Hi, fellows welcome to another new interesting post. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to STM32F4. This module is comprised of thirty two-bit Cortex M4 central processing unit having FPU. It has a flash memory of one sixty-eight megahertz. It also comprises of flash memory, static random access memory, PSRAM, NOR memory units.
Hi, fellows welcome to another new interesting post. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at Introduction to STM32F4. This module is comprised of thirty two-bit Cortex M4 central processing unit having FPU. It has a flash memory of one sixty-eight megahertz. It also comprises of flash memory, static random access memory, PSRAM, NOR memory units.
It also has twenty by thirty-two bits back up register with four kilobytes static random access memory as back up. In today’s post, we will have a look at its working, features, pinouts, and some other related terms. So let’s get started with Introduction to STM32F4.
Introduction to STM32F4
- The STM32F4 belongs to the family of thirty-two bit ARM Microcontrollers which is created by the STmicrocontroller.
- The family of STM32F provides different features but all these controllers use a microcontroller of thirty-two bits. The STM32F4 provides eighty-four megahertz clock speed. has a flash memory of five hundred twelve kilobytes, the static ram of having space of ninety-kilo byte.
- There are numerous pinouts exits on this module which can be operated as inputs and outputs and can also be used to provide programming to the board.
- There are numerous applications provided by this module different categories of communications devices can be attached with this controller for linking of different types of electronic instruments such as detectors, motors. etc.
- This board comprises of numerous other devices used for communication and interfacing of different projects without any use of the external device.
- This module also comes with some other components such as digital to analog converter, analog to digital converter, the port of sound, all these components make is the complete board.
Features of STM32F4
- These are some important features of STM32F4 which are described here with the detail.
- It comprises of ARM thirty two-bit Cortex central processing unit with a frequency of one eighty megahertz
- It has RAm having space of one ninety kilobytes.
- The flash memory of one megabyte is exited in this module.
- There are functioning voltage range for this module is five volts.
- there is no debugging port exits in it.
- The power supply to this module can be given by the USB port.
- There are 4 user light-emitting diodes that exist on this board in the color range of orange, green, red, and blue.
- There are 2 push buttons that exist on this board first is for reset purpose and the second one is for the user.
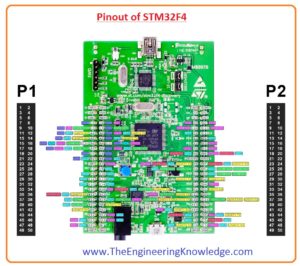
Pinout of STM32F4
- The pinouts of STM32F4 are described here with the details. The pins of this module are divided into two parts which denoted in figure as P1 and P2 and both comprise of five ports A, c, D, E, and H which used to perform different functions.
Power Pinouts
- There is numerous pinout exist on this board for delivering the five volts to the different component connected.
- This used as input power pins in the groups P1 and P2 are given as Third and the fourth pin in group P1 and third and fourth pinout in group P2 are used as input pinouts.
- The pinout which provides power as output in the range of 3 volts and five volts.
- the pins which give five volts are pin three and four in group P2 and pins which provide three volts are pins 5, 6, 15, and 16 in group P2.
GND Pinout
- In group P1 the pinouts used as the ground are 1, 2, 5,23, 49, and 50. and pins used as a ground in group P2 are 1, 2, 49, and 50.
Oscillator Pinout
- There is no inner crystal clock pulse exists in this module. There are 4 outer clock pulse pinouts it has 2 operate for thirty-two-kilohertz crystal and 2 for large value frequency crystal.
- The pinouts used as oscillator are lies in group 2 and named as.
- GPIO7, GPIO, GPIO GPIO10
GPIO Pinouts
- There are six ports that exist in this board which denoted as A, B, C, D, E, and H all these ports have inner pull up resistance and operate as inputs and outputs.
- These pins exit in group P1 is GPIO7 to GPIO22 and GPIO24 to GPIO47 and these pinouts in group P2 have a range of GPIO7 to GPIO21.
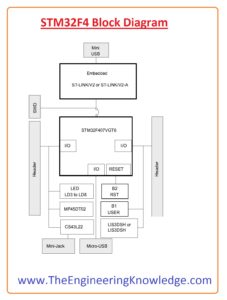
STM32F4 Block Diagram
- Now we discuss the block diagram of this board and know about the different components used in this module.
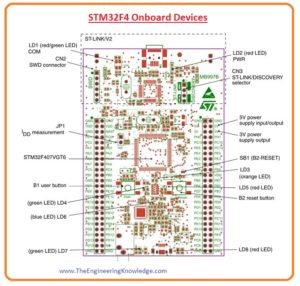
STM32F4 Onboard Devices
Audio Port:
- There is audio pinout exits on this board but with that, it has an audio port which used for linking of outer audio devices.
Universal Serial Bus
- The USB of this module is like OTG which can be used only for programming the MCU. the voltage range for USB should be of five volts and a larger voltage will damage it.
Current Usage Pinout
- There is a current usage pinout that exists on this board used jumper and can be eliminated for calculation of current through the ammeter.
Accelerometer:
- For the measurement of force exerted on the board, there are three line accelerometer is connected on the board.
- It provides protection to the board when it is using in the robotic and such projects in which movement is involved.
Debugging Port
- For debugging this board there are JTAG and SWD ports that exist on this board.
Applications of STM32F4
- These are some important applications of these modules which are described here with the details.
- It used in different types of embedded and robotic projects.
- As it provides numerous functions so it used in industries for controlling machines.
- It also used in sound communicating projects.
So friends it is a detailed post about STM32F4 if you have any further query ask in comments. Thanks for reading