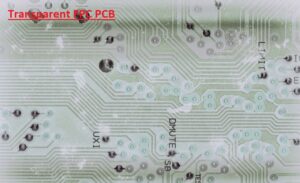
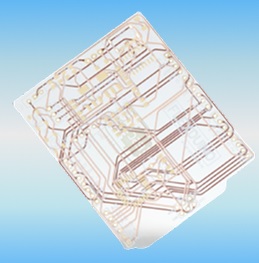
Transparent PCB board is an emerging technology for PCB design and manufacturing. It is used for increasing the board and final assembly appearance with different features. A transparent PCB board is a flexible circuit board that employs PET film, which makes transparent, light blue, light green, and other color combinations.
FPC transparent boards use a material called transparent PET and use a flexible process like that used for transparent boards, like the manufacturing process of flexible circuit boards. In this post we cover features for transparent FPC and learn where to get these boards.
What is a transparent PCB?
- Normal flexible printed circuits come in black, white, yellow, and other color combinations that are used for different applications.
- Transparent board is a new material type that comes with some new features compared to older materials.
- transparent PCB made with use of high-temperature-resistant PET and high transparency, and its layout comes with a transparent substrate, conductor layer, and insulating layer.
- It provides high features like flexible design, conductivity, low weight, high transparency, high temperature resistance, and works well for different conditions.
Transparent PCB Features
- These boards help to get about 85 percent light transmittance for clear visuals.
- It has features to handle about 200 degrees, based on demanding projects.
- Transparent substrates are also compatible with SMT stencils.
- It has a low cost compared to other materials without affecting quality and has a cost that is 30 to 50 percent lower.
Advantages of Transparent PCB Board
- These boards have easy bending, folding, and rolling features and are easily stretched in three-dimensional space.
- It also provides good heat dissipation and minimizes size through transparent FPC flexible circuit boards.
- It has low weight, miniaturization, and thinness features that help to connect components and wiring and the main part of electronic components.
- FPC transparent boards made with PET that make transparent designs.
Transparent PCB vs. PCB
- Transparent boards come from substrate materials through which light passes easily. These materials are polycarbonate.
- PET glass, reinforced epoxy, PMMA, and liquid crystal polymers are used.
- • A conventional board comes with an opaque substrate that is a fiberglass material, for example, FR4. With that, some metals like ceramic or aluminum are used.
Transparent PCB Substrate
- The transparent board comes with glass and a ceramic substrate. Ceramic materials’ transparent substrate comes with higher thermal conductivity features than glassboard.
- Glass PCB substrate has good optical transmission as compared to ceramic. Light transmission of the glass board substrate is 99.5-99%, and the ceramic value is 75-80%.
Base Materials of Transparent Boards
These come in rigid or flexible designs, like rigid ceramic boards that come with aluminum substrates that come in different configurations, like aluminum oxide, an amalgam of magnesium and aluminum, magnesium oxide, etc.
- the main use of materials to provide 80 percent transparency. Oily, water-based blue nano alumina provides the hardness of resin materials from 6H to 8H.
- The base materials of flexible transparent PCB are polyester and polyimide, which come with 95% transparency.
- Polyamide-based boards are a strong design that handles mechanical and electrical losses. They have resistance to thermal pressure.
Ceramic Transparent Circuit Boards
- PCB makers make transparent ceramic circuit boards through the use of materials such as aluminum oxide, magnesium oxide, etc.
- These boards come with a transparent substrate and a glass-based solder mask that provides 75 to 85 percent substrate transparency.
- But conductors and conductive traces have less transparency.
Features of Ceramic Transparent Circuit Boards
- It has high thermal conductivity (24-31.4 W/mK).
- It has a low and stable thermal expansion coefficient and is highly temperature resistant (over 2000°C).
- It does not absorb water through using good electrical insulation.
- Multiple optical features it provides
PCB Transparent Manufacturing
Follow these steps to make a transparent board.
- First of all, arrange materials like copper foil, ferric chloride, etc.
- Then prepare the board design layout and make the printing process.
- Now make a substrate through the use of transparent materials.
- In this step add copper foil and use photoresist.
- In this phase, apply sunlight or artificial light, then make photoresist.
- In the last phase, board etching is performed through the use of ferric chloride solution that removes undesired copper.
- in the last clean and dry circuit board
One-Stop Transparent Circuit Board Manufacturer
The one-stop PCB manufacturer JLCPCB fabrication house is the main supplier of transparent circuit board manufacturing and assembly to customers all over the world. They provide their services for different industries like industrial, medical, communications, defense, and consumer electronics.
JLCPCB provides high-quality custom FPC solutions and expert support to help realize even the most advanced designs.
They also provide speed services with competitive prices and compatibility for standard and advanced boards with transparent flexible PCBs.
To get a transparent board from JLCPCB, choose Transparent at the time of placing your flex PCB order.
Design a Flex PCB using EasyEDA Pro and get a $7 discount when you upload Gerber files directly from EasyEDA Pro.
JLCPCB, in addition to providing quality transparent PCB services, also provides SMT stencil services, and you can get a laser-cut stencil starting at $3 (380 mm × 280 mm), and 0$ with a new user coupon. through upgrading to nanocoating or electropolishing for just $4.72 more.
Their automated laser cutting provides manufacturing in 6 hours. Stencil orders ship in 24 hours of confirmation.
reliable global shipping with trusted carriers (e.g., DHL, FedEx, others)
Limitations of Transparent PCBs
These boards have a better appearance than conventional opaque boards. Transparent boards come with some limitations and manufacturing processes.
Lower Fabrication Process
- The manufacturing of these boards needed certain processing steps that made it difficult to have operational boards at the end of the manufacturing line.
Higher Manufacturing Cost
- With low production output, manufacturing transparent boards since material processing is more expensive than fiberglass, which makes boards costly.
Higher Warping
- Transparent board materials warp easily as compared to fiberglass since they do not have a solid design. Working for these boards can be difficult and result in high losses that minimize manufacturing productivity.
Laser Drilling Limitations
- • The substrate of the transparent board can crack due to laser beam applications.
Applications of Transparent PCB
- This board is used for displays and medical devices and is now used as an innovation.
- It is used in wearables for durable and ultra-flexible design.
- It is used for vehicles that provide low-weight designs.
- It increases products’ looks and provides high-performance applications.
- It is used for display tech for 85 percent light transmittance, good for LED panels, and makes transparent screens and LED panels.
Transparent PCB Design and Manufacturing Difficulties
- When designing and manufacturing a transparent board, some technical limitations occur. First of all, the selection of materials.
- Electrical and mechanical features of transparent materials are not as good as those of conventional materials.
- Transparent FPC needed a proper balance for working and transparency.
- With that high cost of transparent materialsthat increases overall manufacturing cost.
- The design of the transparent board needed proper cost and appearance considerations.
- Another difficulty of transparency for manufacturing is the manufacturing process, since these boards use conductive materials, and they have high resistance as compared to copper.
- There is a need to optimize circuit design that reduces the length and width of the conductor, affecting the resistance.