 Hello guys, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor. The 8085 and 8086 are the 2 types of microprocessors created by the famous computer accessories manufacturer Intel. The basic difference among them is that 8085 is an eight-bit microprocessor means can transmit eight bit of data at a time. While 8086 is the sixteen-bit microprocessor that can transmit data of sixteen-bit.
Hello guys, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor. The 8085 and 8086 are the 2 types of microprocessors created by the famous computer accessories manufacturer Intel. The basic difference among them is that 8085 is an eight-bit microprocessor means can transmit eight bit of data at a time. While 8086 is the sixteen-bit microprocessor that can transmit data of sixteen-bit.
In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both 8086 ad 8085 with the detailed and find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor.
Difference Between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor
8085
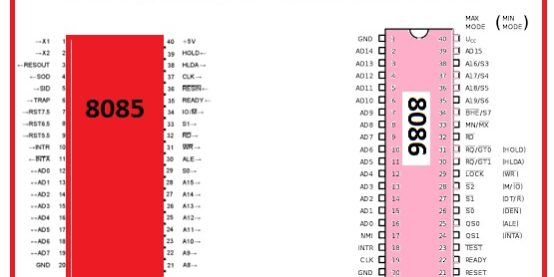
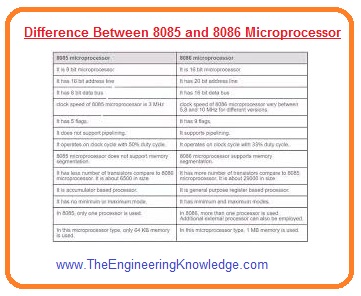
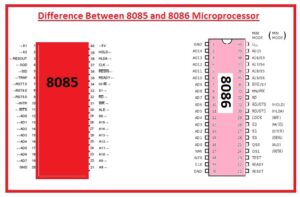
It is an eight-bit controller created by Intel and first time was used in 1976
- Its is small size circuitry usage and simple to use comes with two instructions.
- In its name, the 5 indicates the five volts used by this device.
- It can be operated on plus five minus five and twelve five volts.
- It used in the operating system
- It does not have an instruction queue.
- It has five addressing modes.
- The clock speed for 8085 is 3.072.
- There is no need of exterior hardware for this module.
- It does not follow the multiply and division instruction.
- Comes with the forty pinouts that are configured in dual inline packaging.
- It uses a multiplex address bus for pin configuration.
- Its incorporated with the EPROM, sixteen inputs, and outputs ram of the fifty bytes.
- The dimensions of the data bus used for 8085 is eight-bit.
- The data bus used for 8085 has a size of sixteen bits.
- The supportable memory capacity is sixty-four kilobyte.
- The operating frequency of 8085 is three megahertz.
- Its price is less.
- It supports decimal and integers.
8086
- This Microprocessor is sixteen bits.
- It is sixteen bits process that is created by the intel in 1976.
- It comes in x86 architecture.
- It has twenty address pinouts and sixteen data and can support data up to one megabyte.
- There are 2 modes of working it has max and min.
- Comes ith sixteen-bit LAU sixteen-bit registers and inner data buses.
- There are three main types it has according to ot frequency operation like 5MH, 8MH, and ten megahertz.
- There are two piping uses first is fetch and the second is executed.
- There is two fifty-six vectored it has
- Twenty-nine thousand transistors it has
- The dimensions of the data bus used for 8086 is sixteen bits.
- The size of the address bus for this module is twenty-bit.
- It follows the multiply and division instructions.
- Its price is larger than the 8085.
- It comprises an instruction queue.
- The clock speed for 8086 is ten megahertz.
- Its supportable memory range is one Megabyte.
- Its operating frequency is five Megahertz.
- It consists of twenty-nine thousand transistors.
- It consists of two operating modes minimum and maximum mode.
- This module is supportable with the pipeline.
- It needs a large number of exterior hardware.
- It supports memory segmentation.
- It supports decimal, integer, and ASCII arithmetic.
That all about difference between 8085 and 8086 if you have any queries ask in comments. I will try my level best to resolve your problems. Have good day.