Selection of an accurate wire size is important for a safe solar power system and its connected components, like the inverter. The use of an improper inverter wire size results in overheating, and the inverter stopping operation also causes fire. In this tutorial, we will cover details on how to select the wire size for a 2000-watt inverter. since accurate wire size is important for safe circuit operation. So let’s get started.
Cable Size Importance
Proper cable size is important for off-grid systems since they provide different features.
Low Resistance
- A larger cable causes low resistance, with high efficiency and fewer energy losses.
Overheating control
- If accurate cable sizes are used in the circuit to avoid high heat production and protect wires from damage and circuit devices.
stable voltage
- Faultless cable size reduces voltage losses that are important for stable power transmission from the inverter to devices.
Cable and Fuse Sizes for 12V Inverters
| Inverter Capacity | Fuse Rating | Cable Size 1m Run | Cable Size 2m Run |
| 1000W | 100 Amp | 16 mm² (6 AWG) | 35 mm² (2 AWG) |
| 2000W | 200 Amp | 35 mm² (2 AWG) | 50 mm² (1 AWG) |
| 3000W | 300 Amp | 70 mm² (2/0 AWG) | 90 mm² (3/0 AWG) |
2000-watt inverter wire size units
- American wire gauge unit used for finding wire thickness in the USA. A smaller AWG number shows the wire is high thickness, and a larger AWG means a thinner wire. The normally used wire size chart for AWG is from 0 to 40 AWG.
- applications like 2000-watt inverters, where high current requires small AWG wires to be used. AWG is a commonly used wire gauge in the USA, preferred for electronic devices.
- The inverter gets power from a battery that is DC voltage, with the current value based on efficiency, battery volts, and rated power. For smooth operation, according to NEC details, the wire size is selected according to 125% of the calculated current.
Cable Ampacity = Inverter Power ÷ Inverter Efficiency ÷ Battery Voltage × 1.25
Inverter AC wire size
- An inverter converts DC power into AC in the range of 110 V or 220 V according to the area and grid demand. The AC output side has low current compared to the DC side since it has high voltage.
- for calculating AC wire size for the inverter AC output voltage is used
Inverter wire ampacity = inverter power ÷ efficiency ÷ AC output voltage × 1.25
What size wire for 2000w inverter
Suppose we have a 2000-watt inverter with 90 percent efficiency that uses 2220 watts of power. For the DC side, a 2000-watt inverter is configured to a 12V battery circuit with 4/0 AWG wire for a short distance that manages 230 amps. For longer distances, thick cables are used for voltage loss compensation.
For the DC side of a 2000-watt inverter with an output of 110 volts, 10 AWG wire size is best for handling 25 amp current.
For output voltage, 220V 12 AWG wire is used to handle 13 amps of current from the inverter to a 10-foot load.
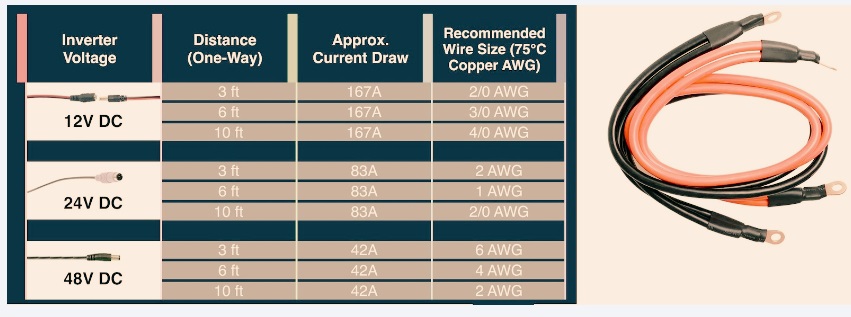
At 12V, a 2000W inverter draws about 167 amps, requiring very thick wire:
Use 2/0 AWG for runs up to 3 feet
Use 4/0 AWG for runs up to 10 feet
At 24V, the current is halved to 84 amps:
Use 4 AWG to 1/0 AWG, depending on distance
At 48V, the current drops to 42 amps, so:
Use 8 AWG to 4 AWG for most short runs
In the diagram, copper wire size for different voltages and one way wire lengths having voltage losses less than 3 percent
2000 watt inverter wire size selection factor
The main factors for selecting wire size for a 2000-watt inverter are as follows.
Voltage level:
- Low-voltage circuits cause high current, so thick wire is used. While circuits where high current, about 24V to 48V, were generated, low current was used, so a thin wire was used. High current uses thick wires for handling the load to avoid overheating.
Wire length:
- Wire length is based on resistance, so longer wires come with higher resistance, which causes high voltages. Voltage losses affect power transmission and also reduce the energy storage features of the inverter for effective voltage that also affects working. Longer distance cable uses thick wires to minimize resistance and voltage losses.
