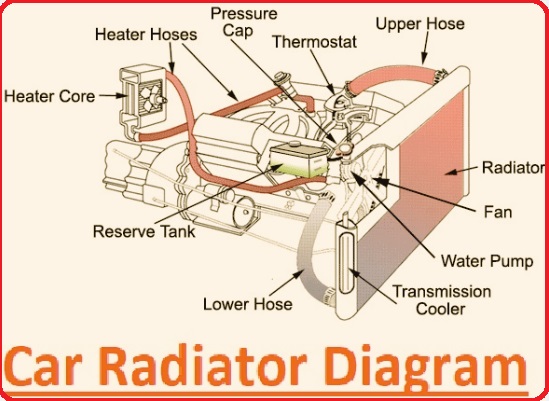
The radiator is the main part of the vehicle engine cooling system. Its main feature is dispersing the antifreeze mixture and water through fins that help engine heat of different engine parts and enter the cooling air. The spur line provides warm coolant to the heater core for generating hot air, and the water pump delivers coolant that flows in the engine. The fan clutch helps to get air into the radiator and reduce the temperature of the water mixture and antifreeze.
In this post we will cover detailed features of the radiator in a car, so let’s get started with. What is a radiator in a car?
What is car Radiator?
- A radiator is a heat exchanger used to cool internal combustion engines, such as those found in vehicles, motorcycles, and railway locomotives.
- Its main function is to transmit heat from high-temperature coolant fluid through air flow in the radiator. In this method, the fluid becomes cool before being recirculated through the engine, thereby maintaining the engine’s temperature.
- The internal combustion engine becomes cooled through the circulation of fluid engine coolant through the engine block and cylinder, where temperature rises, and after that through the radiator heat is released, and then moves towards the engine.
- Normally, water is used as a coolant, and sometimes oil is also employed. The water pump used for engine coolant circulation and the axial fan cause air to pass through the radiator.
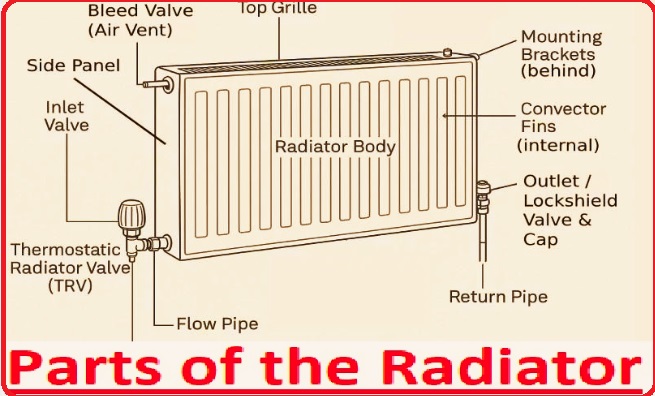
Parts of the Radiator
There are different parts of a car radiator that perform different operations.
Core
- It is the main part of the radiator that exchanges heat through using small tubes and cooling fins. The design of the core with a metallic structure causes high-speed heat transfer from hot coolant to cool external air.
Tank
- • The radiator comes with upper and lower tanks. that causes fluid distribution of fluid in the core through small tubes. It also adds coolant fluid parts.
Fan
- • The radiator comes with a cooling fan configured in its design. that manages heat in the radiator core, which causes cooling capacity for high airflow
Overflow Tank
- This tank gets extra coolant fluids when heat increases and it expands, helping us to maintain coolant level.
Mounts
- It is a strong design; durable radiator mounts are parts that strongly connect parts and manage vibrations that can cause cracks.
Radiator Construction
- The radiator of the vehicle is made with a plastic header tank that is also made with metal, connected with a core through a narrow path to provide a high surface area.
- The core is made with stacked metallic sheet layers that make channels and are soldered to each other.
- The radiator is also made with brass and copper cores and soldered with a brass header.
- Some new types of radiator core are made with aluminum, and they is low-cost since it have a plastic header with gaskets.
- That design can be damaged, and we can repair it easily
- Honeycomb radiator design is also used. round tubes configured into hexagons at end points, and connected with soldering.
- Vintage cars have radiator core coiled tubes, but low effectiveness.
Read more guides What Do Struts Do On A Car
Radiators Working
- During the working of the radiator, the radiator hose makes a connection of the radiator with engine parts that causes the circulation of coolant in the tank.
