 Hello guys, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit. The basic difference among series and the parallel circuits is the direction with which components are connected in the circuit. In series, a combination element is attached with each other in a cascaded away like the first point of one component attached with the second point or tail of other elements.
Hello guys, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit. The basic difference among series and the parallel circuits is the direction with which components are connected in the circuit. In series, a combination element is attached with each other in a cascaded away like the first point of one component attached with the second point or tail of other elements.
But in parallel configuration components are connected in such way their head join at fist point and tail at other points. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at the series and parallel circuits and find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit.
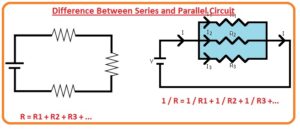
Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit
Series Circuit
- In a series configuration, components of circuits are attached in a sequence with each other.
- The current flowing all the components is similar in series combination.
- Its equation is R=R1+R2+R3+—Rn
- the total resistance is the sum of all resistance in circuitry.
- If there is any fault that occurs in one component of the circuit the flow of current or operation of the complete circuit will disturb.
- The troubleshooting of this configuration is difficult.
- The voltage is equal to the summation of all volts in circuitry
- The value of voltage is different at all components present in the circuit.
- There is one path exits in the series circuit for the flow of current.
- The equivalent resistance of the series circuit is larger than the largest value of resistance connected.
- Series circuits used in batteries.
- It used for lighting purposes.
Parallel Circuit
- In parallel combination, the elements of circuits are linked in such a way that their heads at connecting at one point and tail at other points.
- The value of the current flowing through every component is different.
- Rt=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3—-1/Rn
- Parallel resistance used to define the circulatory system
- Series resistance is used for blood vessel configuration
- The voltage across every component connected in the parallel configuration is the same..
- The value of equivalent resistance for the parallel combination is less than the resistance connected in the circuit
- If there is any fault that occurs in one component of the circuit the flow of current or operation of the complete circuit will disturb.
- The troubleshooting of this configuration is difficult.
Series and Parallel Circuits
Series Circuit
- The series circuit comes with components connected in a series combination.
- Components are connected in line, and the same current flows in each connected component.
- It has different voltages across components and provides a single path for current flow.
Parallel Circuit
- The parallel circuit has connected components in parallel configuration with similar points.
- Its components are connected in such a way that they have different current values for each component.
- There is the same voltage across each component. It has more than one path.
FAQs
What are series circuits?
- The series circuit has connected components in sequence, and each has the same current flowing with different voltage.
What are parallel circuits?
- • A parallel circuit has components in parallel and connected at a common point. Voltage for each component is the same, and current is different.
What is the total resistance formula for the series circuit?
- The formula for total resistance in series is R = R1 + R2 …..+ Rn.
What is the total current in the parallel circuit?
- • The net current for a parallel circuit is I = I₁ + I₂ + … + Iₙ.
What is the rule for series and parallel?
- In a series circuit, the current of each component is the same with different voltages for the components. For a parallel circuit, voltage is the same for each component, and current is different according to their resistance values.
Why is series better than parallel?
- Series-connected circuits are easy to make and need fewer wires. The use of fewer wires and switches makes it a low-cost option.
Current in Series Circuit
- Current for each connected component in series is the same and equal to the power connected. It has a single path for each component, and the total current for the series circuit is as follows.
IT = I1 += I2 = I3 + … In
Voltage in a Series Circuit
- The voltage losses for each component in a series circuit are the same as the voltage source. The voltage in a series circuit is divided over components based on resistance. So voltage losses about each component are different and based on the resistance of the components.
VT = V1 + V2 + V Vn
… Vn
Resistance in Series Circuit:
- If resistors are connected in series, total resistance is added, and the sum is equal to the resistance of each resistor.
Req = R1 + R2 + R Rn
Capacitor in a Series Circuit:
- • A capacitor connected in series has total capacitance in less value since voltage about each capacitor reduces and charge stored due to voltage reduction. Net capacitance in a series circuit is less compared to individual capacitance.
1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3 + … + 1/Cn
Inductor is a Series Circuit:
- The net inductance of two or more inductors in a series circuit is the sum of individual inductance. The net inductance increases and is larger than the individual inductance in a series circuit.
Leq = L1 + L2 + L3 + … + Ln
That is a detailed post about the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit. I tried my level best to make simple for you if you have any query ask in comments. See you in next post.