Current
- The current carried in a wire is called the current strength. High current uses thick wire for the transmission of current without overheating or any other effects. for selecting the 2000-watt inverter wire size for low voltages, a thick wire is used
Power
- 2000-watt inverter uses high current normally in a 12V system, where the amperage is higher than in 24V or 48V systems.
- For high current flow, a thick wire is used to avoid overheating and power losses.
AWG Standards
- These standards define wire selection according to diameter and current-carrying features. Low AWG means a thick wire that manages high amperage. The use of accurate AWG is important for system efficiency and avoiding heat losses.
Distance
- Longer wire length causes high resistance and voltage losses. So for longer cables, use high-gauge wire for voltage stability and to avoid losses. Short cables are preferred, but where longer runs are not needed, use oversized wire for accurate operation.
2000-watt inverter Recommended wire size
- American Wire Gauge wire system is employed for measuring wire thickness. Voltage and cable length define the recommended wire size for a 2000-watt inverter. for 12v circuit, high power inverter causes a high current range of 165 to 170 amps. so thick wire is used
| Cable Length (Feet) | 2000 watt inverter wire size (AWG) recommended |
| 1-10 Feet | 2/0 AWG |
| 10-20 Feet | 3/0 AWG |
| 20-30 Feet | 4/0 AWG |
What Will a 2000-Watt Inverter operate?
2000watt inverter commonly used for houses and off grid devices. thier operteddevices are
| Appliance | Power Consumption (W) | Surge Power |
| Refrigerator | 150–600 W | Up to 1200 W surge |
| Microwave | 700–1000 W | |
| Coffee maker | 800–1500 W | |
| Toaster | 800–1500 W | |
| TV | 100 W | |
| Laptop | 100 W | |
| LED lights | 10 W per bulb | |
| Fan | 100–500 W | |
| Space heater | 1000–1500 W | |
| Power tools (drill, saw) | 600–1200 W | |
| CPAP machine | 30–60 W | |
| Blender | 300–700 W | |
| Small washing machine | 500–1000 W | |
| Electric cooktop (1 burner) | 1000–1500 W |
Now, let’s look at example combinations:
| Appliance | Power Consumption (W) | Features |
Off-Grid Morning Routine 1740 | ||
| Coffee maker | 1000 W | |
| Toaster | 700 W | |
| Phone charger | 10 W | |
| LED light (1 bulb) | 10 W | |
Home Office + Essentials (Total ~860 W) | ||
| Refrigerator (running) | 150 W | |
| Laptop | 100 W | |
| TV | 100 W | |
| CPAP machine | 60 W | |
| Fan | 150 W | |
| 5 LED bulbs | 50 W | 10 W per bulb |
| Phone charger | 10 W |
Cable Types for a 2000W Inverter
The 2000-watt inverter is used for converting DC power from the battery into AC power to operate devices. different cable types and their connections used for 2000-watt inverter
Battery to Inverter wire
- This wire is used for managing high-current DC coming from the battery to the inverter input connection. The cable used is based on the current flowing in the wire, temperature resistance, flexible design, and distance. Commonly used cables are as
Welding Cable
- It is a flexible design easily managed in an enclosed battery structure. It comes with rubber insulation for heat, oil, and moisture resistance.
- It is preferred for midrange distances for off-grid, RV, and solar design for flexible configuration.
Marine Battery Cable
- This is tinned copper used for corrosion resistance in different conditions and comes with PVC insulation.
- It is preferred for vans and boats, where weather and vibration resistance are needed.
Inverter-to-loads connection cable
Standard 120V or 240V AC wiring used, with cable connected according to environmental conditions, installation, and distance, needing flexibility and conduit protection. Commonly used wires for these connections are as
THHN
- It is employed in conduit in indoor wiring circuits, and the stranded type is employed in inverter structures since it is more flexible and easily configured in an enclosed conduit than solid wire.
- It also manages heat and oil resistance and is low cost.
NM-B (Romex)
- It is part of the dry area, also walls and ceilings, and is not preferred for outdoor applications.
- It can easily be connected to a fixed indoor circuit where conduit is not used.
UF-B Cable
- It is direct burial rated wire and has resistance to moisture and sunlight. It is part of wiring outlets and buried feeder connections.
SOOW Cable
- It is a durable design, and the rubber jackets employed with it have resistance to moisture, abrasion, and sunlight.
- It is preferred for managing mobile AC loads like RV projects and cabin setups.
Solar Wiring Connection
- The inverter in the solar system uses distinct DC wiring for solar input.
Solar panel connection with charge controller
- It is a DC cable and part of outdoor rating applications and connects between the solar panel and charge controller.
