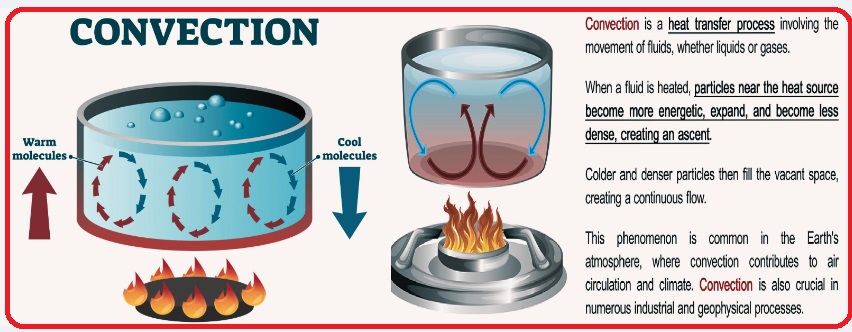
Convection is a phenomenon for the transfer of heat that is important for different natural and man-made processes. Convection heat transfer is a process used in thermodynamics and is part of different processes. We can practically observe convection during boiling water and heat exchange during heating systems.
In this post, we will cover the detailed features of convection and learn practical examples. So let’s get started.
What is Convection?
- Convection is a single- or multiphase fluid flow process that spontaneously occurs with applications of some effects, like material property, body forces, and heterogeneity, on fluids like gravity and density.
- If the convection occurrence causes are not known, convection, thermal expansion, and buoyancy are the main causes.
- Convective flow can be transient or steady state. Convection also occurs due to gravitational and electromagnetic forces.
- Earth’s atmospheric structure is based on heat transfer through natural convection. Stellar physics uses natural convection.
- Convection does not exist in solids since high current does not flow, and also, the absence of diffusion occurs.
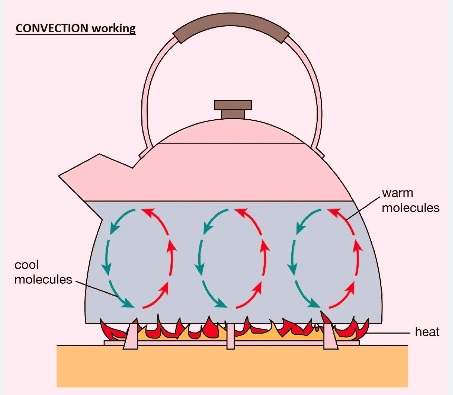
CONVECTION working
- Convection is a process that occurs for heat transfer between solids and liquids, which makes a connection with solids.
- Convection is an important factor for heat transmission from one liquid to another through a barrier.
- In this process, heat transfer occurs through thermal diffusion or advection, a process where heat is transferred by the high motion of heat current in a fluid.
- If we apply heat to fluid at the lower end, thermal expansion occurs, and density reduces at lower fluid layers when the temperature increases.
- High-temperature, low-density fluid parts move upward due to buoyancy and take the place of low-temperature fluid.
- That colder fluid gets heated and rises and is replaced with the upper colder layers, and this process is continuously repeated, and transfer of heat occurs.
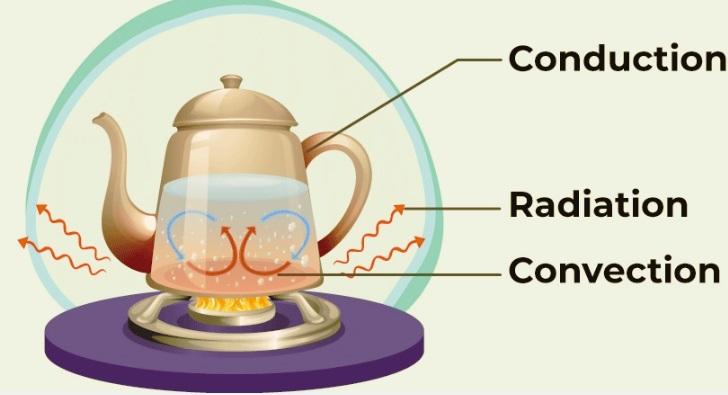
- Here you can see the convection process with the radiation and conduction processes.
