 Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Dielectric & Insulator. The basic difference between dielectric and insulator material is that dielectric has the ability to store charge while insulator creates a hindrance for movement of current.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Dielectric & Insulator. The basic difference between dielectric and insulator material is that dielectric has the ability to store charge while insulator creates a hindrance for movement of current.
In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both dielectric and insulator with the detailed compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between Dielectric & Insulator.
Difference Between Dielectric & Insulator
Dielectric
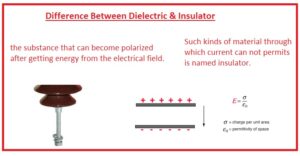
- the substance that can become polarized after getting energy from the electrical field.
- When field given to the dielectric material electrons do not cause current like metals but change their position at a certain point to make poles
- Positive charges move to the negative end of field and negative charges to the positive end of the field
- The bond that exists in the dielectric material is weaker than the insulator.
- The dielectric constant of dielectric material is large.
- The dielectric substance has the ability to store charge.
- Examples of dielectric materials are Dry air, vacuum, distilled water.
- Its common applications are Capacitor, power cable, etc.
Insulator
- Such kinds of material through which current can not permits is named insulator.
- These ingredients do not show conduction since that does not have free electrons like conductors.
- Their large charge of resistance halts to the current movement.
- An instance of this material is all kinds of nonmetals.
- There is no being of the best insulator constituents since transportable charges that occur in insulators can cause a current.
- If an electrical field in standings of large volts is given to insulating it will show a conductor-like feature.
- these materials are used with a different electrical device that offers porcelain form joining to other conductors.
- These materials also used as insulation substantial.
- Transmission line towers are also shaped with insulators
- Pin type insulator used in transmission line has pin-like outline at top.
- They have a hovel on the higher part and the conductor can transfer from it.
- they employed for thirty-three kilovolts lines
- Insulator employed in large voltage lines formed with porcelain glass.
Tha is a detailed post about the difference between insulator and dielectric if you have any query ask in comments. See you in the next post. have a good day.