- It is PV wire, moisture-resistant, and preferred for long outdoor runs.
Charge Controller connection to Battery
In this cable type, the same cable is used for welding cable and marine battery cables from the battery to the inverter. The gauge selected for the wire is based on the current drawn and the length required.
Inverter cable size chart
This chart is used for providing details for DC and AC sides according to the inverter size. here based on the wire length for different connections wire chart is made
DC Side
| Cable Length | 12V 1200W | 12V 2000W | 24V 3000W |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1/0 AWG | 3/0 AWG | 2/0 AWG |
| 10 | 1/0 AWG | 4/0 AWG | 2/0 AWG |
| 15 | 1/0 AWG / 4/0 AWG | 4/0 AWG | 2/0 AWG |
AC Side
| 110 Volt Output | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cable Length (ft, round-trip) | 1200W | 2000W | 3000W |
| 5 | 12 AWG | 10 AWG | 8 AWG |
| 10 | 12 AWG | 10 AWG | 8 AWG |
| 15 | 10 AWG | 8 AWG | 6 AWG |
| 220 Volt Output | |||
| Cable Length (ft, round-trip) | 1200W | 2000W | 3000W |
| 5 | 16 AWG | 14 AWG | 12 AWG |
| 10 | 14 AWG | 12 AWG | 12 AWG |
| 15 | 12 AWG | 10 AWG | 10 AWG |
How to Calculate the Wire Size for a 2000W Inverter
For measuring the accurate wire size for a 2000-watt inverter, first of all, measure the current flow and cable length required. Choosing an accurate wire gauge reduces overheating, power losses, and voltage losses, and the inverter works effectively.
Follow these steps for measuring wire size.
- First of all, measure the current flow. Use this formula for measuring current.
- I=power/volt
- For a 12-volt circuit, current flow will be in a 2000-watt inverter.
- 2000W/12V = 167A
- In the 24V circuit, the current will be
- 2000W/24V = 83A
- For a 48-volt system, current is
- 2000w/48V = 42A
Now select the wire gauge according to the distance.
- Wire size is not set according to the current but also based on the cable run. A longer wire causes high resistance, which reduces voltage and affects inverter efficiency.
- For handling these features, in longer runs, thick wire is used for handling stable voltage and minimizing losses.
Recommended Wire Gauge & Battery Cable for the inverter
The use of an accurate wire gauge and battery cable is important for safe and effective power for a 2000-watt inverter system. Different factors define wire sizes, such as
Wiring distance
- A longer cable causes high resistance and voltage losses that need thick wire for efficiency maintenance.
- If the circuit is a shorter circuit with a 12V system, 1/0 AWG wire is used for managing current safely. In longer distances, 2/0 AWG is used to minimize voltage losses.
- In high voltage, a small wire gauge is used that reduces the current drawn.
Wire material
The material of the wire is important for selecting efficiency and conductivity features.
- Copper cables have good conductivity and less resistance and are preferred for inverters but are high-cost. Aluminum wire is low-cost, but thick gauges are used to provide the required copper-level conductivity.
Fuse and Circuit Breaker for a 2000W Inverter
For safe and accurate working, a 2000-watt inverter requires an accurate protection circuit. Fuses and circuit breakers are important for managing overcurrent or short circuits.
Fuse size
- Fuse used as a safety component for protecting wiring and inverter from damage from current. If the current is higher than safe values, the fuse blows and cuts off power to avoid overheating or fire hazards.
- 2000-watt inverter fuse sizes according to system voltage are as
12V System: 200A fuse
- 24V System: 100A fuse
- 48V System: 50A fuse
High-Efficiency 2000W Inverter importance
Selection of a high-efficiency inverter is important for the system’s working and safe operation. An effective inverter reduces power losses, minimizes battery load, and is preferred for accurate cable size.
For selecting a 2000-watt inverter, follow these points.
Efficiency:
- An efficiency higher than 90 percent provides low losses and proper use of the battery.
Sine Wave Output:
- It provides clean power in a sine wave that operates different electronic devices.
Cooling System:
- For managing overheating and increasing the working life of the inverter and operating devices, a cooling system is employed.
Safety Protections:
- Some safety measures and protection devices are installed for overvoltage, short circuit, overload, leakage, and reverse polarity for system protection
FAQs
What gauge wire is used for a 2000W inverter?
- wire gauge based on cable length and cirucit voltage
- 12V system:1/0 AWG for short runs and 2/0 AWG installed for longer runs.
- 24V systems: 2 AWG
- 48V systems: 4 AWG or larger
How to check if the wiring is safe to operate?
for safe and effective wiring operations.
- Check the wire temperature if cable is high temperature, it means you used overloadded or undersizedcable.
- Voltage losses are also important; if higher than 3 percent means the cable is thin or a longer size