 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will discuss Introduction to Ruby Laser. The ruby laser is a solid-state laser that has a synthetic ruby crystal that works as the gain medium. The first time this laser was created in 1960 by Theodore H TED Maim. This laser generates pulses of coherent visible light having 694.3 nanometers that is red in color.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will discuss Introduction to Ruby Laser. The ruby laser is a solid-state laser that has a synthetic ruby crystal that works as the gain medium. The first time this laser was created in 1960 by Theodore H TED Maim. This laser generates pulses of coherent visible light having 694.3 nanometers that is red in color.
The pulse length of this laser comes in ms. In this post, we will discuss its working structure and some related parameters. So let’s get started Introduction to Ruby Laser.
Introduction to Ruby Laser and Construction
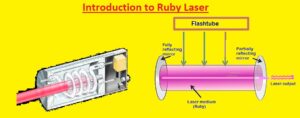
- The ruby laser consists of the ruby rod which is pumped with high energy normally through a flash tube used to get population inversion.
- The rod is positioned between two mirrors that make an optical cavity that oscillates the light generated through the fluorescence of ruby and generated stimulated emission
- Ruby is a type of solid-state laser which generates light in a visible range having a wavelength of 694.3 nanometers with red color
- This layer is a third-level solid-state laser. The active medium used for this laser is a synthetic ruby rod which get energized through optical pumping.
- This laser provides a larger and strong absorption band existing in a visual range that is 400 to 55onm and also has long fluorescence life of three ms
- This makes it for high energy pumping process so the pulse time interval can be larger than other materials
- Ruby later has a wide absorption region and its conversion efficiency is lower than other types of medium.
- In earlier times ends of the rods were polished accurately like the end of the rods were flate in a quarter of the wavelength of the output light and parallel to each other in some seconds of arc.
- The final silver-colored polish is used at the ends, one end is completely polished and the other is half.
- The rod through its reflective ends points work as Fabry perto etalon. The modern laser uses rid having an antireflection coating.
- This reduces te reflection from the endpoints of the rod. For the creation of an optical cavity, outer dielectric mirrors are used. Curved mirrors are used to relax the alignment tolerances and to make a stable resonator
- This laser also has the ability to absorb some light at its lasing wavelength. To reduce this absorption complete length of rod required to be pumped, having non shaded part close to mounting
- The active portion of ruby is a dopant that comprises of chromium ions. The dopant consists of about 0.05 percent of crystal and performs all absorption and radion emission
- On the quantity of concentration of dopant synthetic ruby normally exist in pin or red color

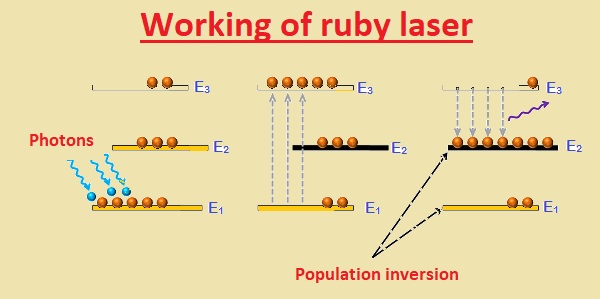
Working of ruby laser
- This laser is three levels of the solid state. In this laser optical pumping process used to provide energy to the laser medium
- Optical pumping is a process where light is used as energy to shift electrons from a low energy level to a high energy level
- Let us suppose that the ruby laser medium has three energy states with N electrons. Energy state are E1, E2 and E3
- Let’s suppose that energy levels are in order E1 < E2 < E3. E1 is a ground state that is lower energy E2 is the metastable state and E3 is a high energy state called the pump state
- Suppose that at start electrons are in lower energy state E1 and very less electrons in the other two higher states E1 and E2
- If length is given to laser medium electrons in a lower energy state get the energy and move to higher or pump state E3
- The duration for pump state E3 is about 10-8 sec, therefore, electrons in this state will not stay for a long time intervals.
- After a small time interval, they will fall into E2 energy level that is metastable through releasing the energy.
- The lifetime of E2 is 10-3 sec which is larger than the E3. So electrons go in the E2 level with speed but do not leave E2 easily. So large number of electrons gather at E2 level that causes population inversion
- After some timer interval electrons in E2 level go to E1 through energy releasing in form of photons. That process is called spontaneous emission
- When emitted photons make interaction with the electrons of the metastable state causing that electron to move to E1 state then again photons released to cause the stimulated emission
- So repeated process generated millions of photons
- For active medium process known as spontaneous emission generates light. The light generated in the laser medium will bounce back and forth between the two mirrors
- That causes another electron to go E1 state and releases energy. That known as simulated emission
Advantages of Ruby Laser
- This laser has a narrow linewidth
- it provides a high value at the output
- Cylindrical mirrors are used for an increment of pumping efficiency
- Its construction is simple and operation also easy
- It provides durable operation hard in structure and has a good thermal conductivity
- It provides the coherent light
- Its output lights 104 to 106watt beam
Disadvantages of Ruby laser
- It needs high energy to trigger laser oscillations
- Cooling material is used to minimize the heat produced during working
- Its output beam is not regular and emits light in pulses
- Thermal distortion and scattering affect the monochromatic impression
Applications of Ruby Laser
- It used in welding, soldering, and in range findings
- Itg used in pulsed holography and as a source of coherent radiation in interferometry
What is a ruby laser used for?
- It is the finest and saves option to remove pigmentation, hair, and tattoos
Why ruby laser is red?
- Ruby crystals have aluminum oxide, some aluminum atoms are replaced with chromium atoms in result chromium gives vibrant red color
Is ruby laser a 4 level laser?
- Ruby is a three-level laser.
Which is better ruby laser or helium laser?
- Helium-neon laser is better than ruby laser since it provides continuous output
That is all about the Ruby Laser all details has explained. If you have any query ask here thanks for reading have good day.