Convection Formula
- Formula for convection is as
Q = h A ΔT
here
- Q is heat transfer
- h is convective heat transfer coefficient W/(m²·°C))
- A is the surface area where heat is transferred in m²
- ΔT is the Temperature difference between the surface and the surrounding fluid
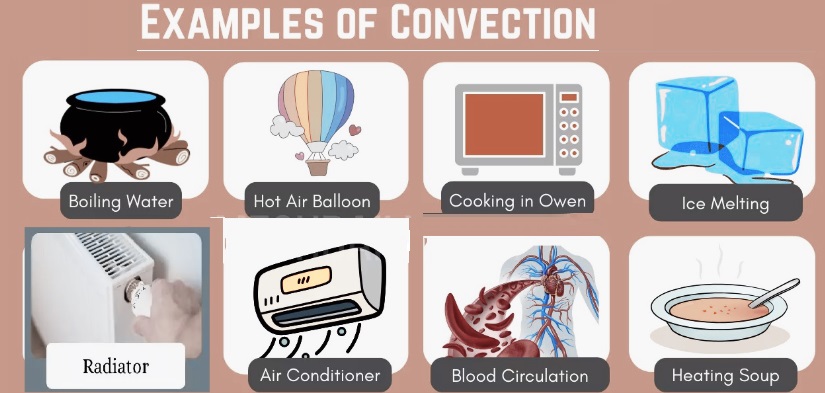
Common Examples of Convection
Air Conditioner
- Air conditioners are commonly used during hot days. process used for air cooling in air conditioners based on convection.
- When the air gets cooled, it is released from the indoor unit of the AC. This released air is at a lower temperature than the external air, which causes it to sink.
- Other air that has a high temperature replaces the air and covers the space of the sunken air. Finally, the air conditioning system comes into play, and the convection current causes the room to cool.
Breezing
- Breezing is a common example of convection. According to convection, high-temperature molecules displace lower-temperature molecules.
- The area near the sea is warmer than the evening. Convection is caused by air that is close to the land area becoming heated and finally rising.
- That warm air close to land is replaced with cool air, causing a sea breeze. At nighttime, the land-to-cool-down factor is higher.
- Air over sea Water is warm and rises. When this air rises, it is replaced with cool air from the land, which is called a land breeze.
Hot Air Balloons
- Hot air balloons also use the convection process. When air in a balloon gets heated, it expands and rises over cooler, denser air externally, causing lift with thermal convection. that causes a convection current. When an air balloon becomes cool, the pilot again provides heat for flight.
- This creates a convection current. As the air in the balloon cools, the pilot must reheat it to maintain flight. This upward movement is a perfect example of convection in real life.
air circulation in the room
- Heating a room through a heater to make it warmer is an example of convection that occurs naturally. The heater warms air and reduces its density, and it moves upward through denser air. It causes a conventional current that makes our room warmer over time.
- Sea breezes and the movement of tectonic plates are heat transfers through convection.
Radiator
- The radiator is working based on convection. The working of a radiator is the same as that of an air conditioner. For the radiator working heating part, put it at the lower side. Cold air is high-density and put into the radiator. that become warmed and released. Hot air covers the space created by cold air. As a result, convection current produces
Hot Air Popper
- The hot air popper that helps to make popcorn which works through convection. A hot air popper has a fan, vent, and heating module. When the popper operates, the fan transmits air into the heating module through the vent. The heating part heats air that rises. Popcorn kernels preheated over a heater, and hot air rising resulted in the kernels popping.
Rainfall & Thunderstorms
- Rainfall and thunder also cause convection. Clouds are made when ocean water becomes warmer and rises upward. Warm water drops become saturated, which makes clouds. Small clouds made during this process combine to make larger clouds. larger clouds called cumulonimbus that result from thunderstorms.
Air-Cooled Engines
- The engines of vehicles are cooled through the use of water jackets. Heated water is used for a longer time, and water exists in pipes that circulate around the engine. To start the engine, water needs to be cooled.
- When water becomes heated, it comes with features that cause hollow bubbling in pipes that are around the engine. Air is cool and moving through pipes that make cool warm water exist in hoses and pipes of the engine.
- The fan also puts in pipes, and here convection works when water gets cooled and moves back to the engine, and the engine stops cooling.
