Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of LCD its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of LCD is a liquid crystal display this module consists of 2 types of the matter first is solid and second is liquid. For displaying the images it uses liquid crystals. The screens of liquid crystal have less thickness so it easily used on the screen of laptops, computers, televisions, cameras, etc. Before the invention of an LCD cathode ray tube was used in the screens of tv, the computer, etc that made the screen bulky and large but after the use of LCD, all displays have become less thick. LCD comprises different layers with the 2 polarized panel filters and probs (electrodes). The lens is used to project light on the liquid crystals.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of LCD its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of LCD is a liquid crystal display this module consists of 2 types of the matter first is solid and second is liquid. For displaying the images it uses liquid crystals. The screens of liquid crystal have less thickness so it easily used on the screen of laptops, computers, televisions, cameras, etc. Before the invention of an LCD cathode ray tube was used in the screens of tv, the computer, etc that made the screen bulky and large but after the use of LCD, all displays have become less thick. LCD comprises different layers with the 2 polarized panel filters and probs (electrodes). The lens is used to project light on the liquid crystals.
The colored image is formed with a mixture of colored light and grayscale. There are 2 types of display in LCD first one is active matrix display grid (it uses a silicon backplane instead of Indium Tin Oxide conductive surface) and a second one is a passive display (uses a grid of vertical and horizontal conductors consists of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) to make an image). Most mobile phones that have liquid crystal display uses an active matrix display. In older screens still passive displays. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at its working construction, applications, and some related parameters. So let’s get started with the full form of LCD.
Full Form of LCD
- The word LCD stands for liquid crystal display also known as flat panel display which operates by using the liquid crystal properties of light modulation.
- Like LED generates light it not generate but uses reflectors to make images in a single color.
- There are 2 types of images shown by the LCD first one is arbitrary images that displayed on a computer or laptop and the second one is fixed images that provide less info.
- The fixed images further provide two features that can be shown or hide like presetting of words, numbers (digits) and numbering display in a digital clock.
- Both of these images display uses similar techniques but also have some difference that arbitrary images are formed by using the small pixel matrix and fixed images have large size matrix.
- The configuration of polarizers decides the on (positive) and off (negative) state of liquid crystal display.
- There are numerous applications of liquid crystal display such as TVs, laptop screens, computer monitors, mobiles, screens, etc.
- Small dimensions liquid crystal display screen are normally used small sizes electronic devices such as mobiles, watches, calculators, clock, cameras, etc.
- With the creation of liquid crystal displays, the size of electronic devices has become also smaller due to the replacement of the cathode ray tube with the LCD.
- In older Cathode ray tubes very fewer sizes variation were exited but now LCD provides a large number of size variations from smaller watches to large size screens of a TV.
- As LCD replaces the cathode ray tube similarly LCD will also replace in the next few years with the OLED (organic light-emitting diode).
- The features provided by the OLED are quick response, many colors, less bulky, and thinner, less use of energy, and no need of a backlight.
- With the benefit of OLED, there are some drawbacks such as is its price is high as compared to the LCD and if damaged it can not be repaired again while LCD can be.
Construction of LCD
- First of all, we discuss some parameters that we should keep in mind before the construction of LCD.
- The light used must be polarized.
- The liquid crystal used in the construction of liquid crystal display has the ability to varied the polarized light and transmission of light.
- The design of liquid crystal can be varied by the input current.
- There are 2 polarized glasses as filters needed for the construction of liquid crystals used in LCD.
- If the glass is not polarized then rub the upper part of the glass with a certain polymer to make it that will make the glass polarizer by making minor grooves on the glass.
- The direction of all groves on the glass should align or in same direction.
- After that put makes the layer of air-filled liquid phase crystal on one polarizing filter of the polarized glass.
- The tiny channel origin the ist layer molecule to bring into line with filter direction.
- When first layer is at ninety degrees then put the 2nd glass having polarized sheet.
- The ist filter is automatically polarized as the light rays collide with the at the initial point.
- As light passes through the first layer and move to others with the guidance of molecules.
- After reaching at the endpoint of liquid crystal it starts to vibrate alike to the vibration of last layer molecules.
- The light is permissible to enter into the expedient only if the 2nd layer of the polarized glass equals the last layer of the molecule.
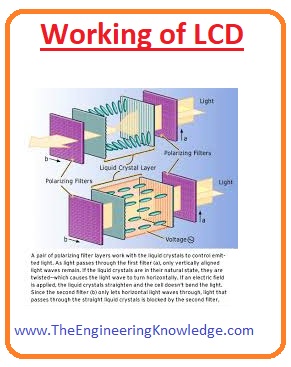
Working of LCD
- The operation LCD is that as current is provided to the molecules of liquid crystals, the molecules show some rotation.
