In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Diffraction and Interference. The basic difference among diffraction and interference is that diffraction occurs when secondary wavelets generated by the numerous portion of wavefront superimpose with each other. Interference The basic difference between diffraction and interference is that diffraction occurs when secondary wavelets generated by the numerous portions of wavefront superimpose with each other. Interference occurs when light waves coming from two coherent light sources superimpose with each other.
In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Diffraction and Interference. The basic difference among diffraction and interference is that diffraction occurs when secondary wavelets generated by the numerous portion of wavefront superimpose with each other. Interference The basic difference between diffraction and interference is that diffraction occurs when secondary wavelets generated by the numerous portions of wavefront superimpose with each other. Interference occurs when light waves coming from two coherent light sources superimpose with each other.
The other difference is that the intensity of bright fringes is the same for interference but not for diffraction. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both interference and diffraction and find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between Diffraction and Interference.
Difference Between Diffraction and Interference
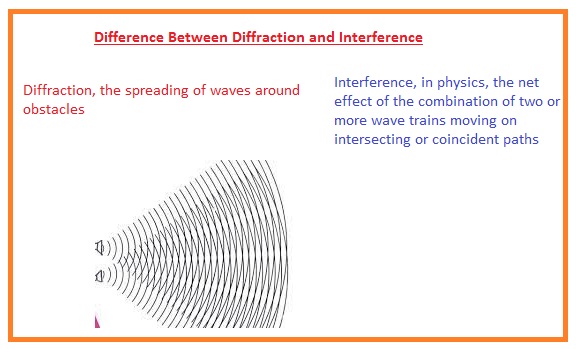
Diffraction
- It occurs when moving waves get involved to the hindrance existing in the path of the wave.
- It also defines that wave bends when moving across the body. This phenomenon first time was first discussed in in 1660
- This process occurs normally when the wave coming from such a source that is coherent has a single wavelength.
- It also works for such systems where the medium has a variable refractive index.
- The DVD shoes diiffent colors it is due to diffraction.
- Mirage is also an example of diffraction.
- It used in the hologram process
- This phenomenon occurs when the secondary wavelets superimpose with each other.
- For this process, the intensity of fringes is not similar for all fringes.
- The direction of propagating waves changes when diffraction occurs.
- The width of the fringes is not equal.
- The space between the fringes is not uniform.
- To observe this phenomenon there is a need for obstacles or slit.
- For this process, there is less contrast between maxima and minima.
Interference
- It is the process in which two different waves mix in such a way that gives a wave of another type having some greater or less amplitude to the previous one.
- If waves are produced from a similar medium then constructive interference occurs.
- It is used in different categories of waves like sounds, light radio. Etc.
- The resultant image form from the interface is known as an interferogram.
- For this process, there is no need for an obstacle.
- For this process, the direction propagating wave does not vary when the superimposition occurs.
- The contrast between maxima and minima is good.
- This process occurs when the light waves coming out from two different coherent light sources superimpose.
- Fringe intensity is similar for all fringes.
- The width of the fringes is equal.
- The space between fringes is uniform
- According to this interference is divided into 2 types.
- Constructive Interference
- Destructive Interference
Constructive Interference
- Constructive interference occurs when 2 waves having a similar amplitude and phase superimpose with each other and their resultant wave amplitude is larger than the superimposing waves.
- In simple words, the resultant wave will have an amplitude two times the amplitude of superimposing waves.
Destructive Interference
- Destructive Interference occurs when the 2 waves of having similar amplitude and opposite phase than their resultant wave have less amplitude than the other 2 superimposing waves.
- When the 2 waves meet they will sum up and cancel each other due to the opposite phase angle.
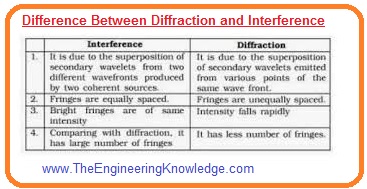
Diffraction vs Interference
| Diffraction | Interference |
|---|---|
| Ir caused due to the superposition of secondary wavelets. | interaction light waves from two sources causes it |
| Fringe intensity is not have same for all fringes | It has the same for all fringes |
| nonuniform fringe space it has | uniform fringe spacing |
| it needed obstacle | not needed |
| the direction of the moving wave changed after diffraction | Direction not changes |
| contrast between maxima and minima, not good | contrast between maxima and minima is good |
That is a detailed post about the difference between diffraction and interference. If you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.