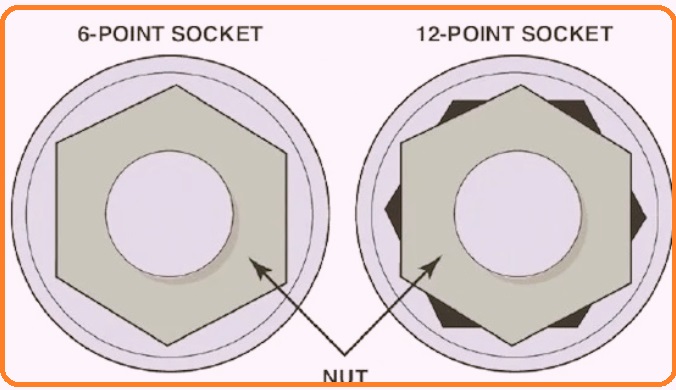
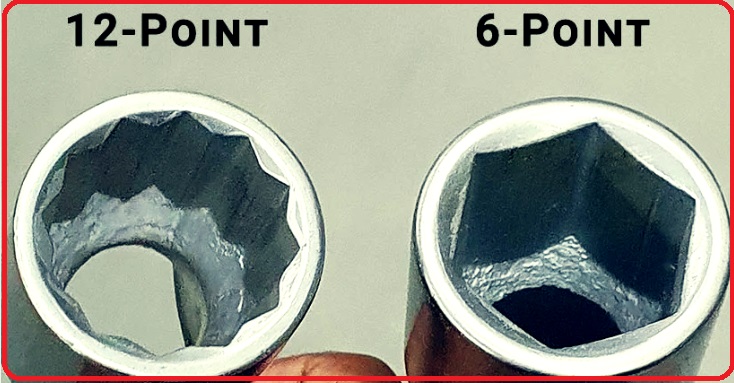
The 6-point end comes with a hexagonal design and has 6 points, or vertices, that are 60 degrees apart around a circle. The 12-point end is a double hexagon that comes with 12 vertices and 30 degrees apart around a circle. The hex nuts come with 6 points; we can fit 6-point and 12-point sockets on the hex nuts. Sockets with larger points have more connection points. A 12-point socket has double points, so it can easily connect to a hex nut.
In this post, we cover details for 6 points and 12 points and related features. Let’s get started. 6-Point vs. 12-Point Sockets
What is the meaning of point of sockets?
- Points of sockets help to make connections with fastener heads. Larger points make connections of tighter spaces that are difficult to reach. The 12-point socket helps to connect fasteners at larger points and tight spaces.
- 6-point sockets make fewer connections
What Is a Six-Point Socket?
- The 6-point sockets come with a standard hexagonal design. It has 6 points that are configured 60 degrees apart from each other. Six-point sockets come with thick walls and larger surfaces and have 6-point fasteners.
- The 6-point socket made a connection to the fastener’s head.
- The 6-point socket wrench comes with 6 corners and sides at a 60-degree angle in the socket well. It is used for tightening and loosening bolts and nuts that are in a deep well shape.
- Standard depth sockets come with a well of ¾ inch (20 mm) deep, and deep well sockets have one inch according to bolt diameter.
What Is a 12-Point Socket?
- The 12-point sockets come with 12 points that are spaced 30 degrees apart with a double hexagonal shape. It has 12-point fasteners and is used for special industries and light clamps where the heads of the fasteners are recessed.
- Standard deep sockets come with a well of ¾ inch (20 mm) deep.
where a 6-point socket is used
- 6-point sockets are used for areas where a larger force is needed. The connection point having flat edges provides a low-slippery area. It provides a strong grip. Normally, 6-point sockets are used for applications where high torque exists, and impact sockets are 6-point sockets.
- The 6-point socket makes a connection to the head of fasteners at corners, and the thick part of the fasteners provides an easy connection.
- that minimizes slipping errors, rounding on edges.
Advantages of 6-Point Socket
- The 6-point socket produces high forces for removing tires or removing rusted bolts. High torque is needed, which can be obtained from the 6-point socket. The 6-point socket has a torque feature.
- The 6-point sockets come with a high contact surface area which comes with high strength since the thick wall is made with strong material. Thick walls reduce socket flex and manage slipping.