- Due to this the angle of light passing through the polarizer varies also the angle of upper polarizer filter varies.
- Due to this small intensity of light passes through the less area of liquid crystal display.
- The working phenomena of LCD have blocked the light. For this light-blocking mirror is placed at the back end.
- The indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode is placed on the upper and polarized glass at the lower part of the LCD.
- The 2nd glass has an electrode in a rectangular shape on the lower side and polarizer sheet on the upper portion.
- The position of both glasses should be at 900 to each other. If the current is not passing then the light moving through the front part will be reflected by the mirror to back direction.
- The electrode linked with the battery the current coming from the battery will source the liquid crystal among the common plate electrode and rectangular electrode to change position.
- So this method the light will stop to pass on and this specific area will be shown no color.
Difference between LCD and OLED
- These are some differences between the LCD and OLED.
|
OLED |
LCD |
| It stands for Organic light-emitting diode | It stands for liquid crystal display |
| Its screen is made with an organic medium like carbon. | It screen made with the liquid crystal. |
| Every pixel on the screen has its own light. | While in this module background light is used normally lamp used. |
| The pixels of OLED can be on and off independently due this OLED shows different colors. | While in LCD pixels are not on and off independently, they use light at the background and pixels panels to block white light and make different colors. |
| Its brightness is high | Its brightness is low. |
| It needs less power when there is less color on the screen | It needs high power. |
| When the color is white it uses large power. | It uses less power. |
| Due to the used of organic material its working life is less. | Its operating life is high |
| Its price is also high | Its price is less compare to OLED |
Difference between LCD and LED
- These are some difference between LCD and LED that is described here with the detailed.
LED LCD
| It is constructed with the semiconductor material and emits light when current flows through it. | This is an optic device that displays information in the shape of pictures and numbers. |
| It stands for a light-emitting diode. | It stands for liquid crystal display. |
| In this module, there is no backlight required. | It uses a fluorescent lamp for a backlight. |
| Its resolution is high. | Its resolution is less. |
| It consumption power is high | its power usage is less. |
| Its displaying area is less compared to LCD. | Its displaying screen is large. |
| This device is expensive. | it is less expensive. |
| It manufactured with the gallium arsenide phosphide. | It constructed with the liquid crystal and glass electrodes. |
| Its switching needs less time. | Its switching is a slow speed |
| It can also operate on Direct current. | DC can damage its operating life. |
| It does not use mercury | It uses mercury. |
Features of LCD
- Now we discuss the features of LCD.
Resolution
- The quality of resolution provided by the liquid crystal display depends on the number of pixels in rows and columns exited in the display.
- Every pixel further has three subpixels, of blue, red and green color.
- In new technologies in the subpixels, there are further subpixels that called Quattron and increases the resolution of LCD.
Color performance:
- There are numerous terminologies that explain the color performance of the LCD.
- Like color gamut that explains the color variations and color depth is accuracy that defines the variations in the colors during color gamut.
- Color gamut is very important specifications it only takes into consideration at a professional level, not on the customers’ purchasing level.
- The are some other feature related to the color that is a white point and gamma correction these features explains how the other colors will be shown according to white color.
Brightness and contrast ratio:
- The ratio among the fully shown (on) pixels to completely off pixels is called a contrast ratio.
- While extreme light shown by the liquid crystal display is called brightness of LCD it depends on the backlight used in LCD.
Advantages of LCD
- These are some advantages of liquid crystal display.
- The physical construction and size are less as compared to the large size cathode ray tube.
- It also uses less energy as compared to older CRT monitors having similar dimensions.
- It losses some heat due to an all amount of power usage.
- In LCD the geometrical distortion is less.
- The background light used in the LCD explains the flickering.
- It does not release harmful radiations like the Cathode ray tube.
- In can be designed in any shape and size according to user requirement.
- It can be created more than eighty inches.
- It does not affect by the magnetic field
- It operates at the twelve-volt power supply.
Disadvantage of LCD
- These are some disadvantages of liquid crystal display.
- Due to less viewing angle in older LCDs causes the decrement in contrast and brightness.
- In less temperature conditions its brightness decreases.
- There is also decrement in contrast due to the temperature.
So friends that is the detailed post on the Full Form of LCD I have written each and every aspect related to LCD. Also,do comparison among the LCD, LED and OLED. If you have any further queries and want something else can ask in comments. Thanks for reading. See you in another next interesting tutorial. Have a good day.