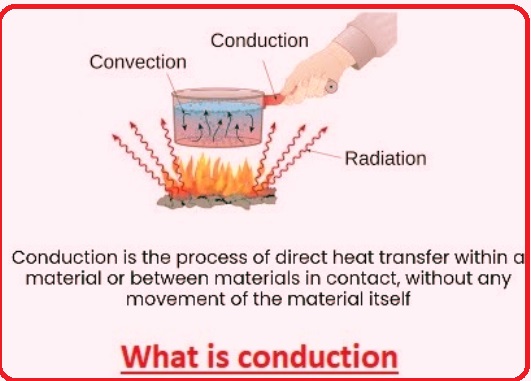
Conduction is an energy transfer process from one body to another when they are in direct contact. When energy is transferred through the conduction process, molecules receive it and start vibrating after they absorb it. Energy obtained at one molecule is transferred to other molecules through constant collision until it becomes a uniform energy transfer. Here we will cover detailed features for conducting and daily life conduction examples. So let’s get started.
What is conduction?
- Conduction is the transfer of heat from a high-temperature body to a cold part of that body and heat transfer through the collision of molecules.
- Heat transfer occurs through the vibrations of molecules of materials. When heat is given to an object at a certain temperature, getting energy for the heat atoms start vibrations.
- Due to vibrations of molecules, atoms collide with neighboring atoms and energy is transferred, which heats other components. In this way, transfer of energy occurs from one molecule to another.
- Let’s take an example: if we put a pan on a gas stove, the pan becomes hot from the fire. If the pan handle does not have insulation covering it, it is also hot after some time due to conduction since heat transfers from the base to the handle of the pan.
- If we remove the pan from the flame, then after some time, we observe that the pan temperature will decrease. since heat transfers from the hot pan to the cold surroundings.
Conduction Formula
- conduction formula used for measuring heat transfer per unit time of thermal conductivity, thickness, area, and temperature of two bodies
Q = [K x A x (Thot – Tcold)] /d
In this formula,
- Q = heat transfer per unit time
- K = coefficient of thermal conductivity of the materials
- A = area of heat transfer
- Thot = temperature of the hot region
- Tcold = temperature of the cold region
- d = thickness of the body
Conduction Unit
- watts measured in watts per meter Kelvin. This unit helps to define the material’s heat conduction feature which helps to determine the heating behavior of materials.
- Thermal conductivity is important for material insulation, heating components, and some industries.
Conduction Types

Ionic Conduction
- This conduction process is seen in electrolytes and exists in the movement of ions. A practical example of this conduction is in a battery electrolytic solution, where ion movements cause electrical energy transmission.
Electric Conduction
- In this conduction type, electrons flow through the conduction process, such as in metals. Wires used in different devices are a basic example of where electrons move in a wire for current flow.
Thermal Conduction
- In this conduction process, heat transfers through the material. The basic example is when we heat a metallic rod at one side, and heat moves in the rod at the low-temperature end.
Conduction Features
- In this process, energy transfer occurs between neighboring particles in materials through direct collection and physical interaction.
- This process is normally seen in solids, such as metals, since they are closely connected, which helps in the easy transfer of energy.
- Conduction needs a temperature difference which is heat moving from a high-temperature area to a cooler end.
- There is no movement of materials occurring as in convection examples for energy transfer.
- Thermal conductivity is different for different materials, normally larger for metals than for insulators.
- rate of conduction based on thermal conductivity of metals, thickness, and cross-sectional area
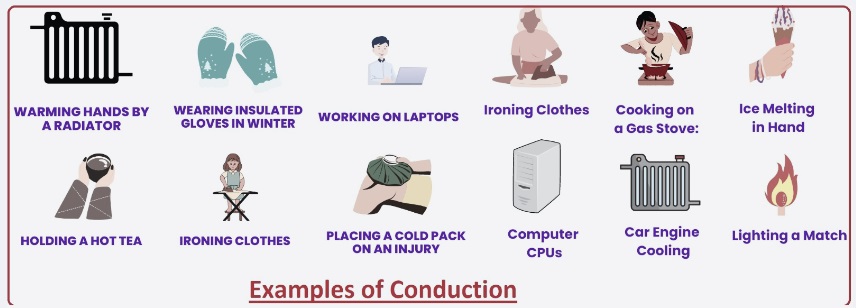
Examples of Conduction
Metallic Spoon in Hot Liquid
- Suppose we have hot liquid in a pan and dip a spoon in that liquid. We will observe after some time the spoon becomes hot after getting heat from the liquid. since particles or atoms of the spoon get energy from the liquid, and that heat transfers to the particles, and we feel it in our hands.
- In this conduction example, heat transfer occurs without the movement of materials.
