 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will know about GSM Channel Coding on Air Interfacing The GSM is a mobile communication system that users to send and get data over different communication modules and make connections and interlinking among the different countries. It is a worldwide accepted and used topology that employed.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will know about GSM Channel Coding on Air Interfacing The GSM is a mobile communication system that users to send and get data over different communication modules and make connections and interlinking among the different countries. It is a worldwide accepted and used topology that employed.
In this post discuss burst used in the GSM and their different elements. and learn how to control the air interfacing from different errors and data usage. So let gets started with
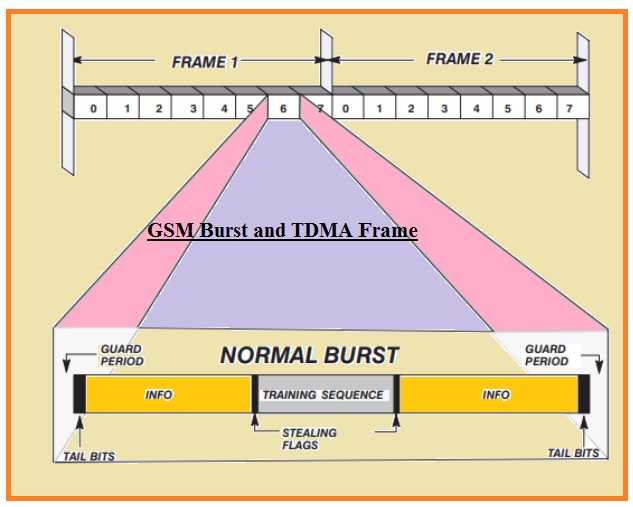
What is GSM Burst
- In the below diagram we can see the configuration of the GSM burst there are different parts of this module has.
- That is discussed here
- Info
- In this part of burst, there is existence of voice data and regulation info exist.
- Guard Period
- There is data received by the BTS and mobile subscribers in the form of burst then they decode it in the required form.
- Stealing Flags
- There are 2 bits adjust in case of traffic channel burst is used without permission.
- The first bit indicates that ½ part of the block is hacked
- Training Sequence
- This part of the burst analyzes the feature of distance among the BBTS and Mobile subscribers and it employed in the equalizer. Its distance is twenty bits
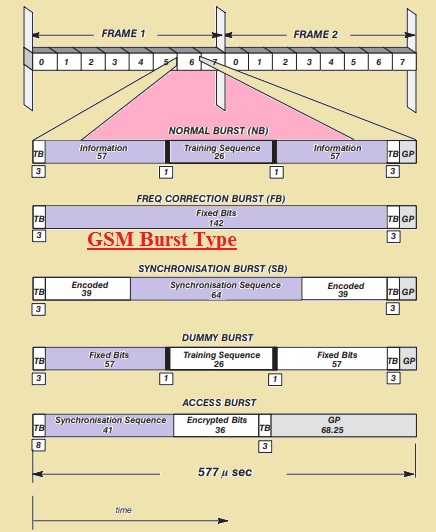
Burst Category
- In the below figure the commonly used types of Burst are mentioned.
- There is a certain value of time is allocated to the burst type that helps to move to the timeslot.
- Normal Burst
- It is a two-dimensional operation that consists of traffic and control channels
- Frequency Correction Burst
- This burst helps to change the value of frequency of mobile subscribers according the bts arrangements
- Synchronization Burst
- It helps to make synchronization between the time allocated to mobile and bts
- Dummy Burst
- It employed when there is no data send through any timeslot
- Access Burst
- The time for this burst is very less than other and enhanced guard time is compulsory since time of communion is not know. It is uplink burst
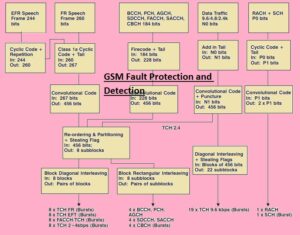
GSm Fault Protection and Detection
- In GSM there is different coding terms are used to provide safety to from errors.
- In the below diagram, we can see the coding procedure in case of info controlling and channels/
- Main coding methods are mentioned here
- Speech Channel Encoding
- The speech data in the case of twenty milliseconds is distributed in 8 bursts.
- It helps to recover the data if the burst is lost due to different places existence
- Common Control Channel Encoding
- Twenty milliseconds data exist in the 4 bursts that help the burst to move in single TDMA
- Data Channel Encoding
- In this technique, data is distributed in twenty-two bursts.
