 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Here we will learn about the Introduction to Thermocouples. The thermocouple is an electrical instrument that has two different conductors to make an electric junction. Its operation is based on the seeback effect and make voltage used to find the temperature value. It works as temperature sensor. Thermocouples are less costly and used for measuring the different values of temperatures.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Here we will learn about the Introduction to Thermocouples. The thermocouple is an electrical instrument that has two different conductors to make an electric junction. Its operation is based on the seeback effect and make voltage used to find the temperature value. It works as temperature sensor. Thermocouples are less costly and used for measuring the different values of temperatures.
Its best feature is that then other temperature measuring devices it not need any power source to get start operation. But has some disadvantages that can not measure the value of temperature for some certain centigrade. In this post we will discuss all details prameters of this temperature sensor. So let’s get started.
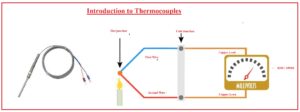
Introduction to Thermocouples
- The thermocouple is sensor used for measuring the temperature. It has two different metallic wires to make a junction-like configuration.
- If these two metallic wires get heat and cooled voltage formed and this voltage give a value of temperatures changed.
- It is a very simple device and less expensive and mostly used for temperature measuring.
- Different types of structures it has such as thermocouple probes, probes with connectors infrared thermocouples.
- There are different types of thermocouples on basis of construction thermocouples created with copper called T thermocouples.
- A thermocouple made with Iron is called J thermocouple and another type that is made with alumel and chrome is called K thermocouple that is commonly used.
- If more then one thermocouples are created with use of different materials called a thermopile.

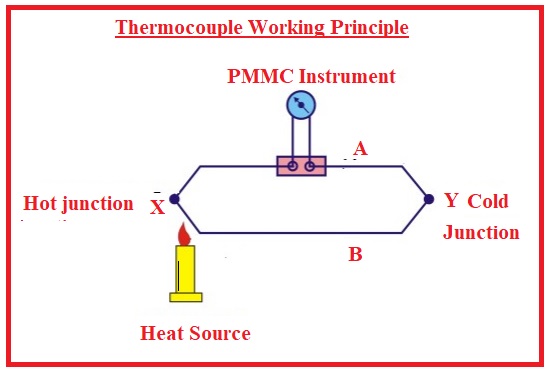
Thermocouple Working Principle
- The working principle of thermocouples is based on the seeback effect. According to seeback effect when 2 different metallic wires join to make a junction voltage is induced in the close circuit that voltage is directly proportional to temperature.
- In the below figure you can see a circuit of thermocouples that measure temperature. Two different metallic wires connect at 2 junctions denoted as X and Y.
- X is the measuring junction and Y is the reference point. In this circuit there is PMMC module is connect
- If these two junctions have different values of temperature cold junction has zero centigrade and value of measuring junction is not known that has to measure.
- Volts or EMF will be generated due to the different temperature values
- EMF generated has values in millivolts. For measuring the EMF PMMC instrument connected in the circuit is used
- If both junctions have same value of temperature EMF produced will be same. So zero current will flow and no movement in the meter
- If the temperature at junctions is not same current will passes in the meter and deflection can seen in meter.
- EMF generated is in direct relation to the temperature difference and current is also in direct relation to temperature difference. Hence meter can measure temperature directly
Advantages of Thermocouple
- It is used for temperature measuring applications since it carries the variation in temperature through a small time lag.
- It is the very finest option for measuring the temperature at a single point
Disadvantages of Thermocouple
- Its accuracy is very less not used for high-value measurements.
- It must avoid the contamination to work for larger time interval
- They have to place at larger distance from the measuring point that decreases the faults in errors
That is all about the Introduction to Thermocouples all details have been explained. If you have any query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a good day see you in next post.