Read also: Daily Life Examples of Mechanical Energy
Hot pan connection or touching
- If you accidentally touch a hot pan, the heat of the pan shifts to your hand after contact. Since the high temperature of the pan transfers energy to the skin through making a connection. Conduction is basically completed through shifting heat from a hot body to a cold one till getting equilibrium.
Barefoot Walk on Hot Sand
- Another example is barefoot walking on hot sand since the heat from the high-temperature sand is transferred to the feet. Energy from high-temperature particles of sand is transmitted to our feet, and we feel the temperature.
Ironing Clothes
- Ironing clothes is also an example of conduction, where heat transfers from the iron to the clothes. Thermal energy transfers to the clothes particles and removes wrinkles, and our clothes become smooth. So wrinkles in clothes are removed through a conduction process in an iron.
Heated Seat of the Car
- If your car seats are hot due to parking in sunlight, and when you sit in the car, you face heat due to heat transfer from the car to your body. Conduction also provides warmth and comfort in cars.
Walking on a Hot Sidewalk
- If you are walking on a hot sidewalk, it is also an example of conduction. Heat from the sun strikes the sidewalk and makes it hot, and when we walk on the road, we face heat through our feet that comes from the shoes.
Icy Windowpane
- An icyis also an example of conduction. Cold glass temperature moves through the material to the hand, which causes cold in our hand.since particles of glass transmit energy to hands. So through conduction, we feel cold in our hands.
Cold Metal Water Bottle
- If we handle a cold metallic water bottle, the low temperature moves from the metal to the hand. Conduction occurs through transferring energy from metallic components to hand particles, which causes the feeling of cold.
- In this way we feel cold temperature in our hands.
Walk on a Cold Tile Floor
- If you walk on a cold tile floor, you also feel coldness through conduction. since low temperature conditions shifted to our feet from the tiles. since energy transfers from tiles to our feet, which causes our feet to get cold.
Boiling of water
- If we pour water in a glass and provide heat, then water molecules close to the glass are heated through getting heat from neighboring molecules. As a result, the entire water gets heated from conduction.
Holding an ice cube
- If we hold an ice cube in our hand, we feel coldness. since heat flows from the hand to the ice cube through conduction.
Conduction Examples in Real Life
- • The heat of a radiator warms our hands when we hold them closely.
- If we have a melting chocolate pan, heat conducts from the stove and melts the chocolate.
- Insulated gloves are also an example of conduction, since they control body heating to conduct and warm our hands.
- When you use a laptop, it feels warm since heat move from the inner components of the laptop to the body, so we feel warm.
What is Fourier’s Law?
- Fourier’s law, also called the heat conduction law. This law explains when heat conduction occurs: a negative temperature gradient and time where heat transfer occurs have a direct relation with the area of the gradient where heat is moving.
It is mathematically an equation.
q ∝ – A (dT/dx)
q = – kA dT/dx
in these equations
- q= heat flux
- A= Area
- dT/dx= Temperature gradient
Everyday Heat Conduction Example
cast-iron skillet onto stovetop
- if we put a cold cast-iron skillet on the stovetop. If the stove gets turned on, the skillet temperature increases through the conduction process of heat that moves from the burner to the skillet. After some time, the handle of the skillet is hot; after some time, it is due to heat conducted through the skillet part connected with the stovetop.
shirt on the ironing board
- When the shirt is placed on the ironing board, the heat from the iron moves to the shirt, which removes wrinkles and makes the shirt smooth. that occurs through conduction
The car engine is in on condition.
- When the car engine is in the on state, the hood temperature increases due to heat that comes through the engine following the conduction process towards the hood.
Burning Fire
- When we burn fire and move around, we burn logs with a poker. Heat moves from burning logs to the poker, in the poker end, becoming hot due to the conduction process for long-term fire use.
Some examples of conductions are as follows:
- When you grab a penny from the tabletop, it feels cold. After some time, heat shifts from your hand to the penny, and it becomes heated through the conduction process.
- If we put anything on the radiator after turning it on, it becomes warm through getting heat from the radiator through conduction.
Conduction vs Convection vs Radiation
Read more: Difference Between Conduction and Convection
Transfer of heat takes place via conduction, convection, and radiation. The difference between them is listed in the table given below:
| Features | Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
| Medium | Medium needed for the process | Medium needed | Medium is not needed and occurs in a vacuum. |
process of Heat Transfer | heat transfer through making a connection with objects. | heat transfer through particle movement | Heat transfer through electromagnetic radiation. |
| occurance | Occurs due to a difference of temperature between two materials. | difference in density between two materials | Occurs when particles where a temperature more than absolute zero (0K). |
| Process | slow. | faster process than conduction. | It is faster than three processes |
| Heat Transfer | ansfer of heat is irregular way | transfer of heat is irregular. | linear heat transfer |