- That helps to recover the data if it lost small part at the receiver
GSM Speech Channel Encoding
- At bts data get is in coded form through BSC then BTS categorized the data in different channels.
- This channel then further converted in the distinct channel before further send
- The transcoded data is got in the form of a frame there are two sixty bits in the frame.
- These bits are categorized in subtypes mentioned here.
- Class 1a
- 3 parity bits operate in the fifty class 1a bits type.
- Class 1b
- The one thirty-two class 1b bits are not monitored but send with the class 1a and parity bits to make encoding
- speech channel coding
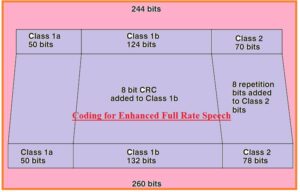
How Channel Coding occur in Enhanced Full Rate
- There are a twenty milliseconds frame comprising two twenty-four bits for channel coding at the air interfacing.
- After application of a certain process, there is sixteen bits added to this frame to make it two sixty bits enhanced full rate.
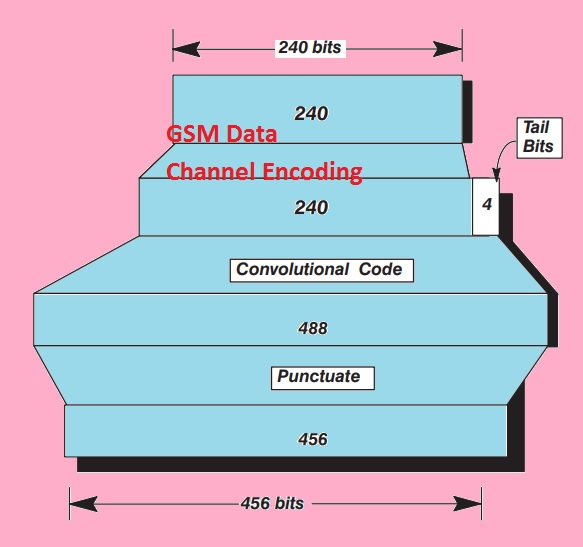
GSM Data Channel Encoding
- In below figure, we can see the rules to protect the channel having a data rate of 9.6 kilobits per second.
- There is a somewhat similar technique used for 4.8 and 2.4 kilobits with some change.
- Their convolutional code is used to encode the channel.
- In the case of 9.6 bits per second, there is a limitation of some coded part then make it to interleave.
- To transmit data there is a need of a larger data rate than transmitted.
- For instance, to transmit 9.6 kilobits there is a need of twelve bits per seconds
Map Logical Channels onto the TDMA Frame
- What is Interleaving
- After doing the encoding and protection data from the logical channel the other process is to make its sequence of bits in the burst which can be sent in the TDMA
- This process is called interleaving.
- That distributes the data of a single data block at the different TDMA timeslots.
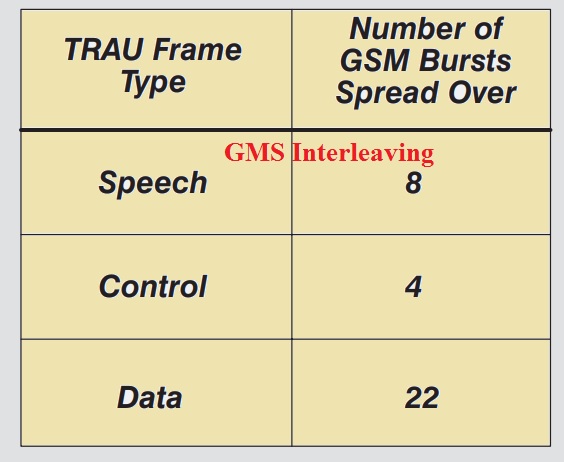
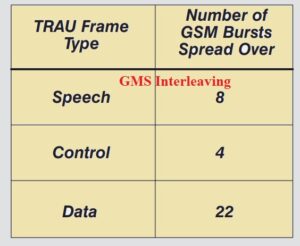
- There is these interleaving parts are used mentioned here
- Speech carries 8 blocks
- Control carries 4 blocks
- Data carries 22 block
- This phenomenon is very significant that provide protection to data from severe cases.
- In case of interference, buts will be affected from outer environment moving from mobile to BTS
- The interleaving is to save data from the traffic block to lost.
- In this process, burst remains to save and data lost not make any effect over the total signal