 Hi, readers welcome to another interesting post. In this post we will have a detailed look at Introduction to Amplifier Distortion. Amplifier Distortion has numerous types like Amplitude distortion, frequency, and phase. For any signal amplifier to work in a proper way without any hindrance, it needs DC biasing at its Base or gate terminal. DC biasing is necessary to the amplifier so it amplifies the input signal during its complete cycle.
Hi, readers welcome to another interesting post. In this post we will have a detailed look at Introduction to Amplifier Distortion. Amplifier Distortion has numerous types like Amplitude distortion, frequency, and phase. For any signal amplifier to work in a proper way without any hindrance, it needs DC biasing at its Base or gate terminal. DC biasing is necessary to the amplifier so it amplifies the input signal during its complete cycle.
The amplification given by any amplifier like power, voltage amplification is the ratio of output values to input values. If we create our circuit in a wrong way and put Q point of biasing at the wrong location on line of load or if we apply voltage beyond amplifier capacity due to these effects the output signal will not create the exact desired waveform. In a simple way, we can say that it is amplifier distortion.
Introduction to amplifier distortion
- The amplifier is fundamentally intended to intensify smaller signal input to the larger output signal and this explains that the output signal is continually altering by some values which named gain.
- Ther are some factors that cause distortion.
- If biasing is not proper then amplification not occur properly.
- If the input signal is large beyond the transistor limit it will cause to distortion in the signal.
- If signal is not linear during its cycle at the frequency range input signal.
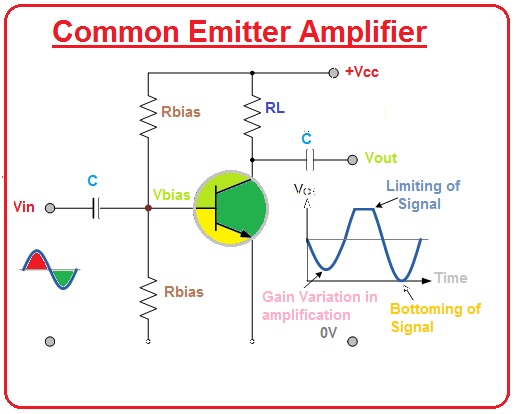
- To understand amplifier distortion we explain an example of a common emitter amplifier.
- The common emitter circuits operate for smaller input AC signals but it cause some problems during their working, the intended location of the biasing point Q of a BJT amplifier be contingent on the similar Beta(β) value for all transistors.
- But, this (β) value will fluctuate from transistors of the similar kind, it means, the Q-point for one transistor is not essentially the similar for another transistor of the similar category due to the characteristic productions acceptances.
- Due to this imbalance of Q point signal becomes distorted.
- Then amplifier distortion produces since the amplifier nonlinear this category of amplifier distortion is known as Amplitude Distortion.
- Appropriate options of the transistor and biasing elements can help minimize the effect of amplifier distortion.
Amplitude Distortion
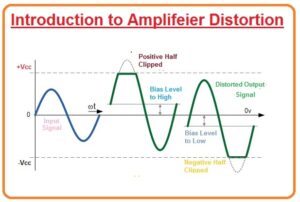
- · This type of distortion occurs when th change happens in the maximum value of the frequency waveform which causes distortion due to changing in the position of Qpoint and intensification of signal not occur during the complete cycle. In the given diagram due to incorrect biasing amplitude, biasing has been explained. Let’s discuss it.
Amplitude Distortion due to Incorrect Biasing
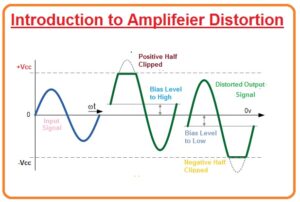
- If the biasing point of the transistor is correct position means at the center of load line then the shape of the output waveform will remain the same as the input signal.
- If biasing is not good and Q point lies below the center of the load line then out will wave shape will be like right side waveform which is shown in the given diagram. In this waveform, we can see that the lower half of wave is clipped.
- If biasing is not correct again and Q point now lies at above of the midpoint of load line inn this case upper half of the output wave will be cut off.
