A spark plug is a small device that is part of an internal combustion engine and works as a main component of a vehicle engine. It comes with an insulated electrode in the middle, an insulated wire, and an ignition coil connected to the ground terminal.
All parts of the spark plugs are connected to create a spark gap. The main operation of a spark plug is to cause a lightning bolt in the combustion chamber of the engine. High voltage is produced to produce a spark. In this post, we will cover detailed features of spark plugs and related factors. So let’s get started. How do spark plugs work?
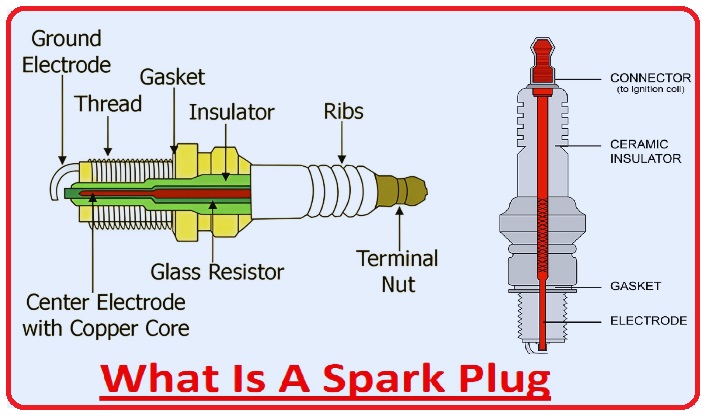
What Is A Spark Plug?
- A spark plug is the main component of an internal combustion engine, where it causes ignition of compressed air-fuel gasoline through a spark. Its basic function is to convert gasoline, which is an energy source, into vehicle movement.
- A ceramic insulator separates the metallic component of the spark plug from the central electrode to avoid an electric hazard.
- The central electrode makes a connection with the output terminal of the ignition coil through an insulated wire. connection with the cylinder head of the engine, spark plug grounding on the spark plug.
- Spark plugs come in two types: regular replacement and working performance.
- spark gaps made between the inner end of the central electrode when moving through the porcelain insulator and moving into the combustion chamber.
- side, or ground, electrodes connected with the inner end of the threaded shell.
What is the Spark Plug Gap?
- For accurate engine working, the selection of an accurate heat range and plug. A gap for an accurate distance is also important. For getting details, read the vehicle manual for getting details of the gap, and we can also use tools for the plug gap.
How do spark plugs work?
- The basic function of a spark plug is to generate a spark for the ignition of a combustible mixture. The plug connected with high voltage is produced through a magneto.
- When current moves through the coil, voltage is produced between the side and central electrodes.
- At the initial phase, no current exists since the fuel and air between them work as an insulator. The voltage increment it affects the gas configuration between the electrodes.
- When the voltage is higher than the dielectric strength of gases, they get ionized. These ionized gases work as a conductor, and current flows in the gap.
- A spark plug needs a voltage of 12000 to 25000 volts to cause fire. It provides high current at the time of discharging, causes high temperature, and has a longer spark time.
- When the electronic current increases in the gap, increasing spark channel temperature up to 60,000 K.
- High heat in the spark channel causes the ionized gases to expand fast and causes an explosion.
- Gases make a reaction through heat and pressure, and at the end of the spark, there is a small fireball in the spark gap when gases burn.
- The composition mixture between electrodes defines the fireball size and combustion chamber turbulence during spark.
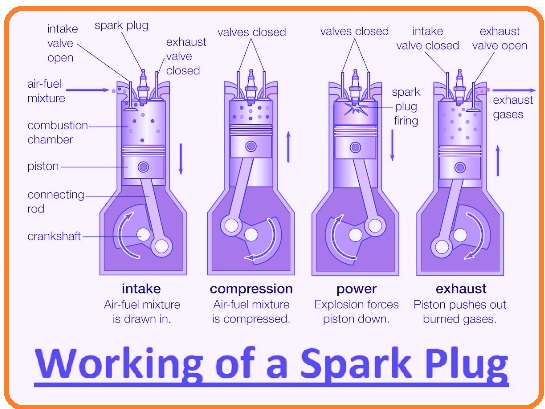
Working of a Spark Plug
- A spark plug performs two functions. The first one is ignition of the air mixture; through electrical energy transmission in components, it causes mixture ignition in the combustion chamber.
- spark plugs normally heat and do not produce. The temperature of the firing plug end remains low to avoid early ignition but must be high to avoid fouling.
- Spark plugs also work like heat exchangers since they release extra thermal energy from the combustion chamber. That heat moves to the engine cooling system.
- Another operation of spark plugs is Saab direct ignition. This module measures cylinder ionization in the absence of firing.
- This iconic current causes the replacement of the cam phase sensor, misfire measurement, and knock sensor.
- Spark plugs also perform air mixture in furnaces, where spark plugs operate as flame igniters.
Construction of a Spark Plug
There are different parts of the spark plug structure that each perform certain operations. Each is explained here.
Ribs
- The main function of insulator ribs is to protect from spark flashover and ensure a strong grip of the rubber spark plug to the plug body.
