Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss Introduction to 75160B. It is SN75160B eight-channel general-purpose interface bus or GPIB transceiver. That is monolithic high-speed low power consuming Schottky component that is configured to transmit the data in two-way communication through a single point transmission line.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss Introduction to 75160B. It is SN75160B eight-channel general-purpose interface bus or GPIB transceiver. That is monolithic high-speed low power consuming Schottky component that is configured to transmit the data in two-way communication through a single point transmission line.
Its feature is such that can be functioned in passive pullup or three-state mode. In this post, we will discuss its working, features, and some other parameters. So let’s get started. Introduction to 75160B.
Introduction to 75160B
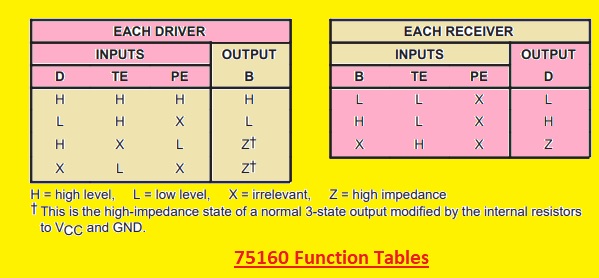
- The 75160B is a transceiver that is designed according to IEEE standards 488 to 1978. Its output is configured in passive pullup or three-state output mode through PE in the high state.
- It talks enable or TE is in a high state these ports provide the feature of passive-pullup outputs when pullup enable PE is low and three-state output if PE is the high state.
- Getting TE low mode these ports are in a high impedance state. Driver outputs are configured to handle loads up to forty-eight milliamperes of sink current.
- Output glitches through power up and power down are removed through inner circuitry which disables both bus and receiver outputs.
- The output does not load the bus if Vcc=0. If there is the configuration of the SN7516B bus transceiver pair offers the complete sixteen-wire interfacing for the IEEE-488 bus.
- The structure of SN75160B is featured from zero to seventy centigrade.

75160B Features
- Its main features are explained here
- It is compatible with the IEEE Standard 488 to 1978 GPIB
- It is eight channel bidirectional transceiver
- It is a high-speed device, uses less power, and has Schottky circuitry configured device
- It has less power dissipation about seventy milliwatts for one channel
- Its propagation time is about 22ns maximum
- It has high impedance PNP configured inputs.
- Receiver hysterics is about 650mV TYP
- Its structure is open collector drive output point
- It is no loading of nus for Vcc=0
75160 Pinout
- 75160 Pin are explained here
| Pin No | Pin Name | Pin Function |
| 01 | TE | It is Talk Enable Pinout |
| 02 | B1 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B1 |
| 03 | B2 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B2 |
| 04 | B3 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B3 |
| 05 | B4 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B4 |
| 06 | B5 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B5 |
| 07 | B6 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B6 |
| 08 | B7 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B7 |
| 09 | B8 | It is GPIO or General purpose interface input/output pin B8 |
| 10 | GND | It is the ground pin and ground attached here |
| 11 | PE | It is the Pullup Enable terminal |
| 12 | D8 | It is Input Output Pin D8 |
| 13 | D7 | It is Input Output Pin D7 |
| 14 | D6 | It is Input Output Pin D6 |
| 15 | D5 | It is Input Output Pin D5 |
| 16 | D4 | It is Input Output Pin D4 |
| 17 | D3 | It is Input Output Pin D3 |
| 18 | D2 | It is Input Output Pin D2 |
| 19 | D1 | It is Input Output Pin D1 |
| 20 | VCC | Here positive power is provided |
75160 Function Tables
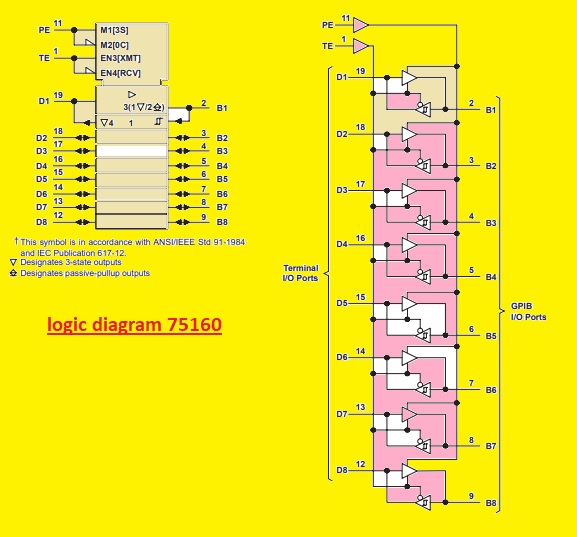
logic diagram 75160
That is all about the 75160B all details has explained about this transceiver. If you have any query ask here thanks for reading have a nice day.