- If input voltage is lesser then a biasing point then also during negative have of wave amplitude distortion happens.
- Same if the voltages are higher than for proper biasing than amplitude distortion occurs during the positive half
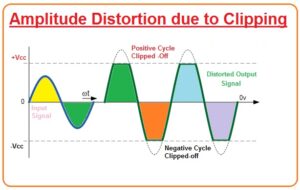
Amplitude Distortion due to Clipping
- In some cases, if the biasing voltage is set at the proper level, it still has a chance to distort the output wave if the input signal which has to amplify is greater than its specified value for amplifier circuity.
- During this condition, the output signal becomes distorted at both halves of its cycle and it doesn’t have a shape like a sin wave. This type of amplitude distortion is called clipping.
- To control this situation voltage level must in a limited range.
- Amplitude distortion significantly decreases the competence of an amplifier circuitry.
- In given figure, we can see that flat tops of the inaccurate output wave either due to improper biasing or over voltage at the input.
What is Frequency Distortion
- Another kind of amplitude distortion frequency distortion it happens when the level of intensification differs with frequency.
- It happens when large no of inputs which have to amplify has a fundamental frequency and a large no of frequencies which called harmonic will distort the original signal.
- In normal working, the amplitude of these harmonics is less than a fundamental frequency due to these has no effect on output wave.
- But if their amplitude is higher than a certain point they will cause a distortion in output waveform.
- Let’s explain this phenomenon by example.
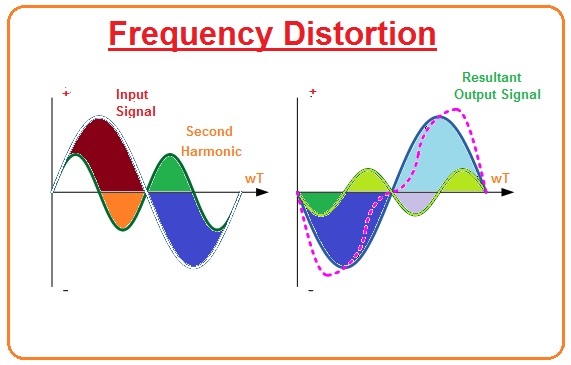
Frequency Distortion due to Harmonics
- In the given diagram, we can see that input waveforms has a fundamental frequency and second harmonic signal.
- Their subsequent output wave is shown in the figure at right.
- The frequency alteration happens when the fundamental frequency syndicates with the second harmonic.
- By we can say that Harmonics frequencies are multiples of fundamental
Frequency distortion due to harmonics is constantly an option in amplifier circuitries comprising reactive components like capacitor or inductor.
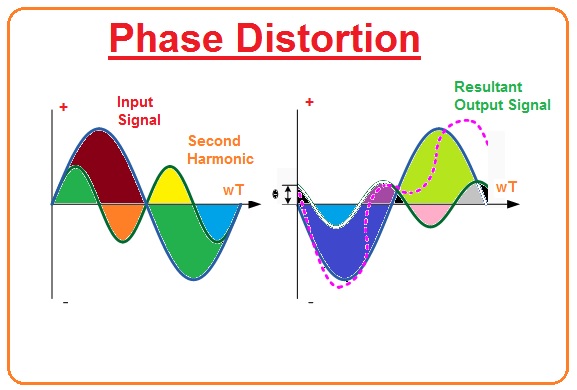
What is Phase Distortion
- This type of distortion happens in a non-linear amplifier circuit when there is time delay between input and output waves happens.
- If the phase variation amid the input and output is zero(0) at fundamental frequency If we say that the phase change between the input and the output is zero at the fundamental frequency, the subsequent phase angle postponement will be the alteration amid the harmonic and the fundamental frequencies.
- This time postponement will be contingent on the structure of the loudspeaker or amplifier and will upsurge gradually with frequency in the bandwidth of the intensifier.
- maximum applied loudspeakers will have some arrangement of Amplifier Distortionby a mixture of both “Frequency” and “Phase Distortion”, collected with amplitude distortion.
- In maximum submissions like in auditory amplifiers or power intensifiers, unless the amplifiers alteration is extreme or unadorned it will not normally disturb the action of the amplifier.