- The 6-point socket bears high tension or force and has a highly durable design. For wrong tools where high force is needed, a thick wall can be damaged
Disadvantages:
- 6-point socket comes with less angle for the configuration of socket on fasteners. if there is a thick bar without a ratchet set socket position on the bar to get the required position
where to use a 12-point socket
- 12-point sockets are mostly used for confined spaces where accessibility is difficult. 12-point fastener sockets are best for tight locations where we can connect fasteners at larger angles.
- The 12-point sockets are used to tighten nuts and bolts strongly. 12-point sockets are used for lightweight repairing.
12-point socket advantages
- The main feature of a 12-point socket is to make a connection with a fastener. 12-point sockets provide easy connection with fastener heads. If the wrong tool is used, connecting with a 12-point socket is difficult for fasteners.
- 12-point fasteners used for 12-point sockets. The 12-point fasteners are difficult to get.
Disadvantages
- The main limitation is that the 12-point socket comes with a small connection point, where the point is required to be close to fasteners. In some conditions, there is not accurate connection point.
- 12-point sockets are not standard to use for high-torque applications since the relative angle of points and surface connection makes slippage with torque
6 Point vs. 12 Point Sockets: basic difference
Material
- The 6-point and 12-point sockets are made with a chrome vanadium finish and are made with the use of steel that has a durable nature. The main difference is that 6 points come in a 6-point area, and a 12-point socket has 12 points.
Quality
- These points work well, but 6-point sockets are used for heavy-weight applications like wrenching and provide difficult work. 12-point sockets are used for lightweight applications.
Installation process
- The 6-point sockets have a strong grip and do not get around corners. The 12-point sockets come at a lesser angle; 6-point sockets have a stronger grip than 12-point ones.
design
- The 6-point sockets have fewer connections for fasteners with bolts and are easy to use. The thick walls of 6-point sockets have larger connection points for fasteners. 12-point sockets are less likely to have a connection since they have a larger number of points.
Durable design
- These sockets come with a durable design since they are made with high-quality materials and alloy steel. 12-point sockets are used for low-weight applications, and 6-point for heavy wrenching, so 6-point sockets need a strong design and materials.
cost
- The prices of socket points are different based on the size of the socket points; the cost of a 12-point socket is $90 to $200. 6 points is $60 to $200/set and more.
When to Use 6-Point or 12-Point Sockets
- We can use 6- and 12-point sockets as replacements, but each comes with certain uses. Normally 6-point fasteners are good to use for high-impact applications that need larger force. They have high wear resistance; fewer chances of bolt head stripping make them useful.
- For confined spaces, use a 12-point socket where high force is not needed. The 12-point socket can easily be used for small spaces. It operates well for high-tooth-count ratchets.
Conclusion
- 12-point sockets used for hexagonal designs and 12-point fasteners are best for confined areas. They are not good for high-impact design since they have a high chance of stripping the fastener head.
- 6-point sockets are used for high-impact designs but not used for 12-point fasteners.
FAQs
Is a 6-point or 12-point socket better?
- If you have 12-point fasteners, that’s uncommon, so use a 12-point tool. For 6-point fasteners, the 6-point tool is good to use.
Are 12-point bolts better?
- The 12-point bolt comes with high-torque features; the 12 points on the head give a larger area between the wrench and bolt as compared to a hex socket cap screw.
What are the benefits of a 12-point socket?
- It is used for making easy connections with fastener heads. That is good when working on fasteners that are difficult to access. 12-point sockets are good to use for tight spaces since they provide a larger number of connections at different angles.
Is it bad to use a 12-point socket on a 6-point bolt?
- The 12-point is a thin wall and easy fastener access with a small rotation needed for handling fasteners. If 12 points are stripping the edge of 6-point fasteners, 6-point has good features for providing uniform forces over the fastener surface.
Is a 6-point socket best for removing tight bolts?
- In some conditions, the 6-point socket handle strongly rusts the nut, which has low damage as compared to a 12-point socket or conventional ring-end spanner.
- not use ratchet spanner sockets for opening bolts since damage is due to high load
When picking a socket to use, is the 6-point socket the best, although the 12-point is the most common?
- The 6-point socket is good for gripping and turning fasteners since it has a good grip and minimizes rounding off.
- The 12-point socket is commonly to use since it is used for tight spaces.