Ice Melting
- Ice melting is a common example of convection. The temperature of the ice surface increases when warm air moves over ice or water that is warmer than the moving air below the ice.
- When the temperature of the surface of ice varies, ice melts.
Convection Oven
- In your daily life routine, you use an oven that works based on the convection principle. Convection ovens use forced convection. For heating, molecules that exist in air get heated and move. The food we place in the oven gets cooked due to the warm air.
Squall Lines
- High wind and rain come with a line of other thunderstorms made through the convection process.
Supercell
- It basically shows a high level of convective thunderstorm, and these storms exist for more than one hour or longer time, and they also cause high tornadoes.
Mantle Convection
- Convection currents convert heat from the Earth’s core to the surface, providing the Earth’s rocky mantle with slow motion. In results, tectonic plates move over the globe slowly.
Types of Convection
Read also:Difference Between Heat and Temperature
Natural Convection
- This convection process occurs when fluid moves slowly through temperature differences, creating density differences without any force. The basic example of natural convection is air rising close to a heater.
Forced Convection
- This process uses external forces from different sources, such as a pump or fan, that move fluids and provide easy heat transfer. Its common examples are forced air heating systems and heat exchangers used in industries.
Mixed Convection
- This convection occurs through natural and forced convection; through a combination of external forces and temperature differences, fluid motion occurs.
Dry Convection
- This convection process occurs without the creation of clouds.
Moist Convection
- This convection involved the creation of cloud formation.
Convection features in Water
- For practical observing of the convection process in water, fill a container with water and add food coloring at a certain point in the water close to the heating source. Now monitor that watercolor rising process and movement that helps us to the existence of a convection current.
- Now again perform this process; put cold dyed water in a container of hot water. Check the difference in direction of cold water motion compared to hot water.
air with Convection
- Find a closed room and light a candle, and check that the heat is rising over the candle. Put your hand at some distance over the flame to define rising warm air.
- Now get an ice plate, and detect the temperature difference over the tray and below the temperature.
Convection vs. Conduction vs. Radiation
These three are processes involved in heat transfer.
Convection:
- In this process, through fluid motion, it uses fluid as a medium.
Conduction
- Heat transfer occurs with direct connection between solids, as you feel that the metallic spoon becomes hot when stirred in a high-temperature fluid
Radiation:
- In this process, heat transfer through electromagnetic waves does not need any medium, like sunlight reaching the earth in the form of radiation.
Convection in Biological Systems
There is a high importance of connection for physiological methods for biological organisms, like for heat and nutrient transfer:
Human Heat
- In our body, convection is used in blood circulation and to distribute heat. Blood redirects to the skin through overheating, which dissipates heat into the surrounding air through the convection process. with that air convection over the skin it provides a cooling process.
Plants’ respiration process
- Air moves inside and outside through leaves through the convection process, which makes photosynthesis and gas exchange easy. The temperature difference between plant tissues and ambient air helps to transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Natural Ecosystems
- water connection process used for nutrient distribution in some ecosystems. such as convection, is the cause of seasonal changes in lakes. that shifts high-nutrient water at the lower part of the surface and is useful for marine life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Define the convection process.
- Convection is a process that is used for heat transfer with fluid movement based on temperature differences in the fluid.
Give an example of convection heat transfer at home.
- Boiling water is a very common example of convection used at home, and it is called natural convection. In this process, heat makes warm water droplets and low-density molecules move in an upward direction. Low-temperature molecules move towards the bottom and cause circulation movement.
What is the difference between convection and conduction?
- Conduction involves heat transfer between solid particles due to connections between molecules. while convection transfers heat in fluids due to the movement of gas or liquid
How does heat transfer by the convection process?
- Temperature differences between fluid particles cause heat flow and help warm liquid move upward and cool particles move downward.
How is convection transferred?
- Heat is transferred in the convection process through the circulation process, where warm molecules are of low density and move upward, and dense fluid moves downward; as a result, fluid circulation occurs.
What are 10 examples of convection?
- 10 examples of convection are blood circulation in warm-blooded animals, boiling water, convection ovens, land and sea breezes, winds, ocean currents, hot air balloons, radiators heating a room, air conditioners circulating air, and campfires heating the air around them.