- Through the inlet tank, hot coolant moves from the engine to the radiator, which reduces the radiator temperature before it reaches back to the engine.
- • The core reduces incoming coolant temperature and causes circulation through the metallic plate. For sealing the cooling system, the radiator cap is used to maintain pressure. It saves coolant from overheating, and the radiator works well.
- • A pressure cap helps coolant remain pressurized and avoid overheating for smooth engine working.
- in motorcycles and automobiles with internal combustion engines that are liquid-cooled, where the radiator is connected with a channel operating with the cylinder head of the engine, where coolant is pumped through the coolant pump.
- Water is used as a coolant, but water and antifreeze materials are used. The normal vehicle cooling system comes with galleries covered with combustion chambers.
- The radiator, having small tubes, has a honeycomb having fins; coolant moves through a centrifugal water pump, and temperature is controlled with a thermostat through changing the coolant quantity moving towards the radiator, and a fan releases cool air through the radiator.
- high heat generated through the combustion process, which can damage the external part of the engine through detonation.
- For managing this effect, coolant moves through the engine, absorbs heat, and delivers it to the radiator.
What maintenance do radiators need?
proper radiator maintenance for accurate working. These points are used for the maintenance of the radiator.
Radiator tank cleaning
- Regularly perform cleaning of the radiator tank through the draining process, which protects components of the radiator from corrosion since metallic materials are used.
- The thorough cleaning temperature of the car engine is maintained, and it does not get overheated.
Pure Water
- Try to avoid tap water for the car radiator, but use pure water that is used for drinking purposes. Tap water has iron that causes corrosion for metallic components in the radiator tank.
Apply Radiator Coolant
- Always use coolant radiator for radiator working that maintains engine temperature and prevents dust on the car tank.
Radiator closed properly
- Check that the radiator is tightly closed. that avoids leakage of fluid that circulates to reduce engine temperature
Car Radiator Diagram
Car Radiator Generation
Read more guides Car Air Conditioning System Diagram
First Generation: Copper/Brass Radiators
- These radiators were made in the 1970s and are the first generation of radiators made with brass or copper since these materials have good heat transfer features.
- Copper and brass are durable and also conduct heat through reducing coolant temperature.
Second Generation radiator
- Copper or brass radiators are used but have high weight; that limitation is reduced through using aluminum, that is low weight.
- But aluminum design causes corrosion and leakage that affect the working. In the 1980s, a hybrid combination of aluminum or copper was used that increased the strength of the radiator.
Third Generation
- From the 1990s to the early 2000s, copper/brass radiators used stepped transmission, plastic end tanks, and proper solder compound. This technique reduces corrosion and leakage errors with aging brass structures.
- Copper/brass-based radiators make durable, efficient, and high-performance designs.
What’s the way to flush a radiator?
The vehicle needed accurate maintenance to work for a longer time. Flushing is also a maintenance measure for longer vehicle working. The steps involved for flushing the radiator are explained here.
Determine Whether to Flush the Car’s Radiator
- different factors involved in the radiator flush process The first one is a car model. Some cars come with 6 quarts of coolant and some with 18 quarts. So car identification helps that this model needed a radiator for a flush.
- • The older car also needed a flush of the radiator. Normally coolant is replaced for vehicles more than five years old.
- Mileage also provides details for radiator flush; normally after 30,000 miles, it is needed to flush.
Make the engine cool.
- After making sure the radiator needed flushing, check the engine block for hotness and coldness. If hot, wait to become cool. Check coolant temperature on the dashboard. When the engine becomes cool, remove the hood of the car.
Remove Coolant
- When the temperature is low, check below the car for the radiator drain petcock. that normally exists in the radiator corner.
- After finding the petcock location, put the pan under the petcock. Removing the petcock releases coolant to drain into the pan. When draining is finished, dispose of older coolant. For releasing coolant, use protective measures and clothing.
Find Radiator
- Radiator metallic tank of engine: remove radiator, radiator pressure gap for starting radiator flush.
Add Water into the Radiator
- For radiator flushing, use distilled water or a cleaner. Put them into the radiator through a funnel for accurate pouring.
Start the engine.
- When completely poured, close the radiator cap and start the engine and turn on the heat. on an engine and run for five minutes. that helps water and cleaners to remove impurity