Insulator
- Aluminum oxide ceramic used for making an insulator structure. For making this component, a high-pressure, dry molding system is employed.
- Then place the mold in a high temperature, more than the steel melting point. In the results, we get high dielectric strength materials that have high thermal conductivity and easily manage vibrations and shock.
- External surface ribbed for strong grip to the spark plug boot and also to protect from spark flashover (crossfire)
Hex
- A hexagon is a connection point for a socket wrench assembly. The hex size used has a uniform value that is set according to the spark plug thread size.
Shell
- for making shell material used following accurate tolerances with the help of the cold extrusion process. Steel billet-type plugs provide shell assembly.
Plating
- The shell has a plated structure, which makes the plug durable and provides resistance from corrosion.
- Steel sheet made for accurate tolerances through the cold extrusion process, and machined steel billet is also employed.
- A hexagon machined over the shell helps to easily connect the socket wrench for connection and disconnection of the plug.
Gasket
- Some plugs employ gaskets, and some do not. A gasket is a folded knot. A gasket is a folded steel structure that helps to provide sealing. Gasketless spark plugs employ a tapered seat shell that provides sealing through close tolerance configured on the spark plug.
Threads
- spark plug threads rolled into shape. That is according to the features of SAE over the International Standards Association.
Ground electrode
- Ground electrodes have different designs and are made with nickel alloy steel. The ground electrode must have resistance for chemicals as well as spark erosion and indifferent temperature conditions.
Center electrode
- center electrode made with use of special alloy that provides resistance from spark and chemical corrosion. combustion chamber temperature change, so the center electrode has features to handle those conditions
Spark park electrode gap
- The space between the ground electrode and the center electrode is known as the gap. Center electrodes are made with a special alloy that provides resistance for spark erosion and chemical corrosion.
Insulator nose
- Different insulator shapes and exist, but the best insulator has features that allow it to shed carbon, oil, and fuel deposition slowly. With high engine speeds, the insulator noise is cooled, so temperature and corrosion are reduced.
Spark Plug different types
There are different types of spark plugs; each performs certain operations.
Copper Spark Plug
- This spark plug uses a copper core center electrode having a nickel alloy coating. It uses high voltage for producing sparks since the center electrode has a large diameter.
- Copper spark plugs need more frequent repairing and replacement than other types, since nickel alloy is affected more quickly due to its soft structure.
- They are so used in some vehicles
Iridium Spark Plug
- Iridium is a hard and durable material, so this spark works longer. Its structure uses low voltage for spark production. so it’s costly and used in different vehicles since it reduces car breakdowns.
Silver Spark Plug
- Silver is a less durable material, so it does not work like iridium or platinum spark plugs. but it’s a good thermal feature preferred in older European performance cars and motorcycles.
Single Platinum Spark Plug
- This plug is like the copper type, with the difference that the center electrode has a platinum disc. That disc connected with the tip compared to the nickel alloy.
- Single platinum plugs are high-cost but work longer compared to nickel alloy. It causes high heat and prevents carbon buildup. This plug is best for vehicles with coil-on-plug ignition systems.
Double Platinum
- This plug comes with a platinum coating for the center and ground electrodes, which makes them effective and lasts longer. It is best for wasted spark ignition, where high wear occurs on electrodes.
- Two spark plugs ignite in a wasted spark ignition system. One spark plug ignites in the compressor stroke cylinder and another in the exhaust stroke cylinder.
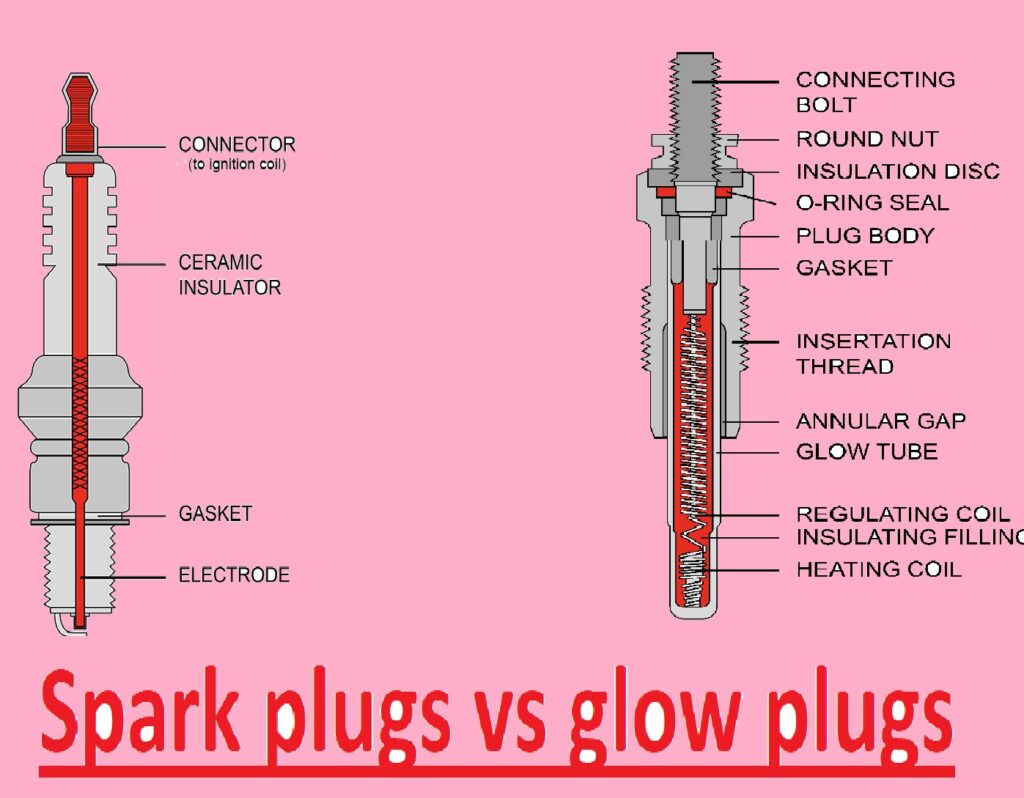
Spark plugs vs glow plugs
Spark plugs
- The spark plug is the main part of the ignition system since it causes the starting of a gasoline car. It is an electrical device that exists in the cylinder head of the engine and gets a high voltage charge through the ignition coil.
