 Hi guys welcome to the new post. Here we will learn Introduction to S8050 – NPN Transistor. The transistor is an electronic device that is used as a switch and amplifier in different projects. Different types of transistors are existed according to features and applications. But most commonly used as NPN and PNP. NPN has a larger doping area for N material and PNP has P types material large doped.
Hi guys welcome to the new post. Here we will learn Introduction to S8050 – NPN Transistor. The transistor is an electronic device that is used as a switch and amplifier in different projects. Different types of transistors are existed according to features and applications. But most commonly used as NPN and PNP. NPN has a larger doping area for N material and PNP has P types material large doped.
Both of these transistors are used for different applications. In this post, we will discuss the main parameters of the S8050 transistor in detail. So let get started.
Introduction to S8050 – NPN Transistor
- The S8050 is less voltage operating and high current used device comes in NPN configuration.
- It is the basic part of class B push-pull amplifiers circuits and is mostly employed as a general-purpose transistor.
- Its gain value is lies between one ten to four hundred. Gain is a term that tell the amplification power of the transistor.
- Its collector current has an extreme value of seven hundred milliamperes.
- Due to NPN configuration collector and emitter in a reverse-biased state if the base is linked to the ground and if the voltage is given at the base it is forward biased state.
- Its complete biased state called saturation value of volts about VCE is about twenty volts.
- If there is no base current it is called a cut-off state.
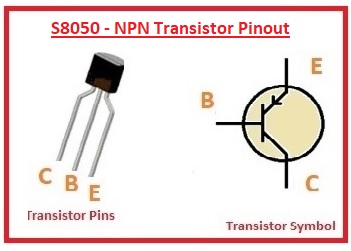
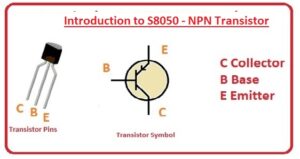
S8050 – NPN Transistor Pinout
- There are three main pinouts it has been described here
- Emitter: Current comes out through this pinout has larger areas than base but less than a collector
- Base: It works as control of transistor-like tap
- Collector Larger part of a transistor and has features to current comes out.
S8050 – NPN Transistor Features
- The main features of S8050 are listed here
- It is available in to 92 packaging
- Used in class B amplifies
- The value of volts for VCB is thirty volts
- The value of VCE is twenty volts
- The value of VBE is five volts
- Gain is four hundred
- The highest value of power is two watts
S8050 Transistor Application
- Its main applications are listed here
- Used in such circuits where the small level signal is used.
- ALso prefer for projects where the gain of large value is needed since it has high value of gain
- The main component of Class B amplifiers
- Used as sound amplifier circuits
That is all about the S8050 transistor i have explained each and every aspect of this component. If you have further query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a good day.