cause failure of the MAP sensor and result in faulty results.
Test process of the MAP Sensor
Different methods are used for testing the MAP sensor; some are explained here.
Visual testing
- First of all, perform a visual inspection of the map sensor to find cracks or damage or leaks or also improper connections.
- Find that the connectors do not have corrosion or loose connections. Also check contamination.
tests with a multimeter
- First of all, on ignition with the engine off, make sure the sensor is getting five volts. This test is called the reference voltage test. Make sure the ECU is at the reference voltage wire.
signal voltage test
- With a voltmeter, we perform a signal voltage test, where the ignition is set on and off, which checks the voltage in the range of 1.0-1.5 volts.
- when the engine speed changes, the voltage needs to be uniform
Find faulty codes.
- With the help of an OBD-II scanner, find different codes for finding map sensor faults. Some faulty map codes are as
- P0105-P0109: MAP circuit not working
- P0237-P0239: sensor low input volts
Read also Top 10 Best Wireless Wii Sensor Bars
Testing with Oscilloscope
- Oscilloscopes are also used for testing digital map sensors. In the result, get a clean square wave pattern where frequency varies with manifold pressure.
- If an irregular pattern occurs, or noise in the signal means a faulty sensor exists
How to Replace a MAP Sensor
- First, locate the map sensor by finding the locations in the car manual. Normally it lies close to the intake manifold.
- Now disconnect the battery to avoid an electric short circuit; for this, remove the negative pin.
- Disconnect the electrical connector on the sensor. For this, press the tab to separate the lock.
- With the help of a socket wrench, disconnect the sensor.
- Now connect the new map sensor in place of the older one. and make a strong connection
- Now again connect screws on the new map sensor.
- Again, put the electrical connector on the sensor for a strong connection.
- Last, connect the battery and drive the vehicle for accurate working and make sure the check engine light is off.
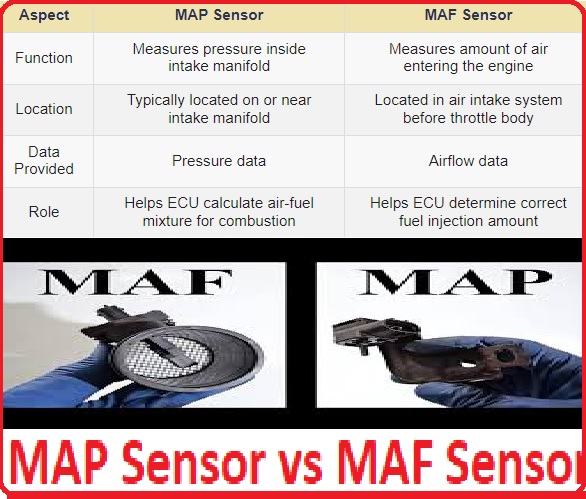
MAP Sensor vs MAF Sensor
| Feature | MAP Sensor | MAF Sensor |
| Measurements | Its measures intake manifold pressure directly. Measures intake manifold pressure indirectly | measures air mass/volume entering the engine directly |
| Syst | D-type fuel injection | L-type fuel injection |
| Calculation technique | ECU calculates air density using pressure, temperature, and engine speed | gets value from air mass |
| Installation | Connected tovacuum tube | connects in the air intake stream |
| Advantages | low intrusive to airflow, easy installation | Direct measurement is typically highly precise |
| Disadvantages | Indirect measurement is affected by different factors | Causes airflow restriction, contamination faults |
Different Fault Codes of MAP Sensor
| Fault Code | Details |
| P0068 | Throttle Position Correlation |
| P0069 | Barometric Pressure Correlation |
| P0105 | MAP Circuit faults |
| P0106 | MAP Pressure Circuit Range/ |
| P0107 | Manifold Absolute Pressure Low Input |
| P0108 | MAP Pressure Circuit High Input |
| P0109 | MAP Pressure Circuit Intermittent |
| P1106 | BARO Pressure Circuit Range |
| P1107 | Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Voltage |
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
Do altitude variations affect how the MAP sensor works?
- The MAP sensor set reading according to altitude variations. For high-altitude low-pressure, it changes the air-fuel mixture for continuous engine working.
Does a bad MAP sensor affect a car’s emissions tests?
- If the map sensor is not working well, it causes high emission of hazard gases like NOx, CO, and unburnt hydrocarbons that affect vehicle emission tests.
How to test the MAP sensor’s accurate working
- Use a multimeter for testing the map sensor at voltage output measuring at the time of ignition with the engine off.
- Check sensor response for variations in vacuum pressure.
What to do for a car that has a MAP sensor error?
- First of all, check the sensor wiring connection for loose connections. If dust accumulates, clean it and find leaks on the sensor. If it still faults, use new sensor.
When do we replace the MAP sensor?
- If the vehicle is driven in difficult conditions, regularly inspect the sensor; use a new sensor if it is showing diagnostic trouble codes or pressure value changes.
Is it good only to clean the MAP sensor instead of replacing it?
- Sometimes cleaning work is required for some sensors, but if they have serious faults, they need replacement.
What is the MAP sensor replacement cost?
- Replacement cost for some parts is 60 to 300 dollars, with labor cost 50 to 200 dollars.
Should we drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
- It is not referred to as driving with a faulty sensor since it uses more fuel and damages ECU parts.
What’s the difference between MAP and BARO sensors?
- The MAP sensor is used for measuring intake manifold pressures, and the BARO sensor measures atmospheric pressure.
Why is the MAP sensor used for cars?
- The map sensor is used to measure intake manifold pressures and transmit to the engine computer, which gives fuel delivery details using this data and ignition duration, engine working conditions.
What are the signs of a bad MAP sensor?
- Basic signs are low acceleration, rough idle, difficult starting process, and the check engine light coming on.
Can a bad MAP sensor affect the engine?
- A faulty sensor causes poor engine working, low fuel efficiency, and affects the catalytic converter’s working due to improper air-fuel mixtures.
How long does a MAP sensor last?
- Map sensors work for 100,000-150,000 miles, but it can differ based on sensor type, driving conditions, and maintenance.