- Charge moves through the spark plug towards the electrodes, then crosses the gap when the spark produces combustion
spark plug design
- Spark plugs come with a central conductor, covered with an insulator, and a shell. The insulator is a ceramic material and causes a spark at the electrode tip.
- The spark plug is connected to the combustion chamber wall, so its fitting should be strong in the chamber to provide sealing from temperature and pressure for longer use.
Glow plugs
- A normally warm diesel engine started without a glow plug due to high intake air temperature and low diesel ignition temperature.
- But it does not provide accurate ignition of injected fuel at different temperatures, which causes high exhaust emissions.
- To solve that error, a glow plug is used. That is, an electrical heating module exists in the diesel engine cylinder for starting in different weather conditions.
- A glow plug is a thin component that has a heating element. Heating element materials are to provide oxidation resistance and maintain high temperatures.
Working
- Glow plugs only perform ignition and operate through electrifying a heating component that heats and releases light.
- Intake air is compressed before the injector sprays direct fuel over the heated tip of the plug when fuel is injected.
- injected fuel mixtures into compressed air, evaporates, and provides combustion, also engine cold conditions
What heat range spark plug is used?
- Spark plug heat range is an important factor to consider during the vehicle manufacturing process and also helps to make modifications in vehicle design. So, ranges are important for vehicle range.
- It is thought that spark plugs cause heat; that is not correct. The main function of the plug is to dissipate heat from the tip; in that condition, the insulator mass is important. The heat range working is defined through the insulator length.
- A short insulator mass has a cooler heat range compared to a larger one. In accurate working, the tip of the plug is cool for avoiding pre-ignition but has a temperature value for maintaining self-cleaning.
- For selecting an accurate heat range and plug, get an understanding of car fuel burning. That factor is constant, so follow the manual of manufacturer for the selection of spark plugs.
Factors Affecting Spark Plugs’ Working
different factors affect the working performance of a spark plug that are
Engine health
- Engine working conditions affect the working life of a spark plug. Some factors, like oil seepage into the combustion chamber and a bad air-fuel ratio affecting the engine, also affect the working of the spark plug.
- We should do maintenance of the engine for accurate working of the spark plug to operate longer.
Driving routine
- Your driving also affects the spark plug. In short-distance driving, where the engine does not get optimal temperature, high fuel consumption causes carbon deposits. Those carbon deposits cause rough idling, misfires, and low fuel efficiency.
- If a vehicle moves over a longer distance, combustion cycles remain effective and increase the working life of spark plugs.
Fuel Additives:
- Fuel used also affects the spark plug’s working condition. UK petrol standards follow high rules, which use low cleaning additives to avoid carbon deposits.
- High-performance vehicles use high-octane fuels that provide maintenance for a cleaner combustion chamber and manage spark plug operation. It reduces deposits with quality fuel applications, and it increases the working life of different parts.
Heat Range
- Working temperature is the main factor for spark plug functions; they do not follow high or very low temperature conditions. A plug that operates below the required temperature causes carbon deposition, and high temperature causes pre-ignition that damages different parts of the engine.
Signs of Failing Spark Plugs
There are different signs of failing spark plugs; some of them are as follows.
Difficult Starting
- If you’re facing a difficult starting process of a vehicle, normally, vehicle starting becomes difficult in cold conditions or with bad or faulty spark plugs. This sign becomes worse slowly and also degrades the engine.
Bad Performance
- Faulty spark plugs also affect vehicle driving. It affects acceleration and causes power losses as well as rough idling.
- Fuel use also increases since the engine causes incomplete combustion cycles. These faults affect the operation of the catalytic converter and transform basic faults into costly repairs.
Check Engine Light on
- Advanced vehicles come with an engine management system that regularly maintains combustion efficiency. When spark plugs are not igniting the air-fuel mixture, the check engine warning comes on; that is a sign of faults.